<<<<<<< HEAD
Keyboard control robot movement case
Function description: Based on Cartesian motion, control the robot arm to move in the XYZ direction through the keyboard
1 Firmware burning
Since the robot needs to use Cartesian motion, it is necessary to burn the pico firmware and basic firmware that support Cartesian motion. However, the firmware that supports Cartesian motion has not been released on mystudio and can only be obtained by contacting after-sales personnel.
2 pymycobot installation
If you want to use Cartesian motion, you need to install or update pynycobot. Open the computer terminal and execute the following command to install or update pymycobot
键盘控制案例
功能说明:基于笛卡尔运动,通过键盘控制机械臂在XYZ方向运动
1 固件烧录
由于机器人需要使用笛卡尔运动,所以需要烧录支持笛卡尔运动的pico固件和basic的固件,但目前支持笛卡尔运动的固件并未发布到mystudio上,只能通过联系售后人员进行获取。
2 pymycobot安装
如果要使用笛卡尔运动,需要安装或更新pynycobot,打开电脑终端,执行下面指令进行安装或更新pymycobot
2350f0e86e2352fe2e8fb62592247280afec2c2d
pip install pymycobot --upgrade
<<<<<<< HEAD
3 Preparation
Before connecting the robot arm to 24V, manually adjust the robot arm to the posture shown in the figure below, and then connect the 24V power supply and communication data cable in turn. There should be no debris around the robot arm to avoid collision
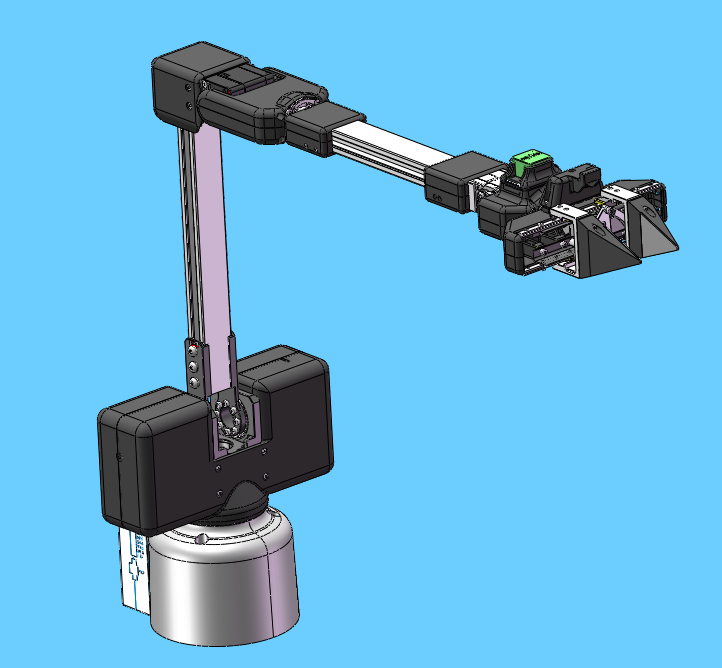
Make sure the base screen displays ok

4 Case reproduction
After running the following program, the robot arm will first move to an initial position, and then print the key prompt information in the terminal. Press the corresponding key according to the terminal information to control the robot movement
3 准备工作
在机械臂接入24V前,先手动将机械臂调整到下图姿态,再依次接入24V电源和通信数据线,机械臂周围不要有杂物,避免发生碰撞

确保底座屏幕显示ok

4 案例复现
运行下面程序后,机械臂会先移动到一个初始位置,之后会在终端打印按键提示信息,根据终端信息按下对应按键即可控制机器人运动
2350f0e86e2352fe2e8fb62592247280afec2c2d

 <<<<<<< HEAD
<<<<<<< HEAD
Note : When performing keyboard control, the firmware version of the robot arm cannot use v1.1.
注意 :在进行键盘控制时,机械臂的固件版本不能使用v1.1的。
2350f0e86e2352fe2e8fb62592247280afec2c2d
import threading
from pymycobot import MyArmMControl, utils
import keyboard
import time
m = MyArmMControl(utils.get_port_list()[0],1000000)
def init():
# 设置初始角度
m.write_angles([-10.19, 8.62, 30.65, 2.19, 50.53, -4.83], 100)
time.sleep(1)
m.set_gripper_state(0,100)
time.sleep(1)
# 用于键盘输入检测的函数
def keyborad_ctrl():
print("开始控制...")
print("按下键盘W,往X+方向运动")
print("按下键盘S,往X-方向运动")
print("按下键盘D,往Y+方向运动")
print("按下键盘A,往Y-方向运动")
print("按下键盘Q,往Z+方向运动")
print("按下键盘Z,往Z-方向运动")
print("按下键盘X,往J6+方向运动")
print("按下键盘E,往J6-方向运动")
print("按下键盘F,获取当前坐标")
print("按下键盘G,控制夹爪开合")
print("按下键盘ESC,结束程序")
blocked_keys = ['w', 'a', 's', 'd', 'q', 'z', 'f', 'e', 'x', 'g']
for key in blocked_keys:
keyboard.block_key(key)
key_processed = {key: False for key in blocked_keys}
else_executed = False
gripper_opened = True # 默认状态为夹爪打开
try:
while True:
if keyboard.is_pressed('esc'):
print("退出控制...")
break
for key in blocked_keys:
if keyboard.is_pressed(key) and not key_processed[key]:
if key == 'g': # 特殊处理G键
gripper_opened = handle_gripper(gripper_opened)
else:
threading.Thread(target=handle_key, args=(key,)).start()
key_processed[key] = True
else_executed = False
if all(not keyboard.is_pressed(key) for key in blocked_keys) and not else_executed:
m.stop()
else_executed = True
for key in key_processed:
if not keyboard.is_pressed(key):
key_processed[key] = False
time.sleep(0.01)
finally:
keyboard.unhook_all()
def handle_key(key):
if key == 'w':
m.jog_coord(1, 1, 60)
elif key == 'a':
m.jog_coord(2, 0, 60)
elif key == 'd':
m.jog_coord(2, 1, 60)
elif key == 's':
m.jog_coord(1, 0, 60)
elif key == 'q':
m.jog_coord(3, 1, 60)
elif key == 'z':
m.jog_coord(3, 0, 60)
elif key == 'e':
m.jog_angle(6, 0, 50)
elif key == 'x':
m.jog_angle(6, 1, 50)
elif key == 'f':
print("当前坐标=", m.get_coords())
def handle_gripper(gripper_opened):
if gripper_opened:
m.set_gripper_state(1, 100) # 关闭夹爪
# print("夹爪已闭合")
else:
m.set_gripper_state(0, 100) # 打开夹爪
# print("夹爪已打开")
return not gripper_opened # 切换状态
if __name__ == "__main__":
init()
keyborad_ctrl()
<<<<<<< HEAD
5 Effect display
=======
5 效果展示
2350f0e86e2352fe2e8fb62592247280afec2c2d
