Others
Q: How to use mycobot test tool?
Mycobot test tool is factory-installed and is not recommended for users. It may cause zero position or pid abnormalities and damage the machine. Please delete this tool directly. If the tool has been used to cause abnormal movement of the robot arm, please refer to the following to readjust the pid and zero position, and do not continue to use this factory test tool in the subsequent use process. Reference link for resetting pid method: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1UWhaaSTuwLFImuEGY1J2tvgxTQDwWxK_/view?usp=sharing Reference link for zero position calibration method: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1XtKH-ykKWPH0q9Z_YHwzkgwNKRhstHhi/view?usp=sharing
Q: How to reset to factory settings when the machine is abnormal?
Restoring to factory settings mainly involves resetting firmware, image, pid and zero position. The following is the reset solution:
About resetting the firmware: It is recommended to ensure that mystudio is updated to the latest version, and then download the corresponding latest Atom version firmware, minirobot firmware (only available in M5 series machines) and pico firmware (only available in 320 series models). For the method of resetting the firmware, please refer to the mystudio chapter of gitbook
About resetting the image: When resetting the image, all contents in the original system will be cleared. If there are important files, please save them in advance. For the method of resetting the image, please refer to the system usage chapter of gitbook
About resetting pid: Generally, when the machine has severe joint shaking, abnormal joint movement speed, and joints curled up, the pid can be reset. For the reset method, refer to: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1UWhaaSTuwLFImuEGY1J2tvgxTQDwWxK_/view?usp=sharing
About resetting zero position: Generally, when the machine has an incorrect zero position and the joint limit is abnormal, the zero position can be recalibrated. For the reset method, refer to: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1XtKH-ykKWPH0q9Z_YHwzkgwNKRhstHhi/view?usp=sharing
Q: Where is the download path of the urdf file?
- A: Please refer to the following path. The urdf of all mycobot models is in this path: https://github.com/elephantrobotics/mycobot_ros/tree/noetic/mycobot_description/urdf
Q: How to troubleshoot when the robot arm cannot be controlled when using Bluetooth or WiFi function?
A: The M5 robot arm supports three communication methods, namely USB serial port, WiFi and Bluetooth communication. The most commonly used USB serial port communication method. Before using each communication method, you need to make sure that the LCD screen of the M5 is adjusted to the corresponding method and maintain this communication state to control the robot arm normally.
wifi communication mode: When using the TCP/IP example in the python chapter, you need to keep the M5's LCD screen in the wifi communication interface, as shown below:

bluetooth communication mode: When using the mobile phone APP control, you need to keep the M5's LCD screen in the Bluetooth communication interface, as shown below:

After ensuring that the communication mode status is selected correctly, try to control the robot arm again
Q: How long is the command transmission delay when controlling the motor through the robot's controller via serial port or socket communication? Is there a communication timing diagram? How about real-time performance?
There is no delay test data for serial or socket communication. According to the feedback from our development and use, the real-time performance is still quite high and there will be no lag.
Q: What is the base coordinate system of the 280M5 robot?
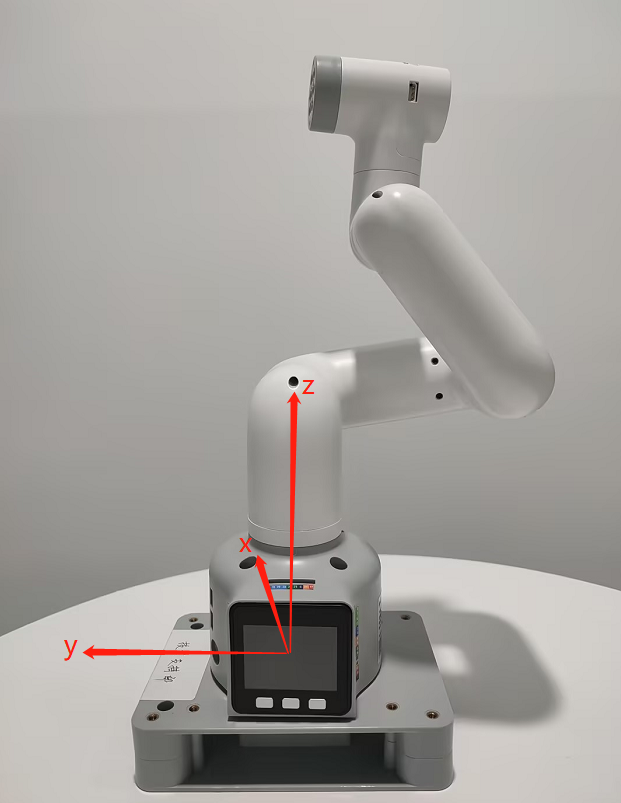
Q: Are the joints of 280 controlled by the serial bus?
A: Yes
Q: Is there more explanation about the understanding of coordinates?
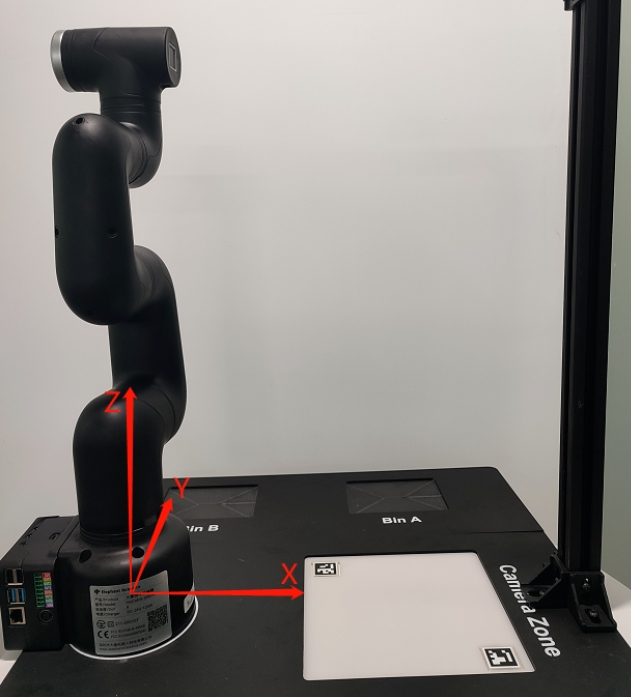
A: The API for controlling coordinate movement is send_coords([x,y,z,rx,ry,rz], speed) x, y, z coordinates: Control the position of the end effector of the robot in space. Changing these coordinate values will move the robot to different spatial positions, thereby achieving positioning in three-dimensional space. rx, ry, rz attitude angles: Control the attitude or orientation of the end effector of the robot. These values are usually given in the form of Euler angles, describing the rotation of the end effector of the robot relative to the base coordinate system, and the order of Euler angles is zyx. Changing these values will rotate the end effector of the robot to different angles or directions. For example: When you adjust +X, this means that the position of the end effector of the current robot arm moves a certain distance along the positive direction of the X axis of the current end effector. This action will cause the robot to move in a certain direction as a whole. And when you adjust RX, this means that the attitude of the end effector of the current robot arm rotates a certain angle around the X axis of the current end effector. This action will cause the robot to rotate as a whole and the direction of the end effector will change. In general, the adjustment of +X and RX will directly affect the motion state of the robot arm. +X controls the movement of the position, while RX controls the change of attitude. If you want to see the changes more intuitively, we recommend that you use myblockly's serial control tool to adjust a parameter at a time and observe its changes in the coordinate system. Please note that when observing rx, ry, and rz, if you want to be more intuitive, please pay attention to adjusting x and ry when the J1 joint is 0, and adjusting y and rx when the joint is 90. You can refer to the coordinate system diagram below:

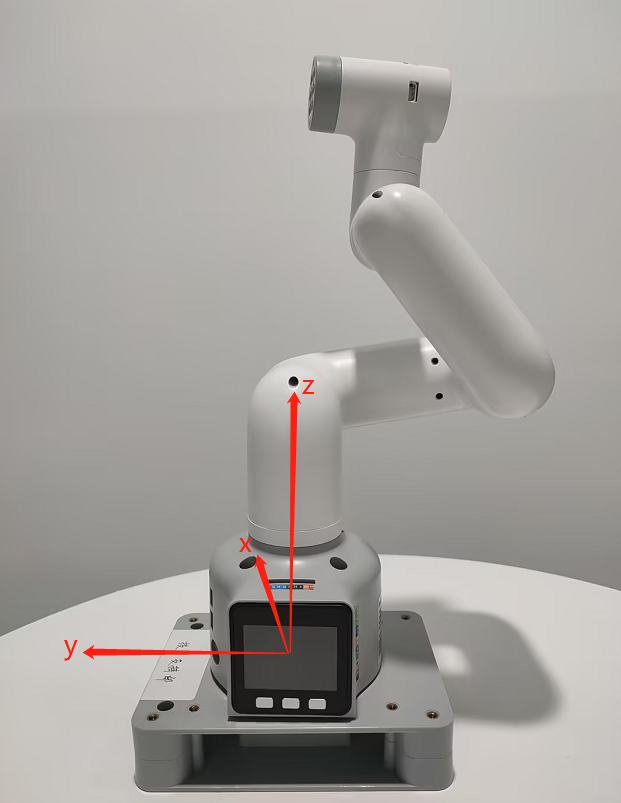
Q: Is there more explanation about the Offset of the DH parameter? Is the Offset rotated around z?
A: The DH parameter describes the geometric and kinematic relationship between adjacent links in the robot arm. In the DH parameter table, the Offset parameter indicates the effect of the previous link rotating around its z-axis on the position of the next link, that is, the offset when connecting two links. For the Offset parameter in the robot arm, it generally indicates the effect of the previous link rotating around its own z-axis on the position of the next link, rather than rotating around the z-axis of the next link. Therefore, Offset is not a rotation around z, but a displacement when connecting two links.
Q: Which API does trajectory planning?
A: Please refer to the API for setting coordinates and joints: send_coords(), send_angles(), which comes with motion planning
Q: If the robot arm calls the API for controlling coordinates, will there be multiple solutions?
A: Because inverse kinematics has multiple solutions, the same coordinate position may arrive at different joint angles, which will occur.
Q: What is the maximum current output of the 24v output pin on the base of the mycobot 320 M5 2022 robot?
A: Maximum 2A, duration cannot exceed 1S
Q: If you want to control the angle and obtain feedback of each axis servo, what is the shortest communication cycle?
A: This needs to be determined according to the speed. The minimum response time is 50ms
Q: Does the mycobot series machine have collision detection?
A: 280 has algorithm collision self-interference, which has been integrated into the API for setting joint angles and coordinates
Q: What are the input parameters of Atom's USB interface?
A: 5V @ 500mA
Q: What are the maximum and minimum joint movement speeds and coordinate movement speeds of 320? What is the acceleration limit?
A: Refer to the following:
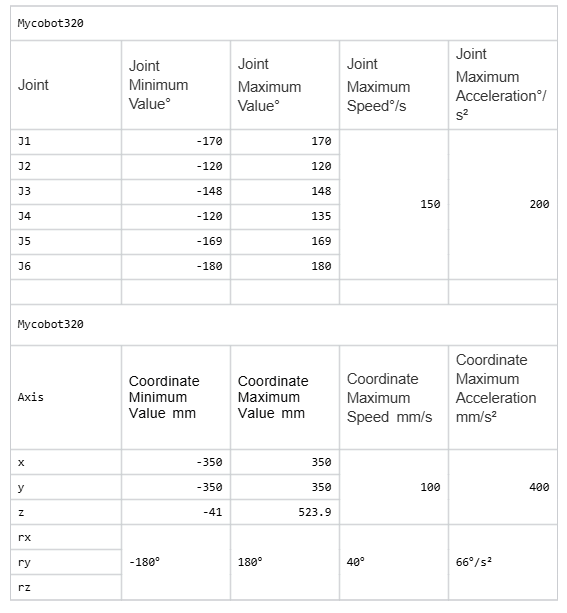
Q: What is the difference between the 320PI and 320M5 versions?
A: M5 is more suitable for beginners and can be directly connected to a computer for programming Pi has stronger computing power than M5 and cannot be directly connected to a computer for development. It is suitable for users who want to use it independently and connect to a display screen for development https://docs.elephantrobotics.com/docs/gitbook/2-serialproduct/2.0-m5-pi.html
Q: I need to repair the machine myself. Is there a repair video?
A: 320 disassembly and assembly video: https://youtu.be/zP2gvLD3kYs
Q: Schematic diagram of voltage parameters of 320 and mybuddy power adapter
A: As shown below
Q: Is the joint torque information provided?
A: Our machines only provide the overall information of the joints, not the internal torque, voltage and current of the servos and motor actuators. The overall parameters of the robot arm are disclosed, such as repeatability, power supply voltage, etc.
Q: How do you understand the relationship between the two coordinates in the figure below?

A: It means that if you want to view the transformation relationship between the coordinate system named "turtle1" and the coordinate system named "turtle2", you can use this command. In layman's terms, when you run this command, it will tell you the position and direction information of an object ("turtle1") relative to another object ("turtle2"). Just like you can know the position of a city relative to another city on a map
Q: The environment of ROS2 has been accidentally changed. Can I just delete the 280pi ROS and reinstall it myself? A: Regarding the issue of reinstalling ROS, we do not recommend users to reinstall it themselves, because the construction of the ROS environment is relatively complex and prone to errors. If you need to reset the ROS environment, we recommend users to re-write the system image. For specific methods, please refer to Development and Use Based on ROS
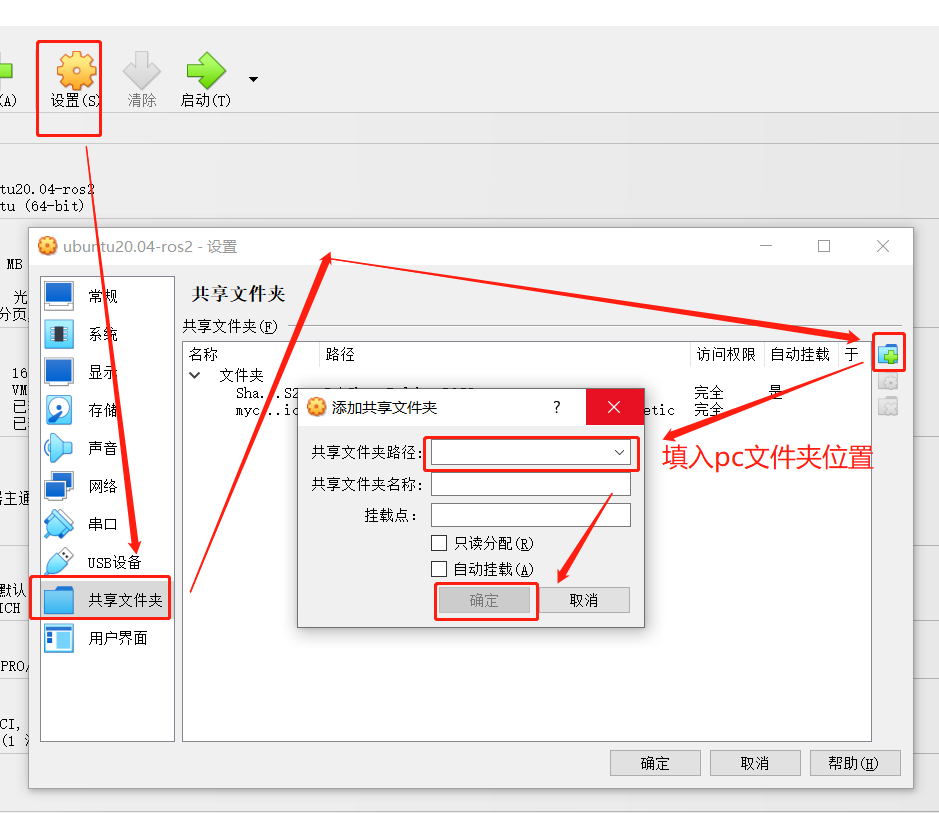
Q: How to transfer files from the host to the virtual machine
A: Set up a shared folder as shown below to transfer files from the PC to the virtual machine
Q: How to solve the problem of excessive repeated positioning deviation after the robot arm is in place at the same position?
Both new and old machines can adjust pid to reduce deviation as much as possible.
Appendix: https://docs.qq.com/doc/DU0VhT2JNVUdNUEJS, https://drive.google.com/file/d/1UWhaaSTuwLFImuEGY1J2tvgxTQDwWxK_/view?usp=sharing However, the old version of the machine has gear gaps in the 2nd and 4th joints of the robot arm, which is easy to produce joint deviations under the action of gravity, which ultimately affects the end precision. The forces of the 2nd and 4th joints in these four sets of joint values are inconsistent, so the precision is also different. It is currently recommended to adjust through the program. When the machine reaches the point, you can read the point again at this point to check if there is a deviation. On this basis, adjust the specific deviation value of the single joint to achieve the effect of reaching the specified point.
Q: What is the difference between API and serial port instructions to directly control joints?
API provides a simplified and abstract interface to make development more efficient and easy, suitable for rapid development and integration. Serial port instructions provide direct, low-level control, suitable for scenarios that require fine-tuning or development of custom functions, but are usually more complex to develop and debug. In general: Using serial port instructions to directly control the robot arm is more flexible, but also more complex, requiring a deep understanding of the communication protocol; while using API control is simpler and more convenient, but may be limited by the functions and performance provided by the API.
Q: Windows runs git instructions and reports an error

A: This is caused by not installing git. You need to install git first and then use git instructions
Q: What is the difference between MDI and JOG?
A: MDI (Manual Data Input) is called the set value direct given operation mode. That is, after the upper controller directly sets the target position, speed, acceleration and deceleration, the axis automatically moves to the target position. MDI is also the most commonly used positioning function in practical applications. JOG moves continuously in a certain direction.
Q: Overseas maintenance policy form

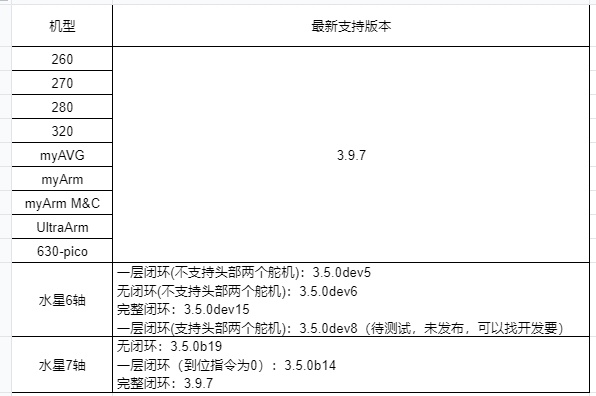
Q: What is the latest supported version of pymycobot for each model?
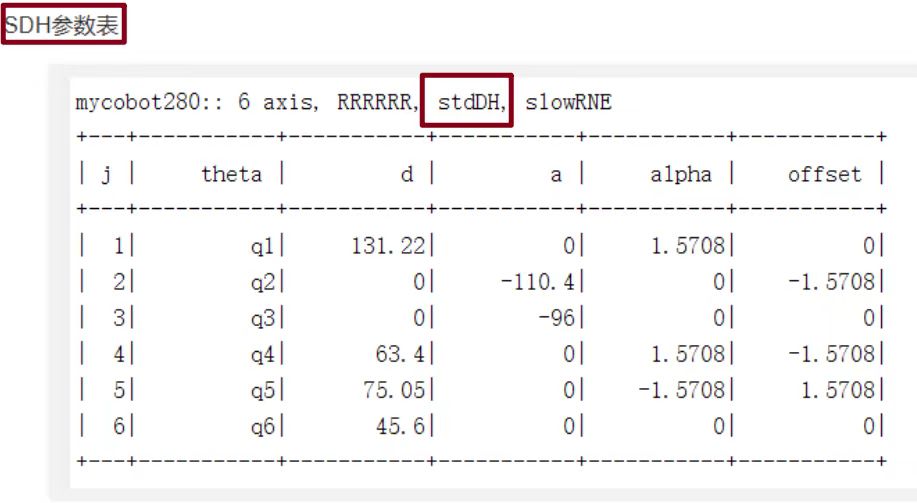
Q: DH table How to distinguish between standard and improved
sdh, std, standard mdh, modify, improved We provide the standard DH table. Customers can convert it by themselves if necessary. It is just two different description methods.
Q: What should I do if the error message "opencv_camera is missing" appears?
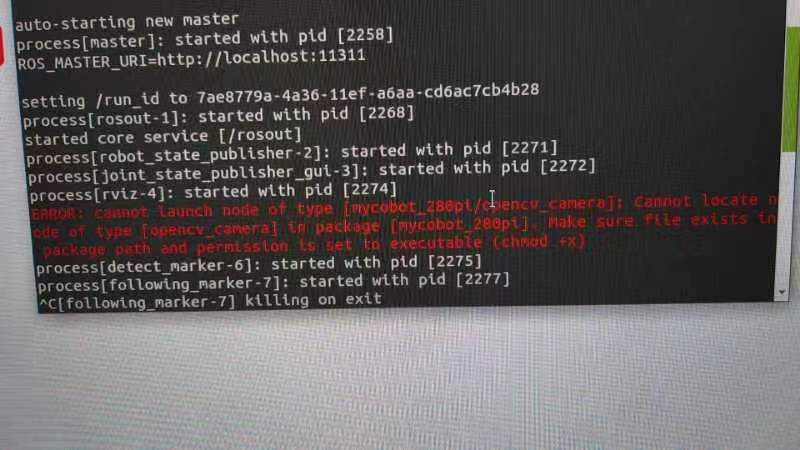
A: The error message indicates that the executable permission is missing. You may need to add the permission.
Change to using mycobot_280 instead of pi itself, because the file is occupied by m5 and both sides cannot occupy it at the same time, otherwise the subsequent compilation will fail.

Q: How to check the data transmission speed? A: Use the following code:
import time
from pymycobot import MyCobot320
mc = MyCobot320("COM8",115200, debug = True)
while 1:
mc.get_angles()

write indicates the issued acquisition instruction, read is the returned message, and the left side is the time. Here it shows 518write +611read, indicating that the read of get_angles is completed in about 100ms, and the frequency is 10hz.
Q: The indicator light of the adapter is not on
A: It is possible that the adapter has been powered off for self-protection after a short circuit. Disconnect the adapter for a few minutes before using it. If it does not work after a few minutes, wait a little longer for 15 minutes and then power on the adapter separately to see if it lights up.
Q: A joint of the robot arm cannot move. How to deal with it?
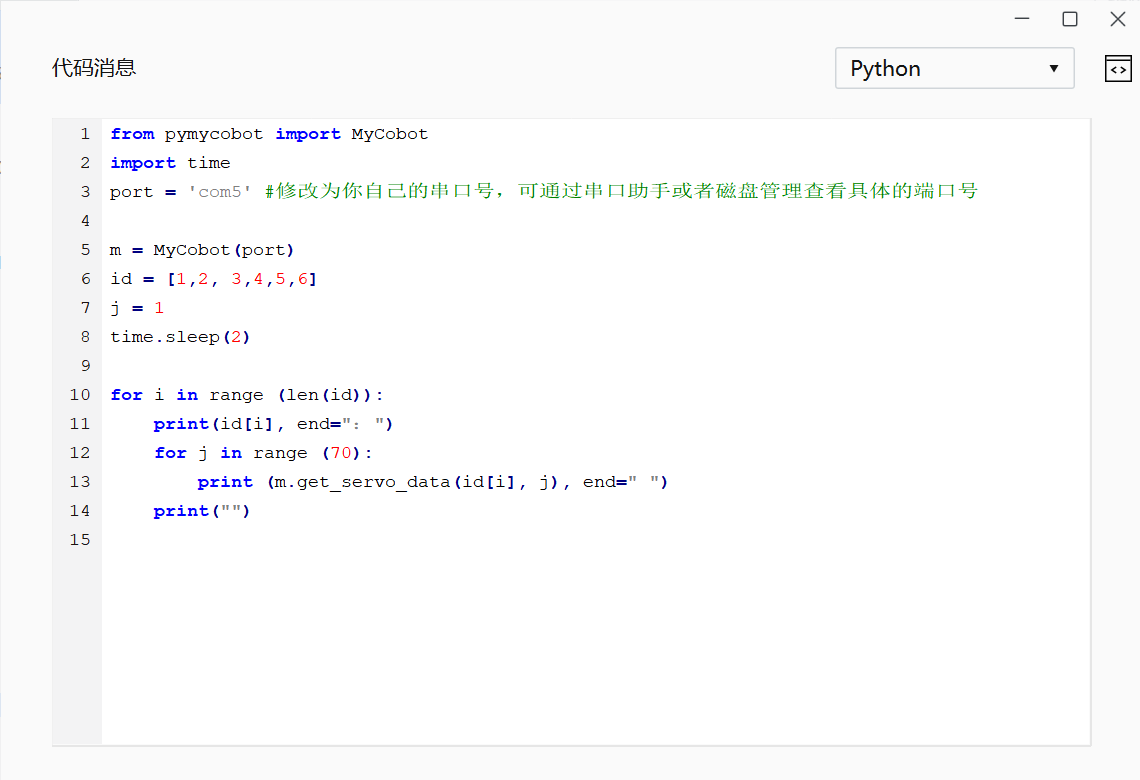
A: You can use a python script to read the angle in a loop, and then manually turn the joint to see if the angle changes.
If there is a return value, check the following points and return the information to the technical support staff.
Use get_servo_status to check if the J2 servo has hardware problems such as undervoltage/overvoltage
Manually turn J2 to see if there is obvious resistance, and compare it with other joints; enable focus_servo(2) on J2 separately
Use the script to check if there is any problem with the parameters
Atom abnormal LED lights up red
320: Next cutecom, serial assistant sends fefe 02 19 fa
Q: End zero position abnormality
A: After using the adaptive gripper to grip objects for a long time, the gripper and end zero position abnormality will appear, and the gripper needs to be stationary.
Q: What are forward kinematics and inverse kinematics?
A: Forward kinematics refers to solving the position and posture of the robot's end effector (such as the gripper of the robot arm) in Cartesian space when the angles (or displacements) of each joint of the robot are known. It is implemented in the get_coords() API, but the specific algorithm is not public. Inverse Kinematics is the opposite of forward kinematics. It refers to solving the angles (or displacements) of each joint of the robot when the position and posture of the robot end effector in Cartesian space are known. write_coords(), send_coords()