Control and following of the robot arm
1 Slider Control
Before use, you need to confirm whether the IP address of the robot arm is consistent with that in the program file. If not, you need to modify the IP address in the program file.View the modifications in the listener function in the program file: https://github.com/elephantrobotics/mycobot_ros/blob/noetic/mycobot_pro/mycobot_600/scripts/slider_600.py.
#!/usr/bin/env python2
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from socket import *
import math
import sys
import time
from multiprocessing import Lock
import rospy
from sensor_msgs.msg import JointState
global mc
mutex = Lock()
# Some code is omitted here...
old_list = []
def callback(data):
"""callback function,回调函数"""
satrt_time=time.time()
global old_list
# rospy.loginfo(rospy.get_caller_id() + "%s", data.position)
print ("position", data.position)
data_list = []
for index, value in enumerate(data.position):
value = value * 180 / math.pi
data_list.append(value)
print ("data", data_list)
if not old_list:
old_list = data_list
mc.write_angles(data_list, 1999)
elif old_list != data_list:
old_list = data_list
# if mc.check_running():
# mc.task_stop()
# time.sleep(0.05)
mc.write_angles(data_list, 1999)
end_time=time.time()
print('loop_time:',end_time-satrt_time)
def listener():
global mc
rospy.init_node("control_slider", anonymous=True)
ip = rospy.get_param("~ip", "192.168.10.159")
print (ip)
mc = ElephantRobot(ip, 5001)
# START CLIENT
res = mc.start_client()
if res != "":
sys.exit(1)
# print ep.wait(5)
# print mc.get_angles()
# print mc.get_coords()
mc.set_speed(90)
# print mc.get_speed()
rospy.Subscriber("joint_states", JointState, callback)
end_time=time.time()
# spin() simply keeps python from exiting until this node is stopped
print ("sping ...")
rospy.spin()
if __name__ == "__main__":
listener()
Open a command line and run:
roslaunch mycobot_600 mycobot_600_slider_control.launch
rviz and a slider component will be opened, and you will see the following interface:
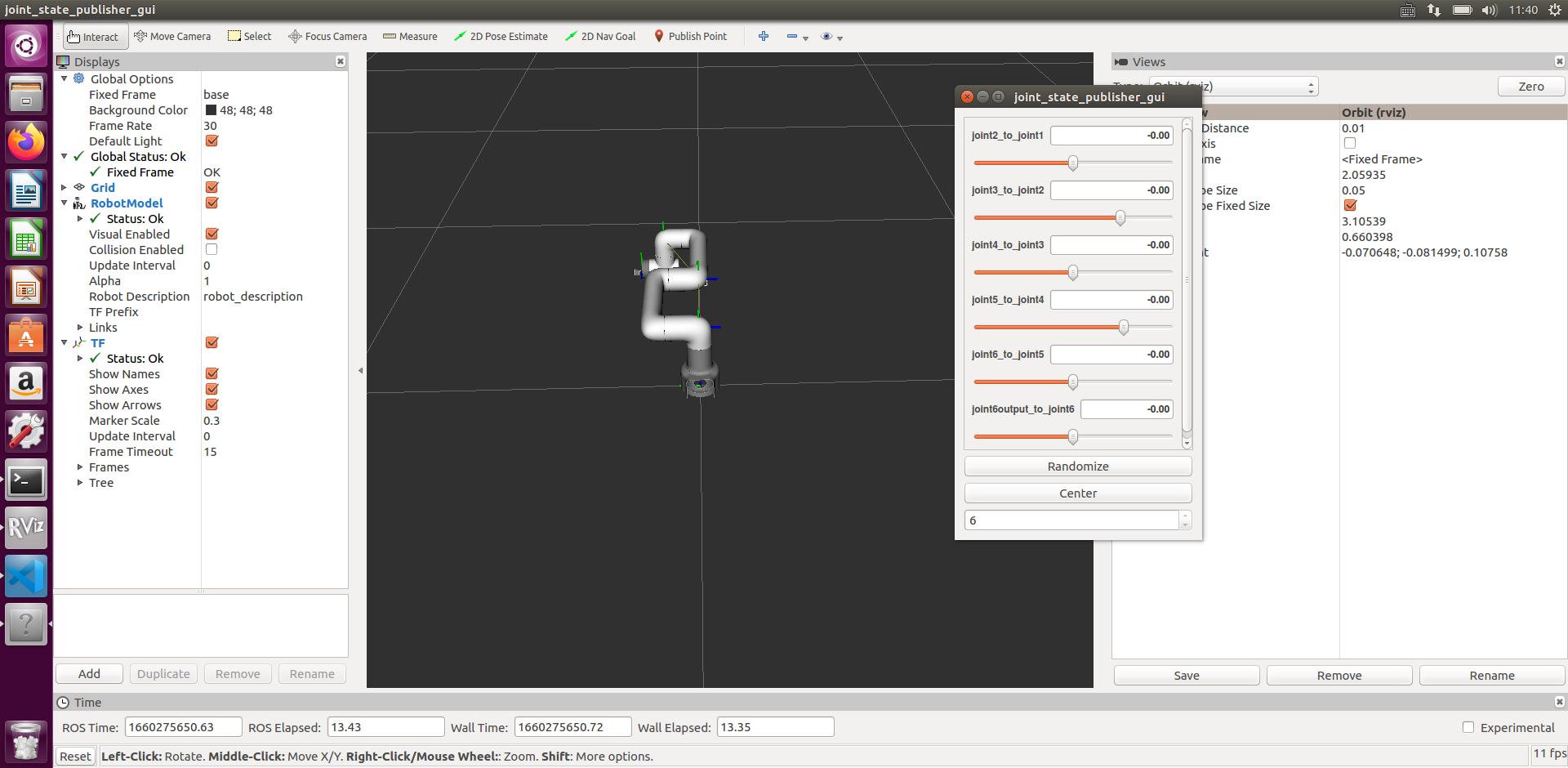
Then you can control the model in rviz to make it move by dragging the slider. If you want the real mycobot to move with the model, you need to open another command line and run:
# The default IP of mycobot pro 600 is "192.168.10.159" and the port number is 5001. The specific IP is subject to the network connected to the actual robot arm.
rosrun mycobot_600 slider_600.py
Note: Since the robot arm will move to the current position of the model when the command is input, make sure that the model in rviz does not appear to be worn out before you use the command.
Do not drag the slider quickly after connecting the robot arm to prevent damage to the robot arm.