Control and follow-up of the robotic arm
1 Slider Control
Open a command line and run:
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to " /dev/ttyACM0".
ros2 launch mycobot_280 slider_control.launch.py
- mycobot 280-PI version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower column of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-PI version is "/dev/ttyAMA0", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 launch mycobot_280pi slider_control.launch.py
- mycobot 280-JetsonNano version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower column of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-JetsonNano version is "/dev/ttyTHS1", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 launch mycobot_280jn slider_control.launch.py
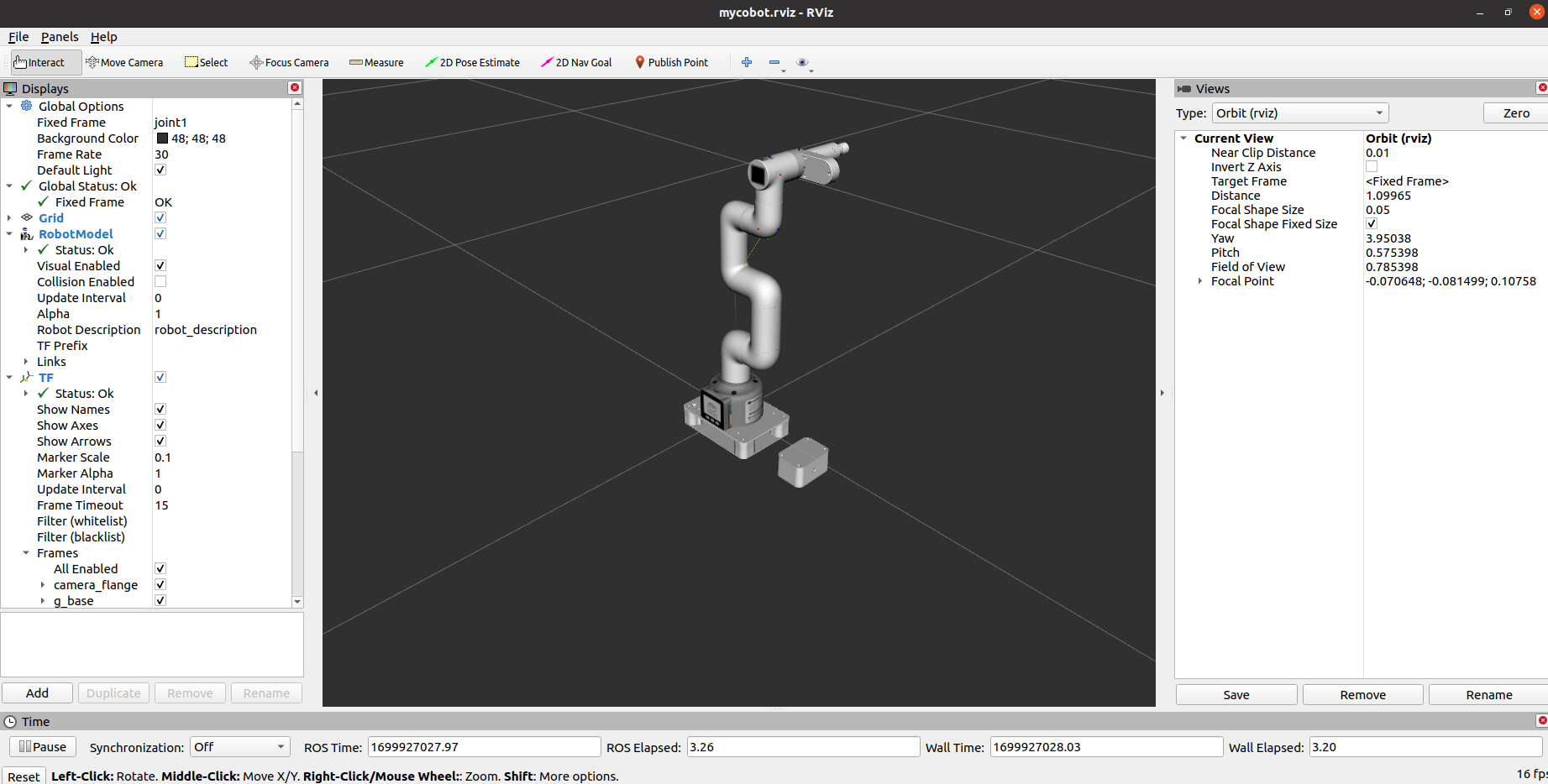
It will open rviz and a slider component and you will see something like this:
Then you can control the movement of the model in rviz by dragging the slider . The real mycobot will move with it.
Please note: Since the robot arm will move to the current position of the model when the command is input, please make sure that the model in rviz does not appear to be worn out before you use the command Do not quickly drag the slider after connecting the robotic arm to prevent damage to the robotic arm
2 Model Follow
In addition to the above controls, we can also make the model follow the movement of the real robotic arm . Open a command line and run:
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to " /dev/ttyACM0".
ros2 launch mycobot_280 mycobot_follow.launch.py
- mycobot 280-PI version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower column of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-PI version is "/dev/ttyAMA0", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 launch mycobot_280pi mycobot_follow.launch.py
- mycobot 280-JetsonNano version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower column of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-JetsonNano version is "/dev/ttyTHS1", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 launch mycobot_280jn mycobot_follow.launch.py
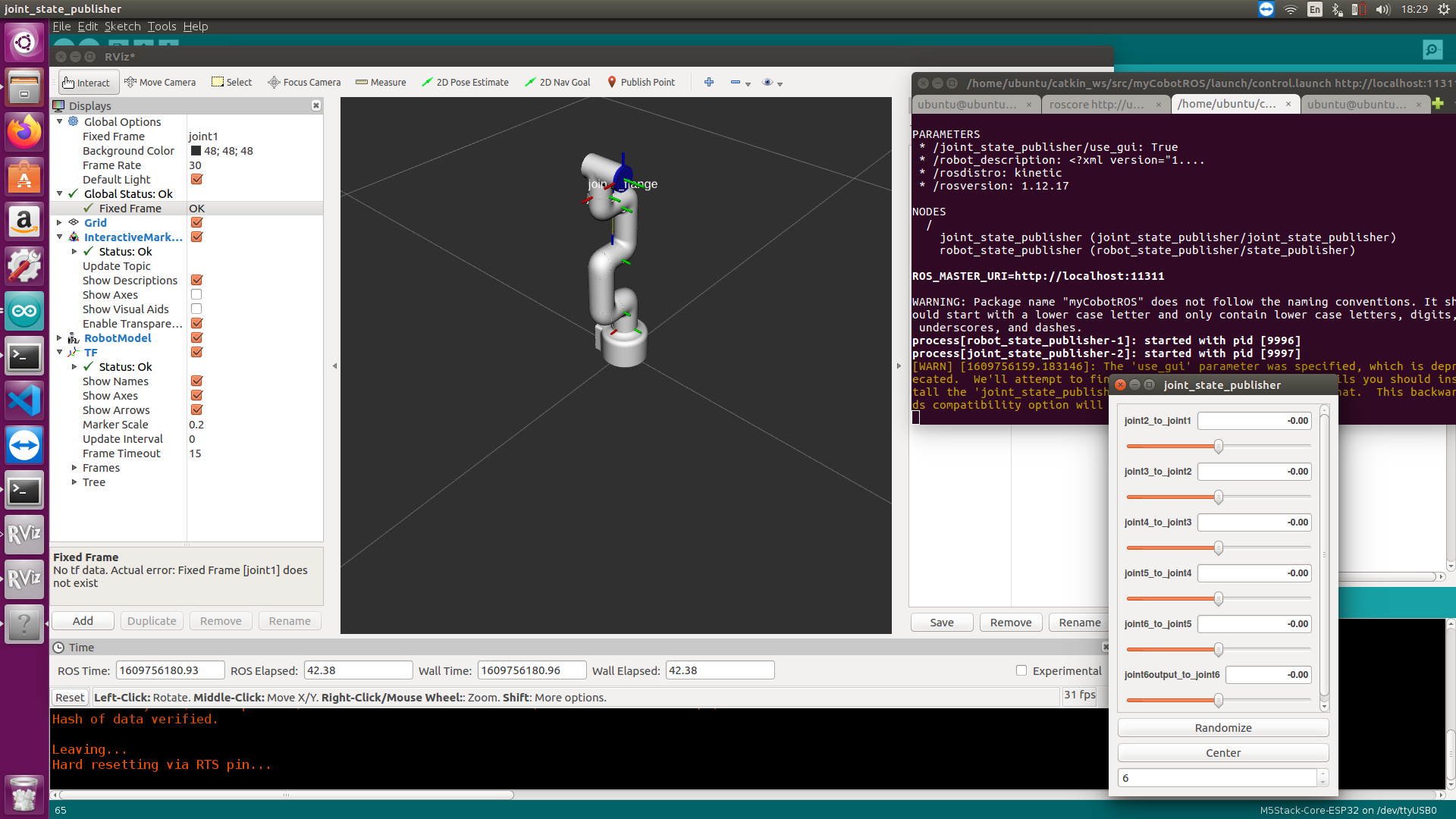
It will open rviz to show the model following effect .
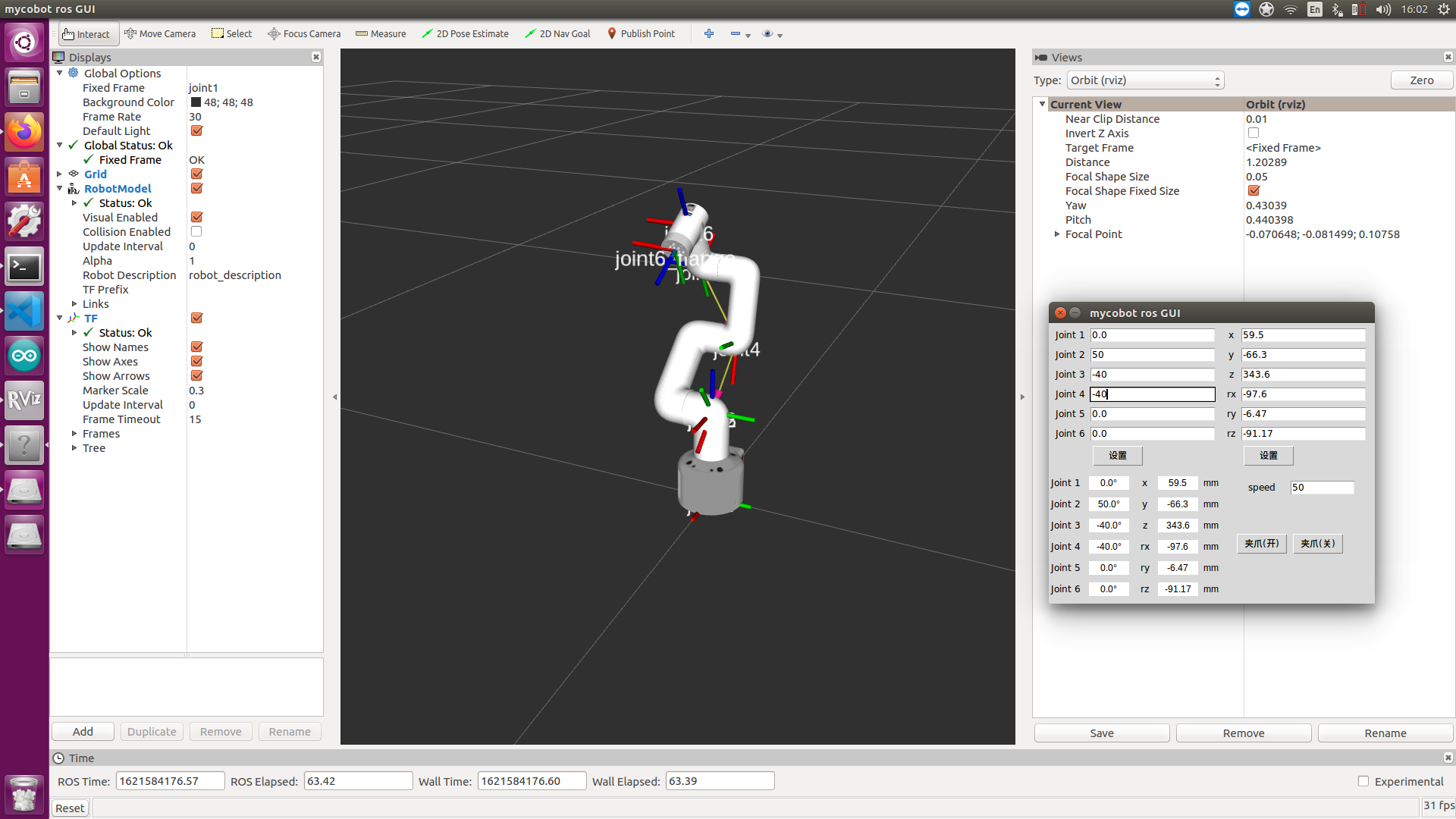
3 GUI Control
On the basis of the previous, this package also provides a simple GUI control interface . This method means that the real robotic arms are linked with each other, please connect to mycobot.
Open the command line::
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to " /dev/ttyACM0".
ros2 launch mycobot_280 simple_gui.launch.py
- mycobot 280-PI version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower column of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-PI version is "/dev/ttyAMA0", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 launch mycobot_280pi simple_gui.launch.py
- mycobot 280-JetsonNano version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower column of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-JetsonNano version is "/dev/ttyTHS1", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 launch mycobot_280jn simple_gui.launch.py
4 Keyboard Control
The function of keyboard control is added in the package of mycobot_280, and it is synchronized in real time in rviz. This function relies on pythonApi, so make sure to connect with the real robotic arm.
Open a command line and run:
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to " /dev/ttyACM0".
ros2 launch mycobot_280 teleop_keyboard.launch.py
- mycobot 280-PI version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower column of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-PI version is "/dev/ttyAMA0", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 launch mycobot_280pi teleop_keyboard.launch.py
- mycobot 280-JetsonNano version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower column of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-JetsonNano version is "/dev/ttyTHS1", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 launch mycobot_280jn teleop_keyboard.launch.py
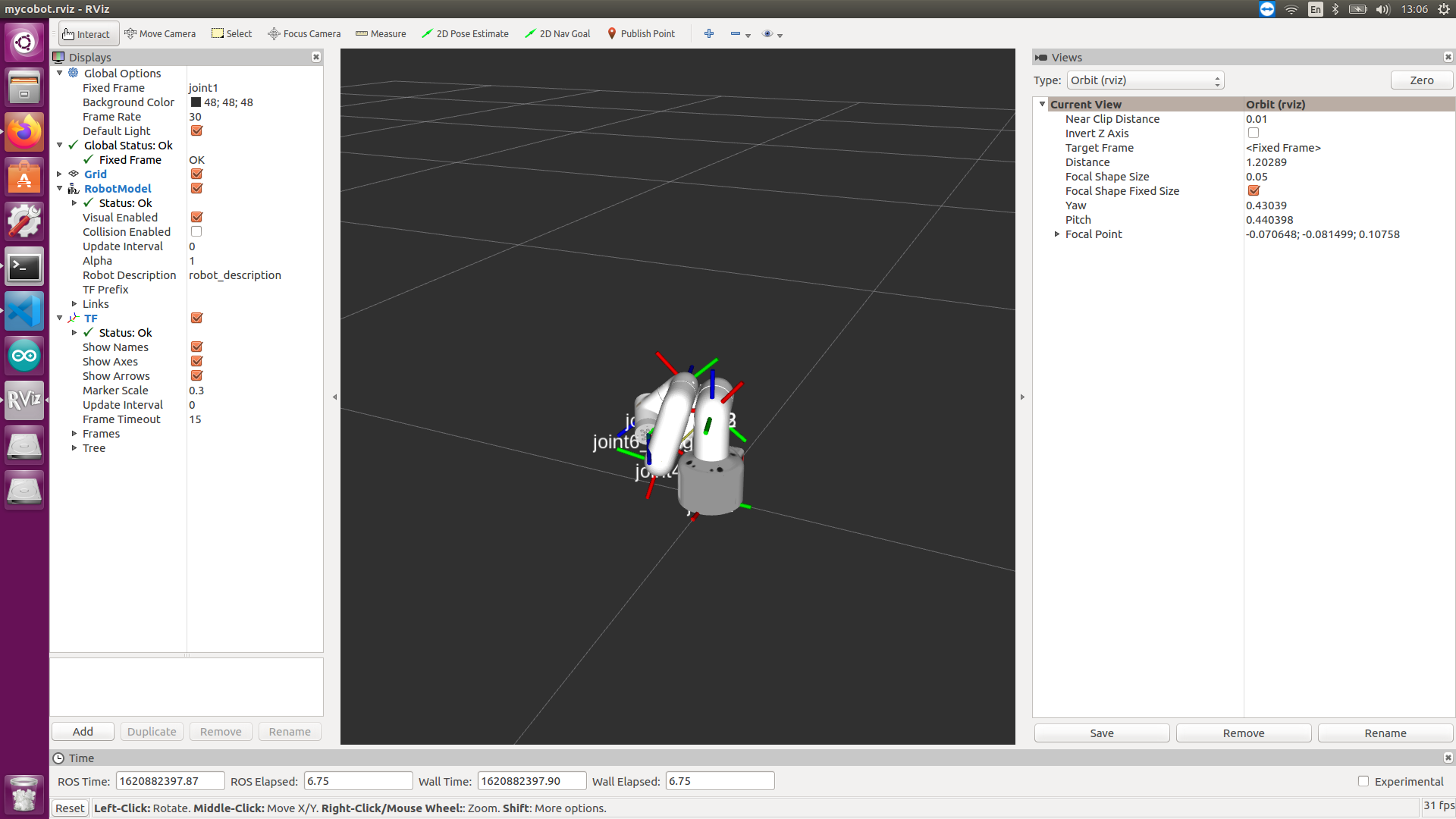
The operation effect is as follows:
The command line will output mycobot information, as follows:
[INFO] [launch]: All log files can be found below /home/elephant/.ros/log/2022-05-19-16-25-45-949761-elephant-virtual-machine-19111
[INFO] [launch]: Default logging verbosity is set to INFO
[INFO] [robot_state_publisher-1]: process started with pid [19114]
[INFO] [rviz2-2]: process started with pid [19116]
[INFO] [follow_display-3]: process started with pid [19118]
[robot_state_publisher-1] Parsing robot urdf xml string.
[robot_state_publisher-1] Link joint2 had 1 children
[robot_state_publisher-1] Link joint3 had 1 children
[robot_state_publisher-1] Link joint4 had 1 children
[robot_state_publisher-1] Link joint5 had 1 children
[robot_state_publisher-1] Link joint6 had 1 children
[robot_state_publisher-1] Link joint6_flange had 0 children
[robot_state_publisher-1] [INFO] [1652948746.290904045] [robot_state_publisher]: got segment joint1
[robot_state_publisher-1] [INFO] [1652948746.290967253] [robot_state_publisher]: got segment joint2
[robot_state_publisher-1] [INFO] [1652948746.290973124] [robot_state_publisher]: got segment joint3
[robot_state_publisher-1] [INFO] [1652948746.290977490] [robot_state_publisher]: got segment joint4
[robot_state_publisher-1] [INFO] [1652948746.290981670] [robot_state_publisher]: got segment joint5
[robot_state_publisher-1] [INFO] [1652948746.290985737] [robot_state_publisher]: got segment joint6
[robot_state_publisher-1] [INFO] [1652948746.290989943] [robot_state_publisher]: got segment joint6_flange
[follow_display-3] [INFO] [1652948746.664601707] [follow_display]: port:/dev/ttyUSB0, baud:115200
[rviz2-2] [INFO] [1652948746.828773551] [rviz2]: Stereo is NOT SUPPORTED
[rviz2-2] [INFO] [1652948746.830452458] [rviz2]: OpenGl version: 4.1 (GLSL 4.1)
[rviz2-2] [INFO] [1652948746.874021926] [rviz2]: Stereo is NOT SUPPORTED
[rviz2-2] Parsing robot urdf xml string.
Next, open another command line and run:
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
ros2 run mycobot_280 teleop_keyboard
- mycobot 280-PI version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower column of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
ros2 run mycobot_280pi teleop_keyboard
- mycobot 280-JetsonNano version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower column of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-JetsonNano version is "/dev/ttyTHS1", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 run mycobot_280jn teleop_keyboard
You will see the following output on the command line:
Mycobot Teleop Keyboard Controller
---------------------------
Movimg options(control coordinations [x,y,z,rx,ry,rz]):
w(x+)
a(y-) s(x-) d(y+)
z(z-) x(z+)
u(rx+) i(ry+) o(rz+)
j(rx-) k(ry-) l(rz-)
Gripper control:
g - open
h - close
Other:
1 - Go to init pose
2 - Go to home pose
3 - Resave home pose
q - Quit
currently: speed: 10 change percent: 2
In this terminal, you can control the state of the robot arm and move the robot arm through the keys in the command line.
5 End Effector
- Supported end effectors: myCobot vertical suction pump V2.0, camera flange
- Applicable devices: myCobot 280 M5、myCobot 280 PI
5.1 myCobot Vertical Suction Pump V2.0
1 Load model
Open a command line and run:
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
ros2 launch mycobot_280 test_pump.launch.py
- mycobot 280-PI version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower bar of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
ros2 launch mycobot_280pi test_pump.launch.py
It will open rviz, and you will see the following screen (the Raspberry Pi version has slightly different screens, which does not affect use):
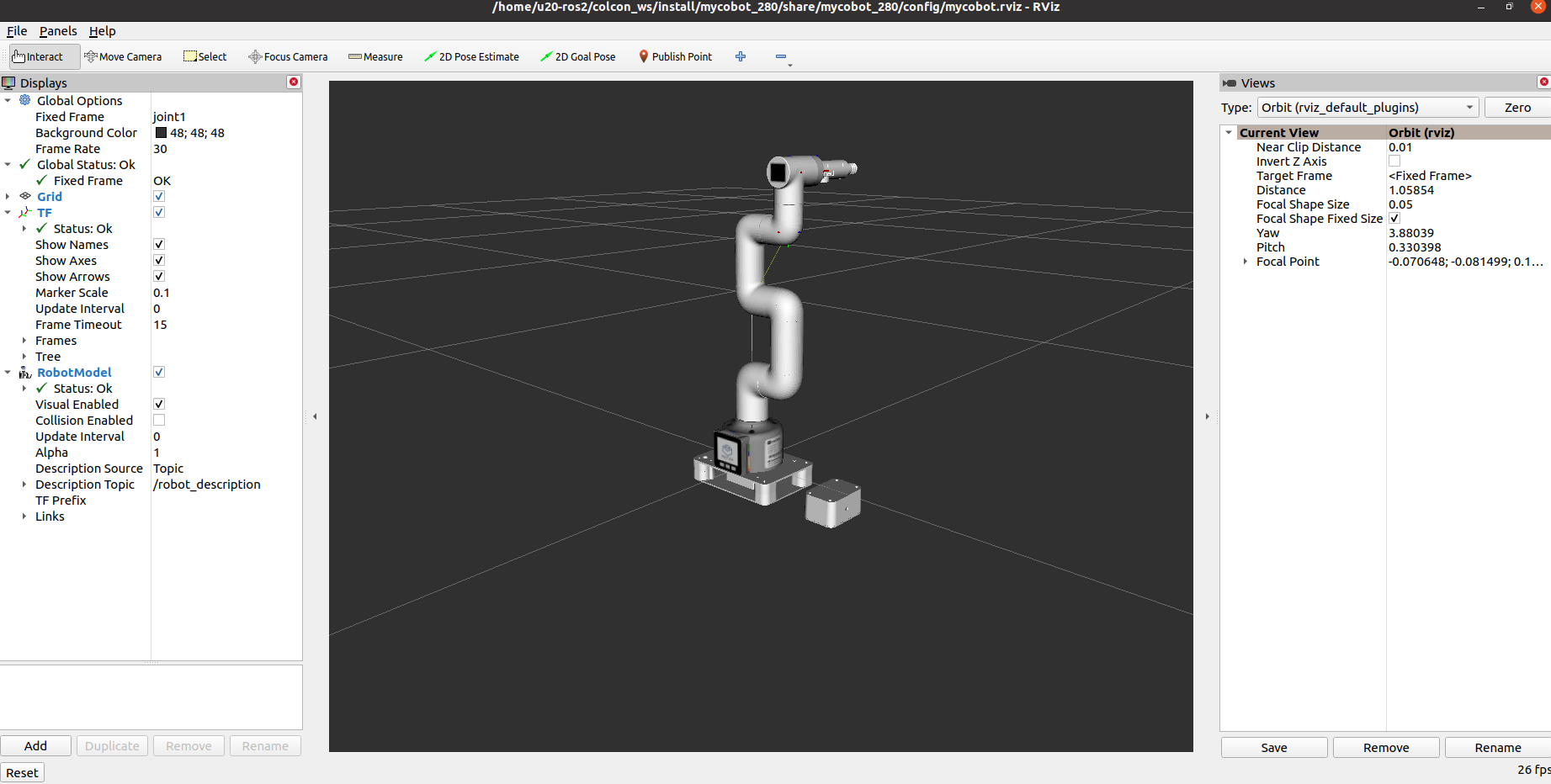
2 Slider control
Note: This function only supports control of the robotic arm
Open a command line and run:
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to " /dev/ttyACM0".
ros2 launch mycobot_280 slider_control_pump.launch.py
- mycobot 280-PI version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower bar of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-PI version is "/dev/ttyAMA0", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 launch mycobot_280pi slider_control_pump.launch.py
It will open rviz and a slider component, and you will see the following screen (the Raspberry Pi version screen is slightly different, which does not affect use):
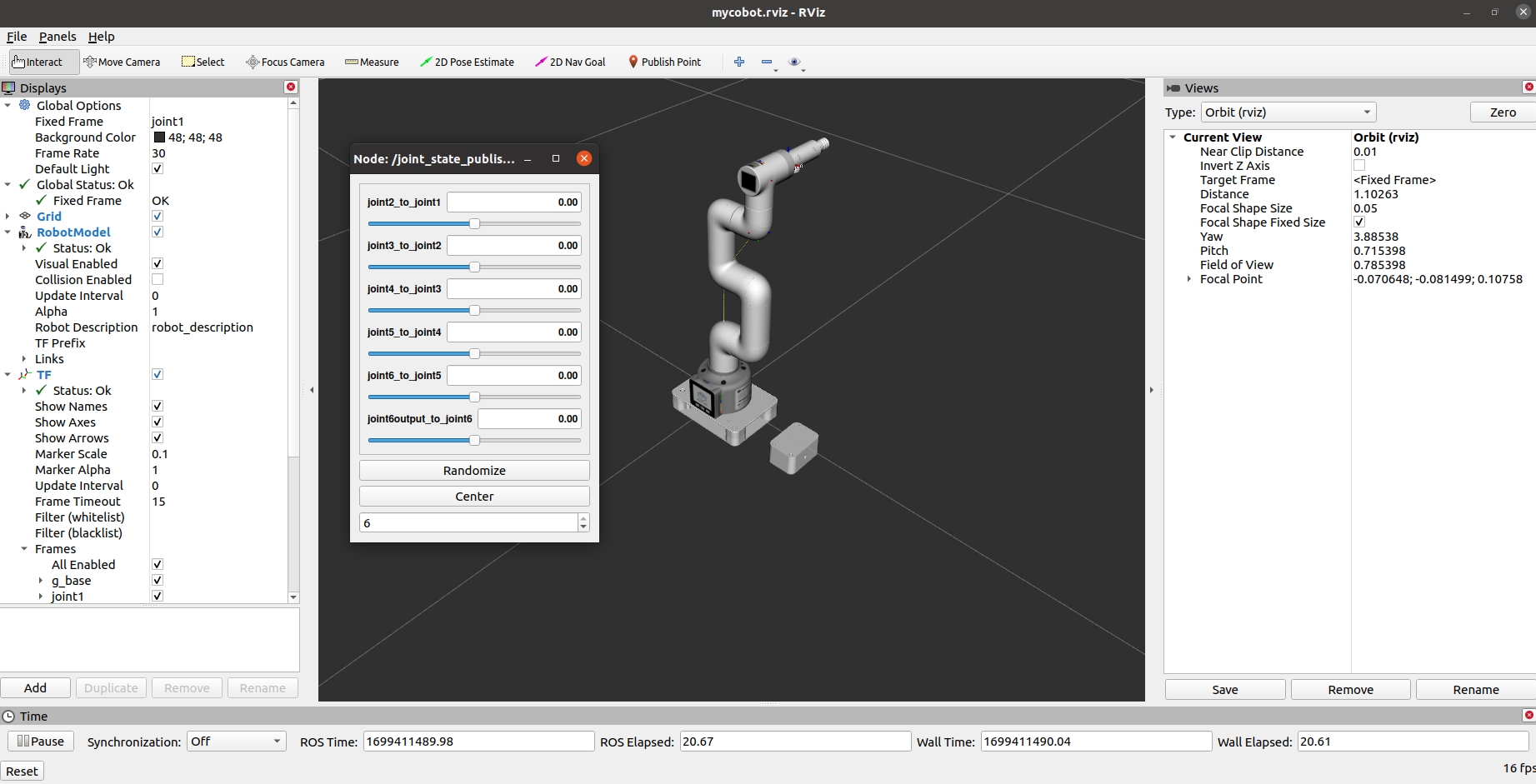
You can then control the model movement in rviz by dragging the slider. The real mycobot will move along with it.
Please note: Since the robot arm will move to the current position of the model when the command is entered, please make sure that the model in rviz does not have mold penetration before you use the command Do not quickly drag the slider after connecting the robotic arm to prevent damage to the robotic arm
3 GUI control
On the basis of the previous ones, this package also provides a simple Gui control interface. This method is intended for real robot arms to interact with each other, please connect to mycobot.
Open the command line:
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to " /dev/ttyACM0".
ros2 launch mycobot_280 simple_gui_pump.launch.py
It will open rviz and a GUI interface, and you will see the following screen:
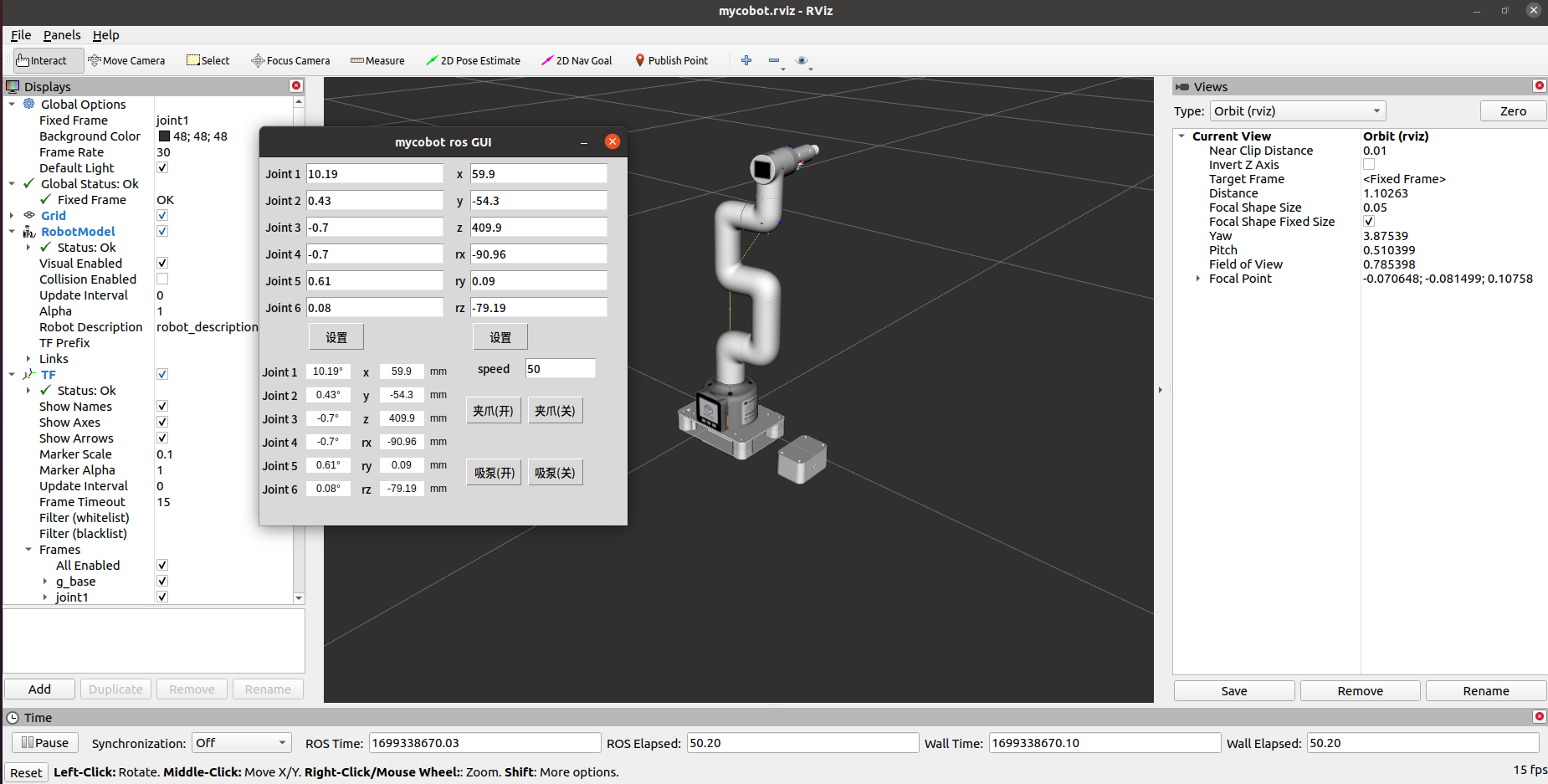
5.2 Camera Flange
1 Load model
Open a command line and run:
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
ros2 launch mycobot_280 test_camera_flange.launch.py
- mycobot 280-PI version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower bar of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
ros2 launch mycobot_280pi test_camera_flange.launch.py
It will open rviz, and you will see the following screen (the Raspberry Pi version has slightly different screens, which does not affect use):
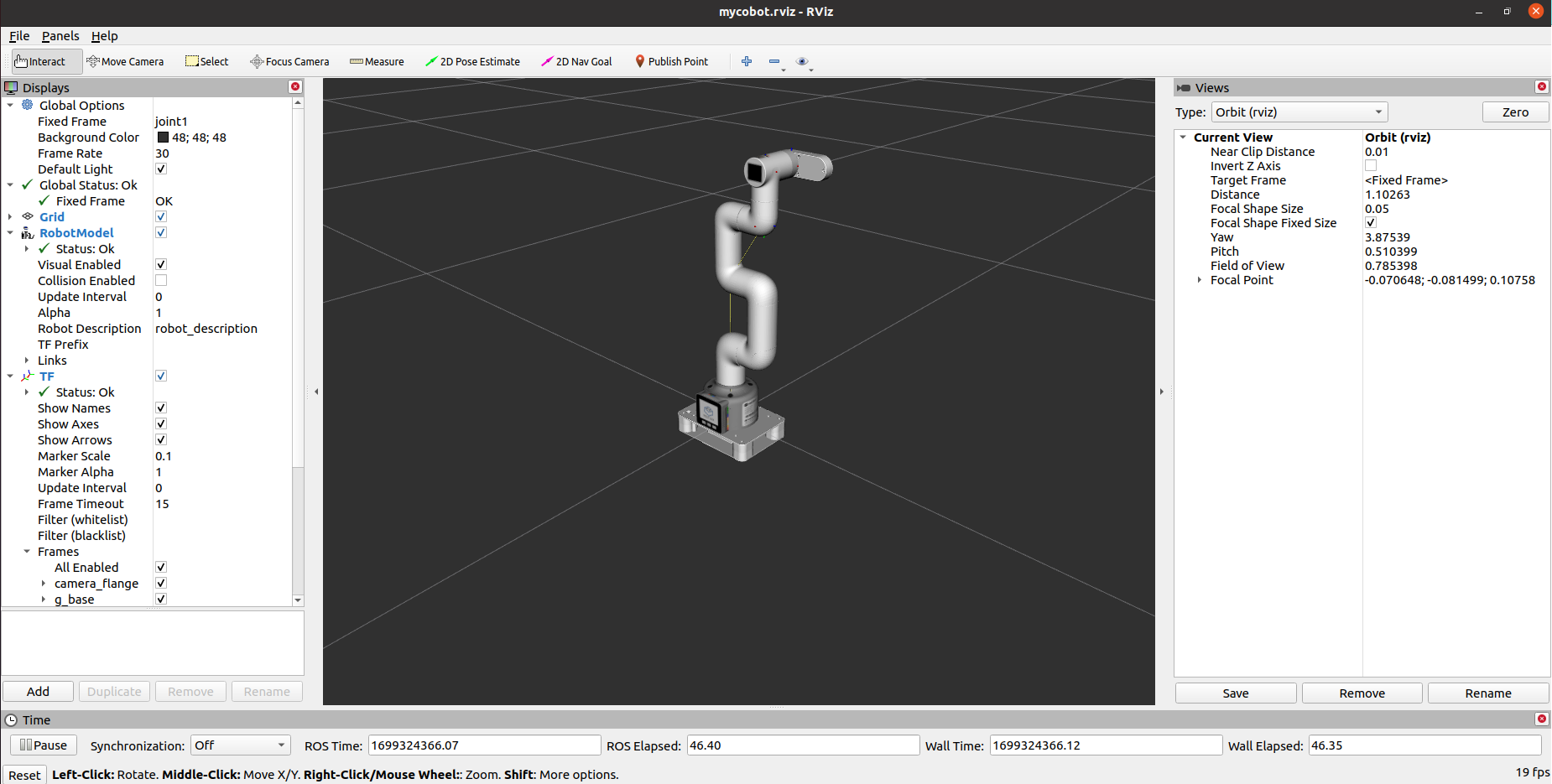
2 Slider control
Note: This function only supports control of the robotic arm
Open a command line and run:
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to " /dev/ttyACM0".
ros2 launch mycobot_280 slider_control_camera_flange.launch.py
- mycobot 280-PI version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower bar of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
# The default serial port name of mycobot 280-PI version is "/dev/ttyAMA0", and the baud rate is 1000000.
ros2 launch mycobot_280pi slider_control_camera_flange.launch.py
It will open rviz and a slider component, and you will see the following screen (the Raspberry Pi version screen is slightly different, which does not affect use):
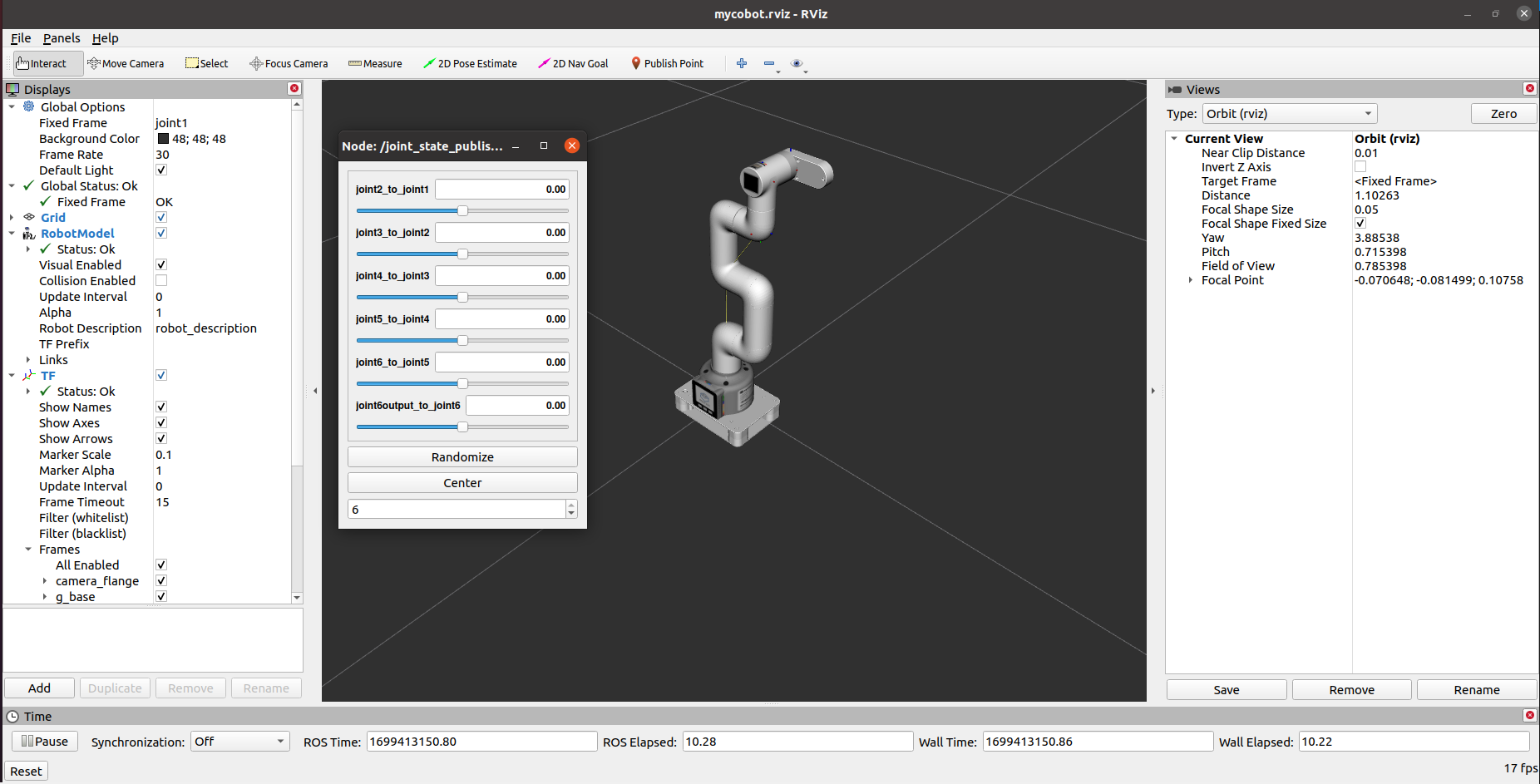
You can then control the model movement in rviz by dragging the slider. The real mycobot will move along with it.
Please note: Since the robot arm will move to the current position of the model when the command is entered, please make sure that the model in rviz does not have mold penetration before you use the command. Do not quickly drag the slider after connecting the robotic arm to prevent damage to the robotic arm.
5.3 Camera Flange && pump
1 Load model
Open a command line and run:
- mycobot 280-M5 version:
ros2 launch mycobot_280 test_camera_flange_pump.launch.py
- mycobot 280-PI version:
Click the ROS2 Shell icon on the desktop or the corresponding icon in the lower bar of the desktop to open the ROS2 environment terminal:



Then run the command:
ros2 launch mycobot_280pi test_camera_flange_pump.launch.py
It will open rviz, and you will see the following screen (the Raspberry Pi version has slightly different screens, which does not affect use):