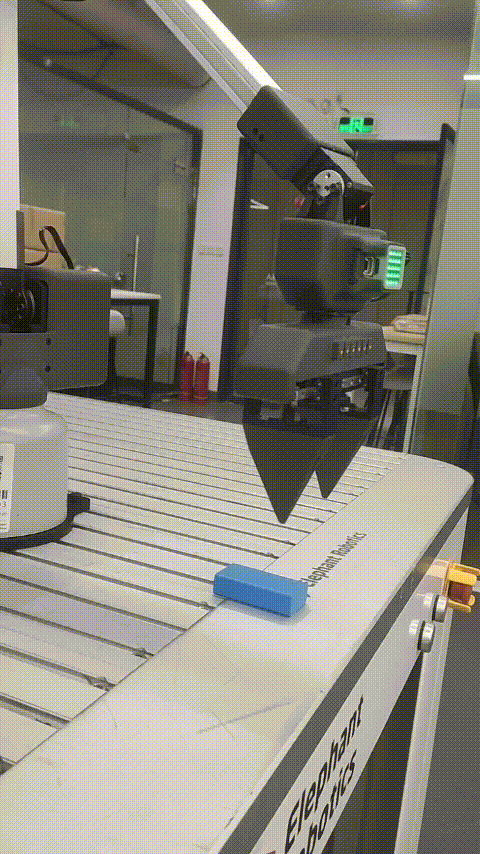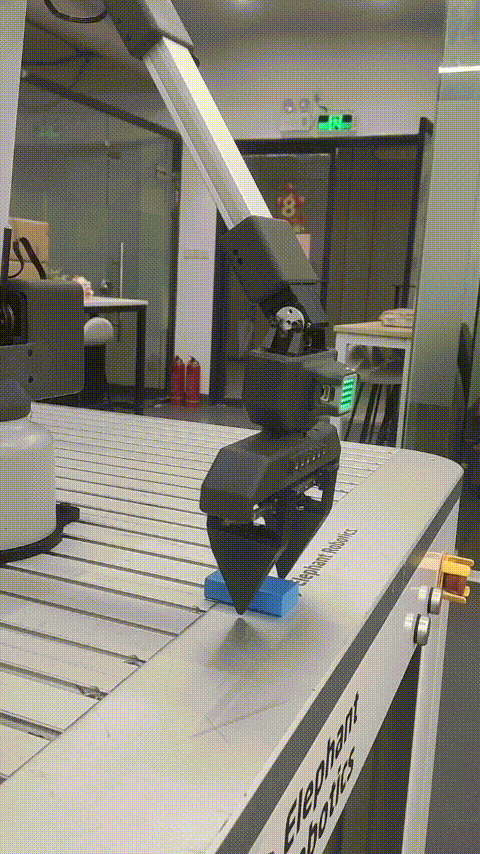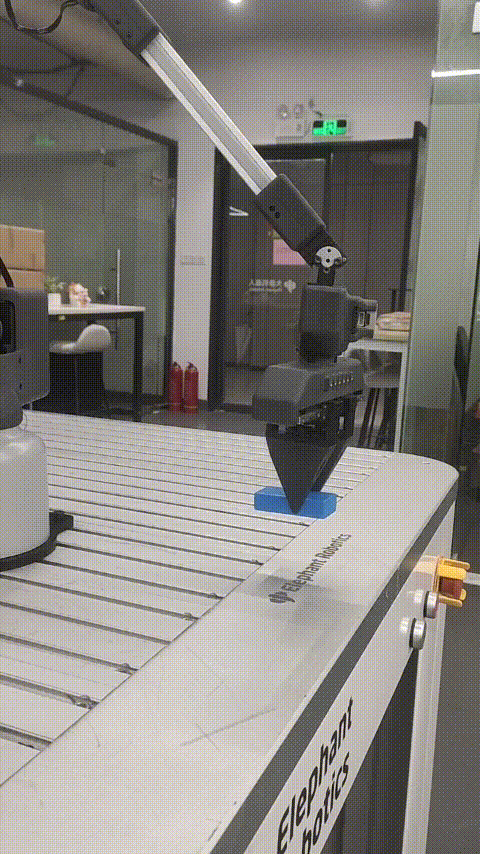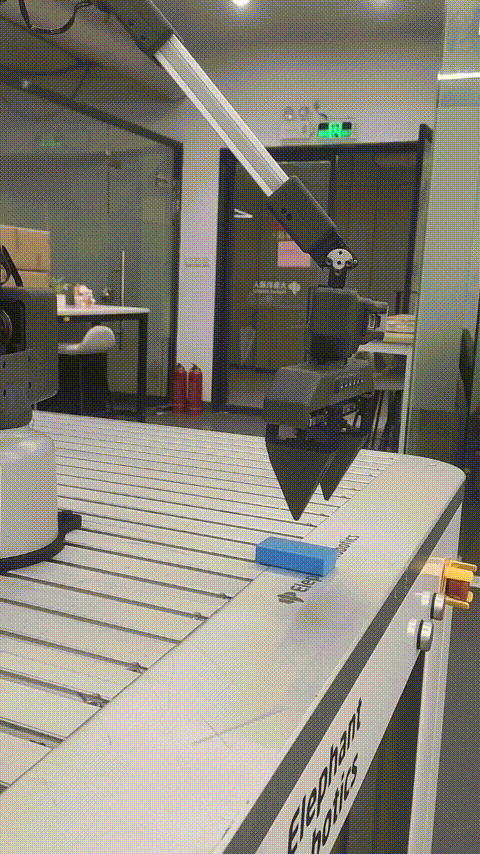
Robot palletizing and handling case
Function description: The robot moves the wood block from point A to point B
1 Firmware burning
Since the robot needs to use Cartesian motion, it is necessary to burn the pico firmware and basic firmware that support Cartesian motion. However, the firmware that supports Cartesian motion has not been released on mystudio and can only be obtained by contacting after-sales personnel.
2 pymycobot installation
If you want to use Cartesian motion, you need to install or update pynycobot. Open the computer terminal and execute the following command to install or update pymycobot
pip install pymycobot --upgrade
3 Preparation
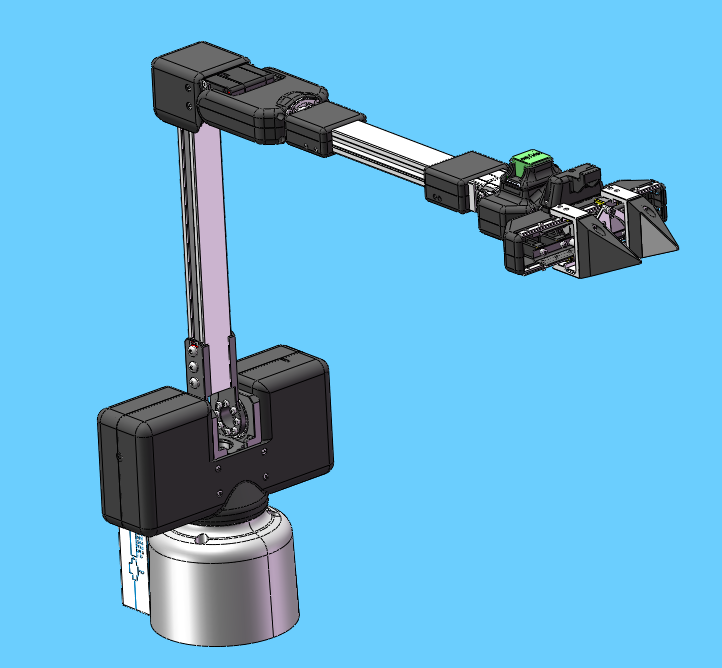
Before connecting the robot arm to 24V, manually adjust the robot arm to the posture shown in the figure below, and then connect the 24V power supply and communication data cable in turn. There should be no debris around the robot arm to avoid collision
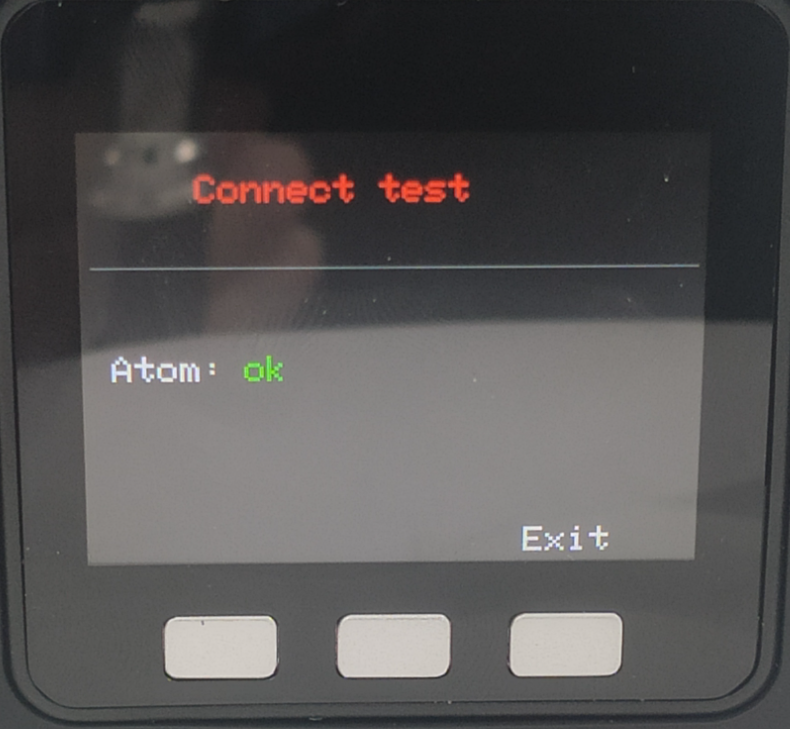
Make sure the base screen displays ok
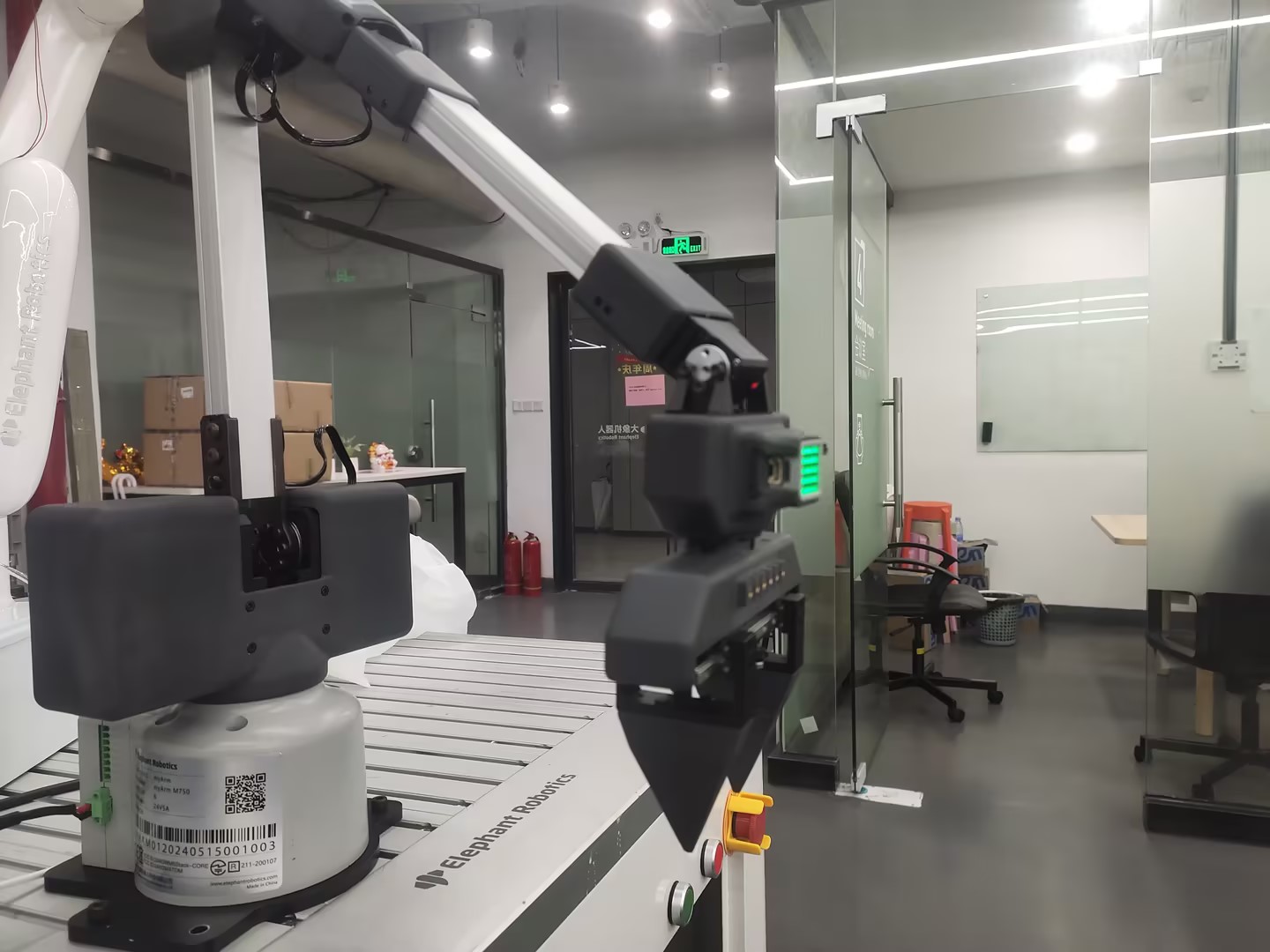
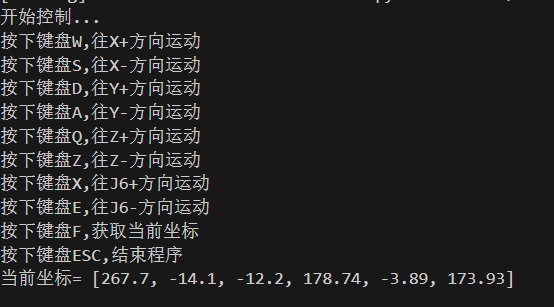
4 Keyboard control
After running the following program, the robot arm will first move to an initial position, and then print the key prompt information in the terminal. Press the corresponding key according to the terminal information to control the robot movement

import threading
from pymycobot import MyArmMControl, utils
import keyboard
import time
m = MyArmMControl(utils.get_port_list()[0],1000000)
def init():
# 设置初始角度
m.write_angles([-10.19, 8.62, 30.65, 2.19, 50.53, -4.83], 100)
time.sleep(1)
m.set_gripper_state(0,100)
time.sleep(1)
# 用于键盘输入检测的函数
def keyborad_ctrl():
print("Start control...")
print("Press the W keyboard to move in the X+ direction")
print("Press the S keyboard to move in the X- direction")
print("Press the D keyboard to move in the Y+ direction")
print("Press the A keyboard to move in the Y- direction")
print("Press the Q keyboard to move in the Z+ direction")
print("Press the Z keyboard to move in the Z- direction")
print("Press the X keyboard to move in the J6+ direction")
print("Press the E keyboard to move in the J6- direction")
print("Press the F keyboard to get the current coordinates")
print("Press the ESC keyboard to end the program")
blocked_keys = ['w', 'a', 's', 'd', 'q', 'z','f','e','x']
for key in blocked_keys:
keyboard.block_key(key)
key_processed = {
'w': False,
'a': False,
's': False,
'd': False,
'q': False,
'z': False,
'f':False,
'e': False,
'x':False,
}
else_executed = False
try:
while True:
if keyboard.is_pressed('esc'):
print("Exit control...")
break
for key in blocked_keys:
if keyboard.is_pressed(key) and not key_processed[key]:
threading.Thread(target=handle_key, args=(key,)).start()
key_processed[key] = True
else_executed = False
if all(not keyboard.is_pressed(key) for key in blocked_keys) and not else_executed:
m.stop()
else_executed = True
for key in key_processed:
if not keyboard.is_pressed(key):
key_processed[key] = False
time.sleep(0.01)
finally:
keyboard.unhook_all()
def handle_key(key):
if key == 'w':
m.jog_coord(1, 1, 60)
elif key == 'a':
m.jog_coord(2, 0, 60)
elif key == 'd':
m.jog_coord(2, 1, 60)
elif key == 's':
m.jog_coord(1, 0, 60)
elif key == 'q':
m.jog_coord(3, 1, 60)
elif key == 'z':
m.jog_coord(3, 0, 60)
elif key == 'e':
m.jog_angle(6,0,50)
elif key == 'x':
m.jog_angle(6,1,50)
elif key == 'f':
print("Current coordinates=",m.get_coords())
if __name__ == "__main__":
init()
keyborad_ctrl()
When the robot reaches the target point, record the current coordinates and close the program
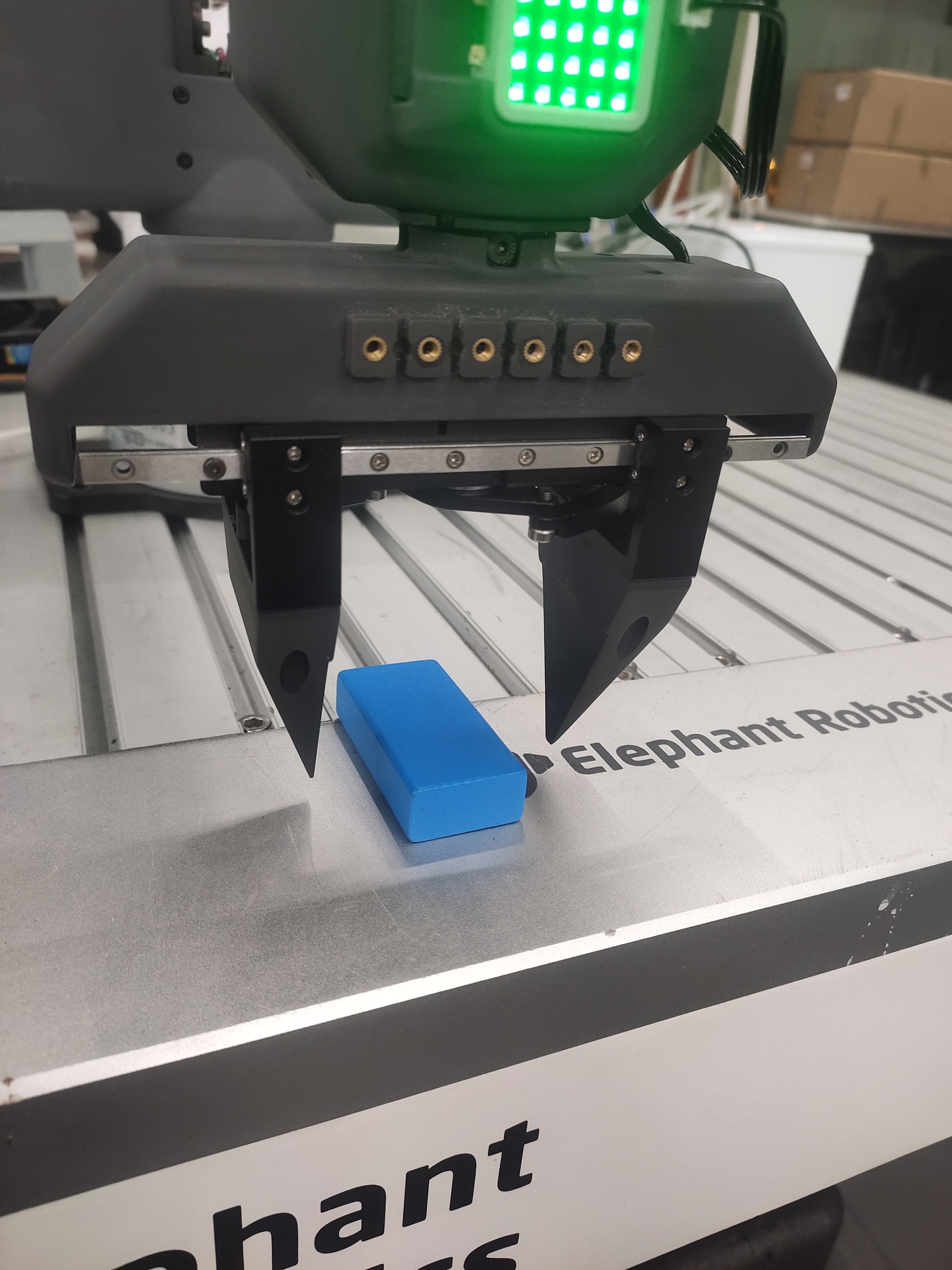
5 Case reproduction
from pymycobot import MyArmMControl, utils
import time
init_angles=[-10.19, 8.62, 30.65, 2.19, 50.53, -4.83]#6 joint angles at the initial position
target_point=[277.7, -14.6, -7.5, 178.74, -2.04, 174.17]#Coordinate position of the gripping target
m = MyArmMControl(utils.get_port_list()[0],1000000)
if __name__=="__main__":
m.set_gripper_state(0,100)#Open the gripper first
time.sleep(1)
m.write_angles(init_angles,100)#Move to the initial position
time.sleep(2)
m.write_coords([target_point[0],target_point[1],target_point[2]+50,target_point[3],target_point[4],target_point[5]],100,1)#Move to 50mm above the gripping point
time.sleep(2)
m.write_coords([target_point[0],target_point[1],target_point[2],target_point[3],target_point[4],target_point[5]],100,1)#Move to the gripping point
time.sleep(2)
m.set_gripper_state(1,100)#Gripper closed
time.sleep(1)
m.write_coords([target_point[0],target_point[1],target_point[2]+50,target_point[3],target_point[4],target_point[5]],100,1)#Move to 50mm above the gripping point
time.sleep(2)
m.write_coords([target_point[0],target_point[1]+100,target_point[2]+50,target_point[3],target_point[4],target_point[5]],100,1)#Move to 50mm above the placement point
time.sleep(2)
m.write_coords([target_point[0],target_point[1]+100,target_point[2],target_point[3],target_point[4],target_point[5]],100,1)#Move to the placement point
time.sleep(2)
m.set_gripper_state(0,100)#Gripper open
time.sleep(1)
m.write_coords([target_point[0],target_point[1]+100,target_point[2]+50,target_point[3],target_point[4],target_point[5]],100,1)#Move to 50mm above the placement point
time.sleep(2)
6 Effect display