Control and following of the robot arm
1 Slider Control
Click the ROS1 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower bar of the desktop to open the ROS1 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of the mybuddy is "/dev/ttyACM0", and the baud rate is 115200".
roslaunch mybuddy slider_control.launch _port:=/dev/ttyACM0 _baud:=115200
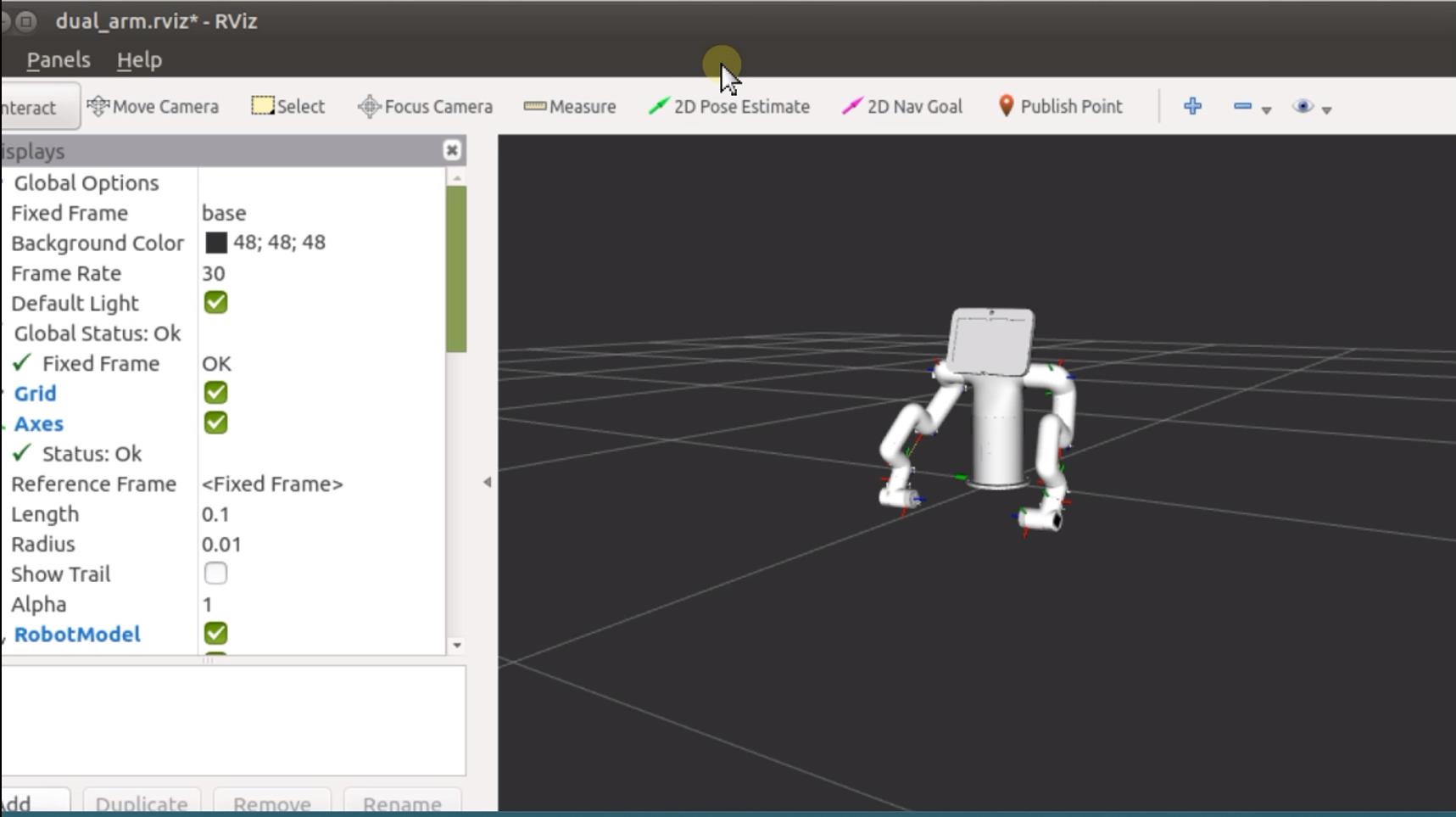
rviz and a slider component will be opened, and you will see the following interface:
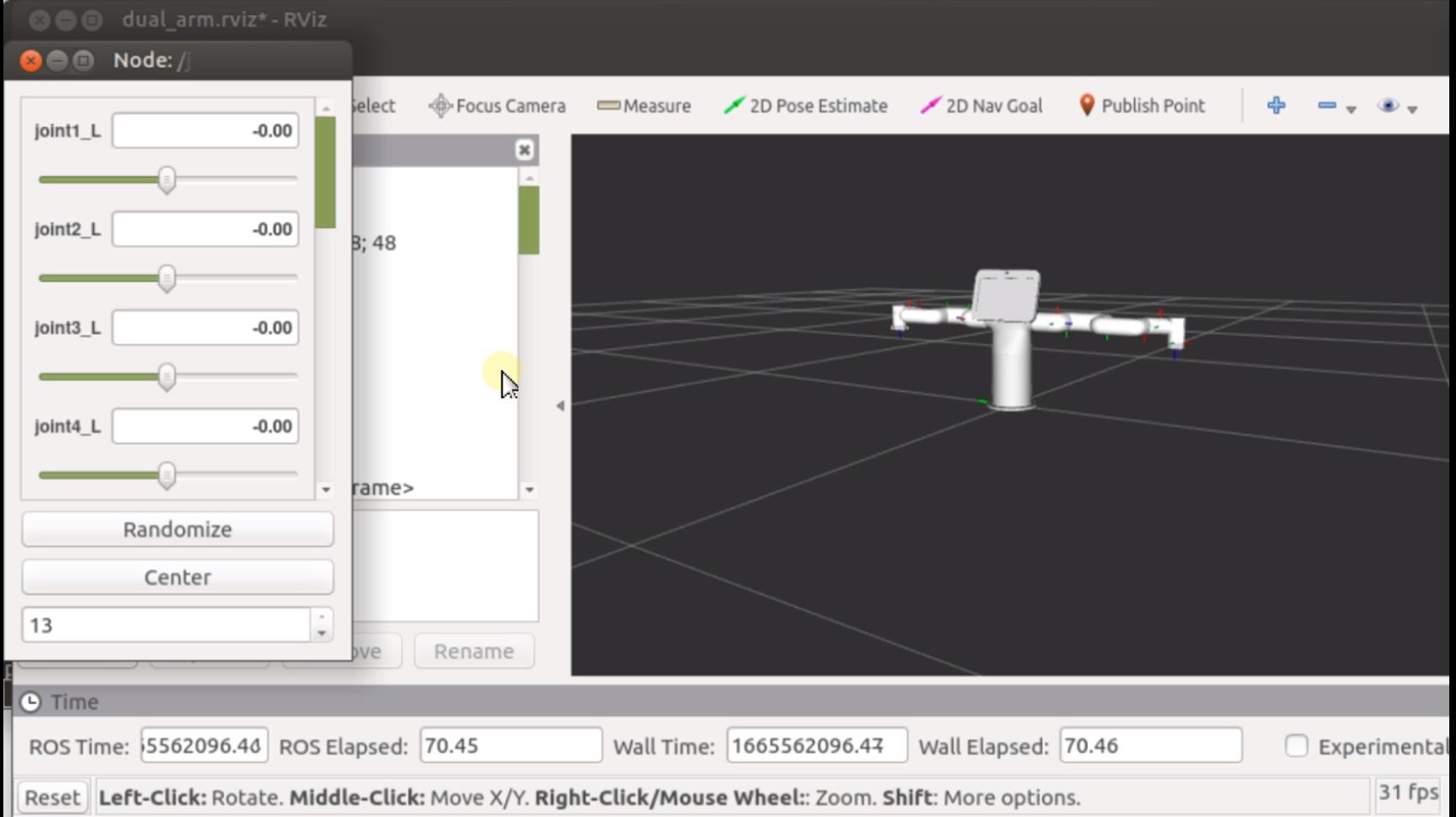
Then you can control the model in rviz to make it move by dragging the slider. If you want the real mybuddy to move with the model, you need to open another ROS1 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of the mybuddy is "/dev/ttyACM0", and the baud rate is 115200".
rosrun mybuddy slider_control.py _port:=/dev/ttyACM0 _baud:=115200
Note: Since the robot arm will move to the current position of the model when the command is input, make sure that the model in rviz does not appear to be worn out before you use the command.
Do not drag the slider quickly after connecting the robot arm to prevent damage to the robot arm.
2 Model Following
In addition to the above controls, we can also let the model move by following the real robot arm. Open a ROS1 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of the mybuddy is "/dev/ttyACM0", and the baud rate is 115200".
rosrun mybuddy follow_display.py _port:=/dev/ttyACM0 _baud:=115200
Then open another ROS1 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
roslaunch mybuddy mybuddy_follow.launch
It will open rviz to show the following effect of the model and the real robot arm, as shown below: