1 ROS工程结构
1.1 catkin工作空间
Catkin工作空间是创建、修改、编译catkin软件包的目录。catkin的工作空间,直观的形容就是一个仓库,里面装载着ROS的各种项目工程,便于系统组织管理调用。
- 创建工作空间:
mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src # 创建文件夹
cd ~/catkin_ws/src # 进入文件夹
catkin_init_workspace # 把当前目录初始化为一个ROS工作空间
cd .. # 返回上级目录
catkin_make # 构建工作区中的代码。
catkin的结构十分清晰,它包括了src、build、devel三个路径,在有些编译选项下也可能包括其他。但这三个文件夹是catkin编译系统默认的。它们的具体作用如下:
src/: ROS的catkin软件包(源代码包)
build/: catkin(CMake)的缓存信息和中间文件
devel/: 生成的目标文件(包括头文件,动态链接库,静态链接库,可执行文件等)、环境变量
一个简单的工作空间如下所示:
workspace_folder/ -- WORKSPACE
src/ -- SOURCE SPACE
CMakeLists.txt -- 'Toplevel' CMake file, provided by catkin
package_1/
CMakeLists.txt -- CMakeLists.txt file for package_1
package.xml -- Package manifest for package_1
...
package_n/
CMakeLists.txt -- CMakeLists.txt file for package_n
package.xml -- Package manifest for package_n
1.2 ROS软件包
Package不仅是Linux上的软件包,也是catkin编译得基本单元,我们使用 catkin_make 编译的对象就是每 个ROS的package。
+-- PACKAGE
+-- CMakeLists.txt
+-- package.xml
+-- src/
+-- include/
+-- scripts/
+-- msg/
+-- srv/
+-- urdf/
+-- launch/
CMakeLists.txt: 定义package的包名、依赖、源文件、目标文件等编译规则,是package不可少的成 分
package.xml: 描述package的包名、版本号、作者、依赖等信息,是package不可少的成分
src/: 存放ROS的源代码,包括C++的源码和(.cpp)以及Python的module(.py)
include/: 存放C++源码对应的头文件
scripts/: 存放可执行脚本,例如shell脚本(.sh)、Python脚本(.py)
msg/: 存放自定义格式的消息(.msg)
srv/: 存放自定义格式的服务(.srv)
urdf/: 存放机器人的模型描述(.urdf或.xacro)、3D模型文件(.sda, .stl, .dae等)
launch/: 存放launch文件(.launch或.xml)
创建自己的软件包:
- 指令格式:
catkin_create_pkg命令会要求你输入package_name,如有需要还可以在后面添加一些需要依赖的其它软件包:
catkin_create_pkg <package_name> [depend1] [depend2] [depend3]
- 例如:
catkin_create_pkg beginner_tutorials std_msgs rospy roscpp
2 ROS通信架构
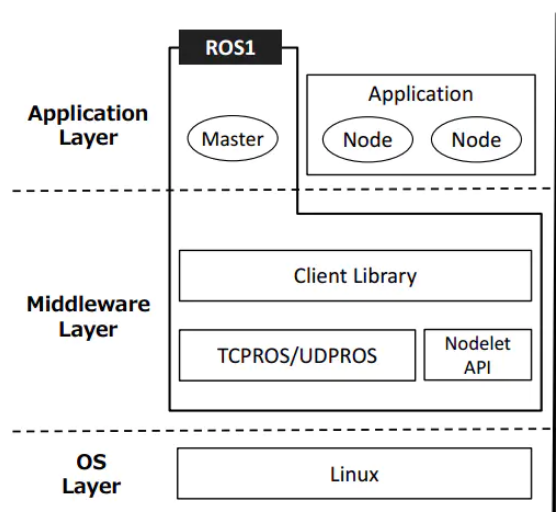
2.1 Master与node
1 Master
节点管理器,每个node启动前要向master注册,管理node之间的通信。
2 roscore
启动master,也会启动rosout(日志管理)和parameter server(参数管理器)
3 node
ROS的进程、pkg里可执行文件运行的实例。
$rosrun [pkg_name] [node_name] #启动
$rosnode list #列出当前运行的node信息
$rosnode info [node_name] #显示某个node的详细信息
$rosnode kill [node_name] #结束某个node
4 launch
启动master和多个node。
$roslaunch [pkg_name] [file_name.launch]
2.2 Service 与 Topic
我们提供一些 service 和 topic, 用以和 mycobot 交互。
1 Service
命令行中输入:
# 显示活动的服务信息
rosservice list
相关的命令与说明:
| 命令 | 详细说明 |
|---|---|
| rosservice list | 显示活动的服务信息 |
| rosservice info [服务名称] | 显示指定服务的信息 |
| rosservice type [服务名称] | 显示服务类型 |
| rosservice find [服务类型] | 查找指定服务类型的服务 |
| rosservice uri [服务名称] | 显示ROSRPC URI服务 |
| rosservice args [服务名称] | 显示服务参数 |
| rosservice call [服务名称] [参数] | 用输入的参数请求服务 |
2 Topic
命令行中输入
# 显示活动的服务信息
rostopic list
相关的命令与说明:
| 命令 | 详细说明 |
|---|---|
| rostopic list | 显示活动的话题目录 |
| rostopic echo [话题名称] | 实时显示指定话题的消息内容 |
| rostopic find [类型名称] | 显示使用指定类型的消息的话题 |
| rostopic type [话题名称] | 显示指定话题的消息类型 |
| rostopic bw [话题名称] | 显示指定话题的消息带宽(bandwidth) |
| rostopic hz [话题名称] | 显示指定话题的消息数据发布周期 |
| rostopic info [话题名称] | 显示指定话题的信息 |
| rostopic pub [话题名称] [消息类型] [参数] | 用指定的话题名称发布消息 |
service与topic的区别:
| service | topic | |
|---|---|---|
| 同步性 | 异步 | 同步 |
| 通信模型 | 发布/订阅 | 服务器/客户端 |
| 底层协议 | ROSTCP/ROSUDP | ROSTCP/ROSUDP |
| 反馈机制 | 无 | 有 |
| 缓冲区 | 有 | 无 |
| 实时性 | 弱 | 强 |
| 节点关系 | 多对多 | 一对多 |
| 适用场景 | 数据传输 | 逻辑处理 |
您可以前往service和topic深入了解这两项功能的使用
2.3 msg和srv简介
- msg:msg文件是描述ROS消息字段的简单文本文件。它们用于为不同语言(c++或者python等)的消息生成源代码。
- srv:srv文件用来描述服务。它由两部分组成:请求(request)和响应(response)。 msg文件存储在包的msg目录中,而srv文件存储在srv目录中。
1 rosmsg
rosmsg是用于显示有关 ROS消息类型的 信息的命令行工具。
rosmsg 演示:
rosmsg show # 显示消息描述
rosmsg info # 显示消息信息
rosmsg list # 列出所有消息
rosmsg md5 # 显示 md5 加密后的消息
rosmsg package # 显示某个功能包下的所有消息
rosmsg packages # 列出包含消息的功能包
rosmsg list 会列出当前 ROS 中的所有 msg
rosmsg packages 列出包含消息的所有包
rosmsg package 列出某个包下的所有msg
//rosmsg package # 包名
rosmsg package turtlesim
- rosmsg show 显示消息描述
//rosmsg show # 消息名称
rosmsg show turtlesim/Pose
# 结果:
float32 x
float32 y
float32 theta
float32 linear_velocity
float32 angular_velocity
rosmsg info 作用与 rosmsg show 一样
rosmsg md5 一种校验算法,保证数据传输的一致性
2 rossrv
rossrv是用于显示有关ROS服务类型的信息的命令行工具,与 rosmsg 使用语法高度雷同。
rossrv show # 显示服务消息详情
rossrv info # 显示服务消息相关信息
rossrv list # 列出所有服务信息
rossrv md5 # 显示 md5 加密后的服务消息
rossrv package # 显示某个包下所有服务消息
rossrv packages # 显示包含服务消息的所有包
rossrv list 会列出当前 ROS 中的所有 srv 消息
rossrv packages 列出包含服务消息的所有包
rossrv package 列出某个包下的所有msg
//rossrv package # 包名
rossrv package turtlesim
- rossrv show 显示消息描述
//rossrv show # 消息名称
rossrv show turtlesim/Spawn
# 结果:
float32 x
float32 y
float32 theta
string name
---
string name
rossrv info 作用与 rossrv show 一致
rossrv md5 对 service 数据使用 md5 校验(加密)
3 URDF介绍
- Unified Robot Description Format,统一机器人描述格式,简称为URDF。ROS中的urdf功能包包含一个URDF的C++解析器,URDF文件使用XML格式描述机器人模型。
- URDF 不能单独使用,需要结合 Rviz 或 Gazebo,URDF 只是一个文件,需要在 Rviz 或 Gazebo 中渲染成图形化的机器人模型。
3.1 urdf文件描述
代码示例:
本处只截取部分代码进行展示:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro" name="firefighter" >
<xacro:property name="width" value=".2" />
<!-- base -->
<link name="base">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/base.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 0 " rpy = " 0 0 0"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/base.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 0 " rpy = " 0 0 0"/>
</collision>
</link>
<!-- body -->
<link name="link_body">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/body.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 -0.11 " rpy = " 0 0 0"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/body.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 -0.11 " rpy = " 0 0 0"/>
</collision>
</link>
<!-- screen head -->
<link name="link_head">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/head.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 -0.1 " rpy = " 0 0 0"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/head.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 -0.1 " rpy = " 0 0 0"/>
</collision>
</link>
<!-- camera -->
<link name="link_eye">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/head_eye.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 -0.0 " rpy = " 0 0 -0.6981"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/head_eye.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 -0.1 " rpy = " 0 0 -0.6981"/>
</collision>
</link>
<link name="link1_L">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/joint1_L.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 -0.084 " rpy = " 0 0 0"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/joint1_L.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 -0.084 " rpy = " 0 0 0"/>
</collision>
</link>
<link name="link2_L">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/joint2_L.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 0.0 " rpy = " 3.14159 0 -1.5708"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/joint2_L.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 0.0 " rpy = " 3.14159 0 -1.5708"/>
</collision>
</link>
<link name="link3_L">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/joint3_L.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 0.038 " rpy = " 0 0 0"/>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="package://mercury_description/urdf/mercury_b1/joint3_L.dae"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz = "0 0 0.038 " rpy = " 0 0 0"/>
</collision>
</link>
......
<joint name="eye" type="revolute">
<axis xyz=" 0 0 1"/>
<limit effort = "1000.0" lower = "0" upper = "0.83" velocity = "0"/>
<parent link="link_head"/>
<child link="link_eye"/>
<origin xyz= " 0.03 0 -0.08 " rpy = "1.5708 0 0"/>
</joint>
<joint name="head" type="revolute">
<axis xyz=" 0 0 1"/>
<limit effort = "1000.0" lower = "-2.4085" upper = "3.2812" velocity = "0"/>
<parent link="link_body"/>
<child link="link_head"/>
<origin xyz= " 0 0 0.22 " rpy = "0 0 0"/>
</joint>
<joint name="body" type="revolute">
<axis xyz=" 0 0 1"/>
<limit effort = "1000.0" lower = "-2.0594" upper = "2.0594" velocity = "0"/>
<parent link="base"/>
<child link="link_body"/>
<origin xyz= " 0 0 0.231 " rpy = "0 0 0"/>
<joint name="joint1_L" type="revolute">
<axis xyz=" 0 0 1"/>
<limit effort = "1000.0" lower = "-3.1066" upper = "3.1066" velocity = "0"/>
<parent link="link_body"/>
<child link="link1_L"/>
<origin xyz= " 0.075 0.186 0.085 " rpy = "-1.5708 0 -0.5235"/>
</joint>
<joint name="joint2_L" type="revolute">
<axis xyz=" 0 0 1"/>
<limit effort = "1000.0" lower = "-1.4311" upper = "2.2689" velocity = "0"/>
<parent link="link1_L"/>
<child link="link2_L"/>
<origin xyz= " 0 0 0 " rpy = "-1.5708 0 0"/>
</joint>
<joint name="joint3_L" type="revolute">
<axis xyz=" 0 0 1"/>
<limit effort = "1000.0" lower = "-3.1066" upper = "3.1066" velocity = "0"/>
<parent link="link2_L"/>
<child link="link3_L"/>
<origin xyz= " 0 -0.11 0 " rpy = "1.5708 0 0"/>
</joint>
</joint>
</robot>
可以看出,urdf文件并不复杂,主要是由link和joint两个部分不断重复而成。
3.2 link部分
link元素描述具有惯性、可视特征和碰撞属性的刚体
3.2.1 属性
name: 用来描述链接本身的名称
3.2.2 元素
<inertial>(可选)- 连杆的惯性特性
<origin>(可选,defaults to identity if not specified)- 定义相对于连杆坐标系的惯性参考系的参考坐标,该坐标必需定义在连杆重心处,其坐标轴可与惯性主轴不平行。
- xyz (可选,默认为零向量) 表示 x , y , z x,y,zx,y,z 方向的偏置,单位为米。
- rpy(可选: defaults to identity if not specified) 表示坐标轴在RPY方向上的旋转,单位为弧度。
<mass>连杆的质量属性<inertia>3×3旋转惯性矩阵,由六个独立的量组成:ixx, ixy, ixz, iyy, iyz, izz。
<visual>(可选)- 连杆的可视化属性。用于指定连杆显示的形状(矩形、圆柱体等),同一连杆可以存在多个visual元素,连杆的形状为多个元素两个形成。一般情况下模型较为复杂可以通过soildwork绘制后生成stl调用,简单的形状如添加末端执行器等可以直接编写。同时可以在此处可根据理论模型和实际模型差距调整几何形状的位置。
<namel>(可选) 连杆几何形状的名字。<origin>(可选,defaults to identity if not specified)- 相对于连杆的坐标系的几何形状坐标系。
- xyz (optional: defaults to zero vector) 表示x , y , z x,y,zx,y,z 方向的偏置,单位为米。
- rpy (optional: defaults to identity if not specified) 表示坐标轴在RPY方向上的旋转,单位为弧度。
<geometry>(必需)- 可视化对象的形状,可以是下面的其中一种:
<box>矩形,元素包含长、宽、高。原点在中心。<cylinder>圆柱体,元素包含半径、长度。原点中心。<sphere>球体,元素包含半径。原点在中心。<mesh>网格,由文件决定,同时提供 scale ,用于界定其边界。推荐使用 Collada .dae 文件, 也支持.stl文件,但必须为一个本地文件。
<material>(可选)- 可视化组件的材料。可以在link标签外定义,但必需在robot标签内,在link标签外定义时,需引用link的名字。
<color>(可选) 颜色,由 red/green/blue/alpha 组成,大小范围在 [0,1] 内。<texture>(可选) 材料属性,由文件定义。
<collision>(可选)- 连杆的碰撞属性。碰撞属性和连杆的可视化属性不同,简单的碰撞模型经常用来简化计算。同一个连杆可以有多个碰撞属性标签,连杆的碰撞属性表示由其定义的几何图形集构成。
<name>(可选) 指定连杆几何形状的名称<origin>(可选,defaults to identity if not specified)- 碰撞组件的参考坐标系相对于连杆坐标系的参考坐标系。
- xyz (可选, 默认零向量) 表示x , y , z x,y,zx,y,z 方向的偏置,单位为米。
- rpy (可选, defaults to identity if not specified) 表示坐标轴在RPY方向上的旋转,单位为弧度。
<geometry>与上述geometry元素描述相同
详细元素以及各个元素的作用可以前往官方文档进行查看
3.3 joint部分
joint部分描述了关节的运动学和动力学,并指定了关节的安全限值。
3.3.1 joint的属性:
name:
指定关节的唯一名称
type:
指定关节的类型,其中类型可以是下列类型之一:
- revolute - 沿轴线旋转的铰链接头,其范围由上限和下限指定。
- 连续 - 一种连续铰链接头,围绕轴旋转,没有上限和下限。
- 棱柱形 - 沿轴滑动的滑动接头,其范围由上限和下限指定。
- 固定 - 这不是真正的关节,因为它不能移动。所有自由度都被锁定。这种类型的接头不需要轴,校准,动力学,极限或safety_controller。
- 浮动 - 此接头允许所有 6 个自由度的运动。
- 平面 - 此接头允许在垂直于轴的平面上运动。
3.3.2 joint的元素
<origin>(可选,defaults to identity if not specified) 从parent link到child link的变换,joint位于child link的原点,修改该参数可以调整连杆的位置,可用在调整实际模型与理论模型误差,但不建议大幅度修改,因为该参数影响连杆stl的位置,容易影响碰撞检测效果。- xyz (可选: 默认为零向量) 代表x , y , z x,y,zx,y,z轴方向上的偏移,单位米。
- rpy (可选: 默认为零向量) 代表绕着固定轴旋转的角度:roll绕着x轴,pitch绕着y轴,yaw绕着z轴,用弧度表示。
<parent>(必需)- parent link的名字是一个强制的属性。
- link parent link的名字,是这个link在机器人结构树中的名字。
<child>(必需)- child link的名字是一个强制的属性。
- link child link的名字,是这个link在机器人结构树中的名字。
<axis>(可选: 默认为(1,0,0))- joint的axis轴在joint的坐标系中。这是旋转轴(revolute joint),prismatic joint移动的轴,是planar joint的标准平面。这个轴在joint坐标系中被指定。修改该参数可以调整关节的旋转所绕着的轴,常用于调整旋转方向,若模型旋向与实际相反,只需乘-1即可。固定(fixed)和浮动(floating)类型的joint不需要用到这个元素。
- xyz(必需) 代表轴向量的x , y , z x,y,zx,y,z分量,为标准化的向量。
<calibration>(可选)- joint的参考点,用来矫正joint的绝对位置。
- rising (可选) 当joint正向运动时,参考点会触发一个上升沿。
- falling (可选) 当joint正向运动时,参考点会触发一个下降沿。
<dynamics>(可选)- 该元素用来指定joint的物理性能。它的值被用来描述joint的建模性能,尤其是在仿真的时候。
<limit> (当关节为旋转或移动关节时为必需)
- 该元素为关节运动学约束。
- lower (可选, 默认为0) 指定joint运动范围下界的属性(revolute joint的单位为弧度,prismatic joint的单位为米),连续型的joint忽略该属性。
- upper (可选, 默认为0) 指定joint运动范围上界的属性(revolute joint的单位为弧度,prismatic joint的单位为米),连续型的joint忽略该属性。
- effort (必需) 该属性指定了joint运行时的最大的力。
- velocity (required) 该属性指定了joint运行时的最大的速度。
<mimic>(可选)
- 这个标签用于指定已定义的 joint 来模仿已存在的 joint 。这个joint的值可以用以下公式计算:
value = multiplier * other_joint_value + offset - joint(必填) 需要模仿的joint的名字。
- multiplier(可选) 指定上述公式中的乘数因子。
- offset(可选) 指定上述公式中的偏移项。默认值为0
<safety_controller> (可选)
- 该元素为安全控制限制,此元素下数据会读入到move_group中,但实际上时无效,move_group会跳过此处限制直接读取limit下的参数内容,同时设置该元素有几率会导致规划失败。
- soft_lower_limit (可选, 默认为0) 该属性指定了joint安全控制边界的下界,是joint安全控制的起始限制点。这个值需要大于上述的limit中的lower值。
- soft_upper_limit (可选, 默认为0) 该属性指定了joint安全控制边界的上界,是joint安全控制的起始限制点。这个值需要小于上述的limit中的upper值。
- k_position(可选, 默认为0) 本属性用于说明位置和速度之间的关系。
- k_velocity(必需) 本属性用于说明力和速度之间的关系。
详细元素以及各个元素的作用可以前往 http://wiki.ros.org/urdf/XML/joint 进行查看
4 常用命令工具
在ROS中,有许多常用的命令行工具,这些工具可以帮助你进行开发、调试、管理ROS节点等。以下是一些常用的ROS命令行工具:
4.1 编译工作空间
caktin_make
4.2 roscore
启动ROS主节点。在运行ROS节点之前,通常需要先启动roscore
roscore
4.3 rosrun
运行指定的ROS节点。
rosrun package_name node_name
4.4 roslaunch
使用Launch文件启动一个或多个ROS节点。
roslaunch package_name launch_file.launch
4.5 rosnode
查看正在运行的ROS节点信息。
rosnode list
rosnode info node_name
4.6 rostopic
查看正在运行的ROS话题信息。
rostopic list
rostopic echo topic_name
4.7 rosservice
查看和调用ROS服务。
rosservice list
rosservice call service_name
4.8 rosparam
获取和设置ROS参数。
rosparam get parameter_name
rosparam set parameter_name value
4.9 rosmsg
查看ROS消息类型。
rosmsg show message_type
4.10 rosdep
安装ROS包的依赖项。
rosdep install package_name
4.11 环境变量
查看ROS_PACKAGE_PATH环境变量
echo $ROS_PACKAGE_PATH