Install different versions of ubuntu systems in Linux
1 Virtual machine installation
Go to the official website to download the virtual machine Virtual Box Or go to the official website to download the virtual machine VM ware
VirtualBox installation package: Windows hosts
VirtualBox Extension Pack: VirtualBox 7.0.10 Oracle VM VirtualBox Extension Pack
Of course, if you already have your virtual machine, you can skip this step.
We chose to download Virtual box because it is free.
2 Create a new virtual machine
2.1 Create a virtual machine
Select New in Control
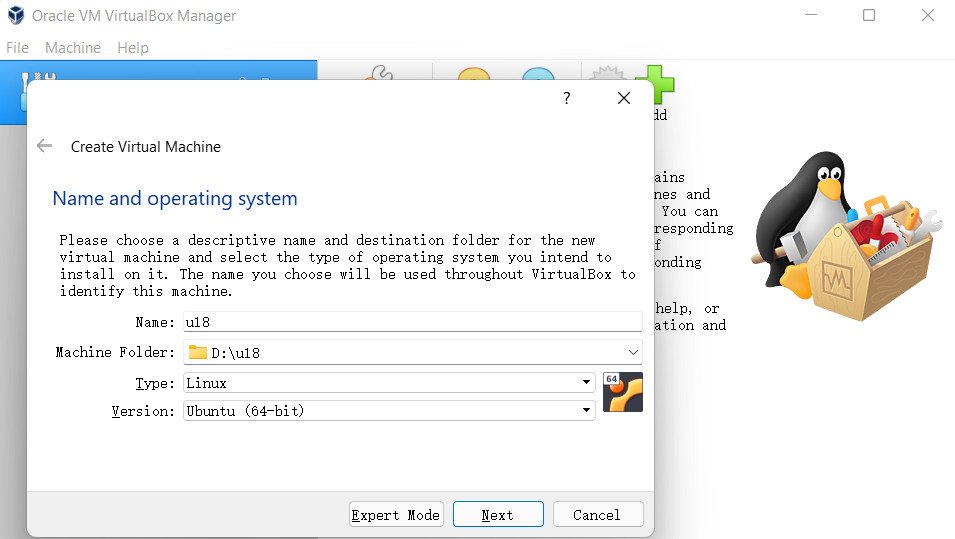
Enter the name of the virtual machine and the location where the virtual machine is stored, select the virtual machine type as Linux, select the ubuntu 64-bit version, and proceed to the next step.
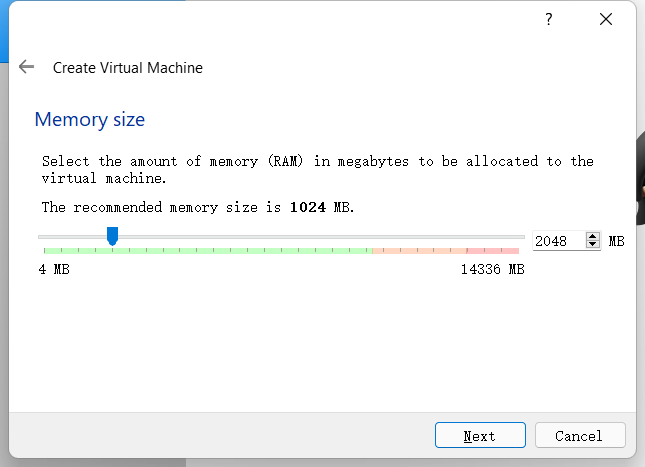
Configure the memory size according to your needs and proceed to the next step.
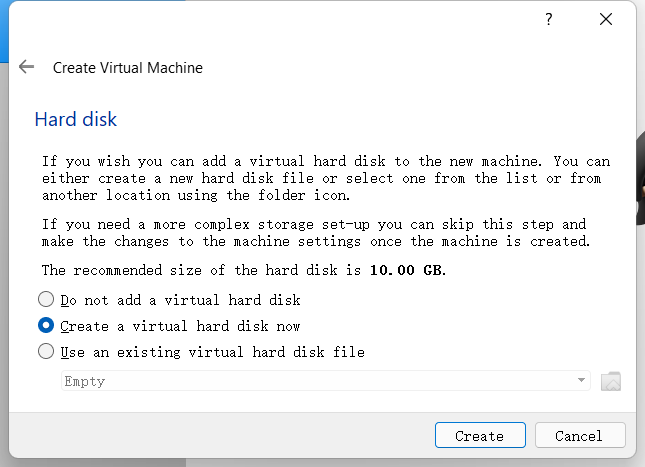
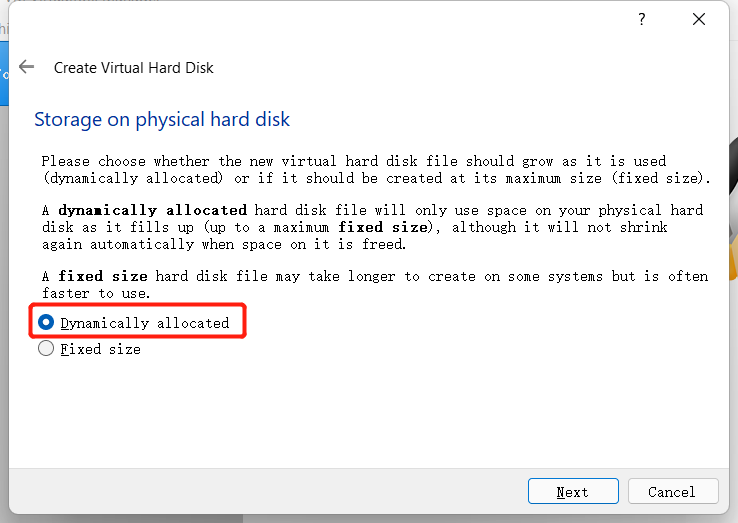
Select Create virtual hard disk now to create it.
Select the VDI type for the virtual hard disk type and proceed to the next step.
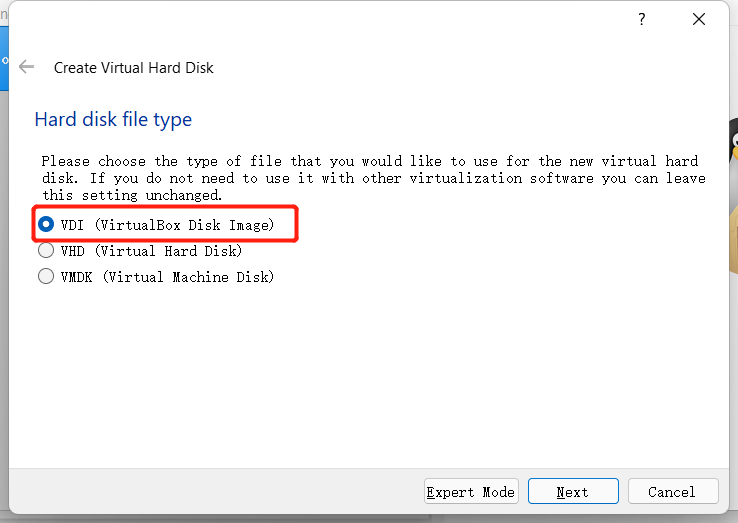
Allocate the size of the virtual hard disk. Since you need to install the ubuntu system and operate in this system, it is recommended that the size should not be less than 20G.

2.2 Import ubuntu system
2.2.1 Download ubuntu system
Please choose the ubuntu version for installation according to your own needs. It is recommended to install version 20.04.
The installation methods and processes of the three versions are the same. Here, version 18.04 is used as an example to install
After the download is completed, there will be a file as shown below:
2.2.2 Import ubuntu into the virtual machine
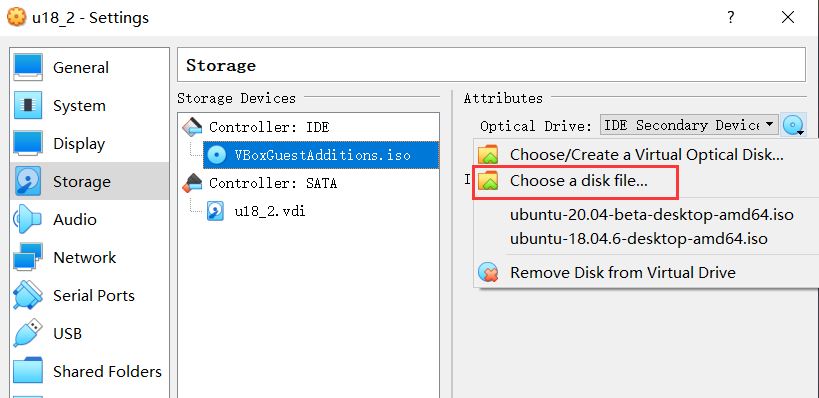
Find the previously installed virtual machine in Virtual box, enter Settings, and assign a disc to the controller in Storage:
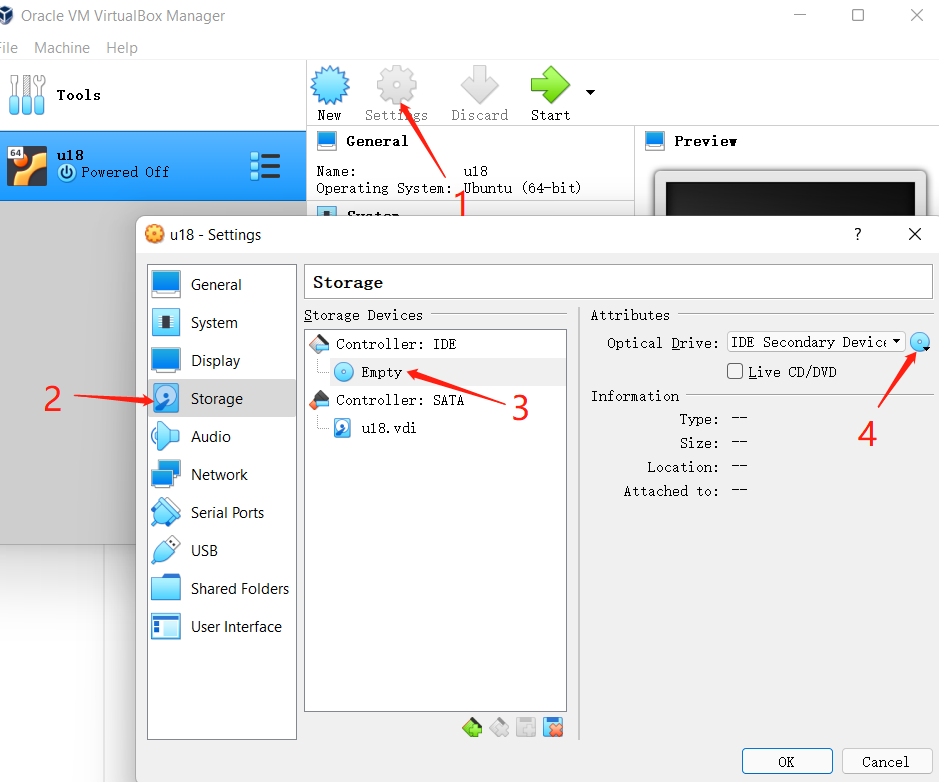
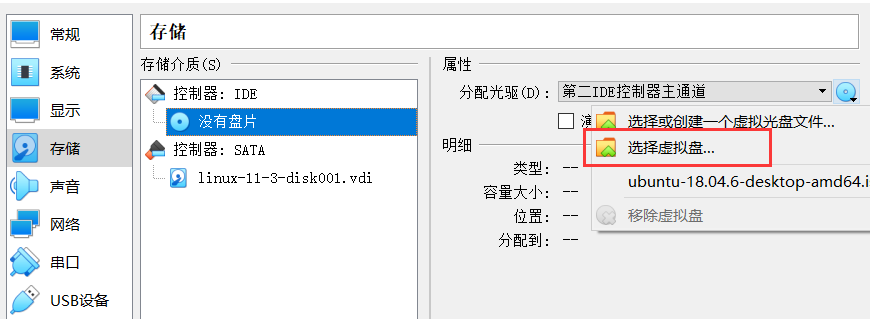
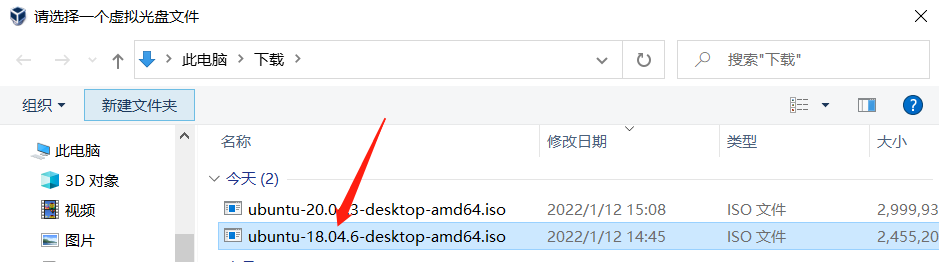
Then open the virtual machine to install ubuntu and click Start.
2.2.3 ubuntu installation
Wait for the system to start, enter the Welcome interface, select "Chinese (Simplified)", and click the "Install Ubuntu" button;
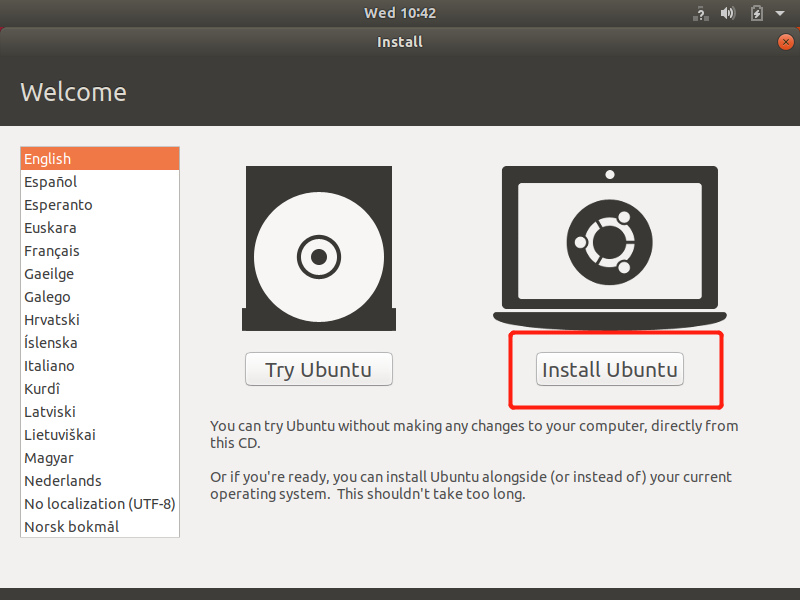
Click the "Continue" button;
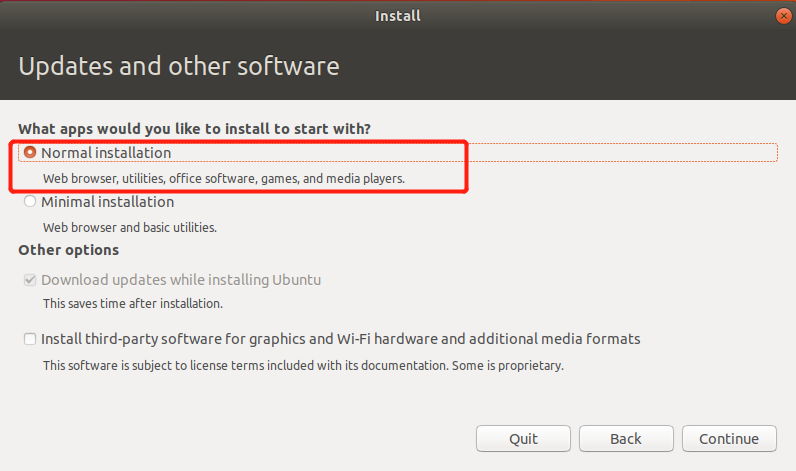
Select the "Erase the entire disk and install Ubuntu" option and click the "Install Now" button;
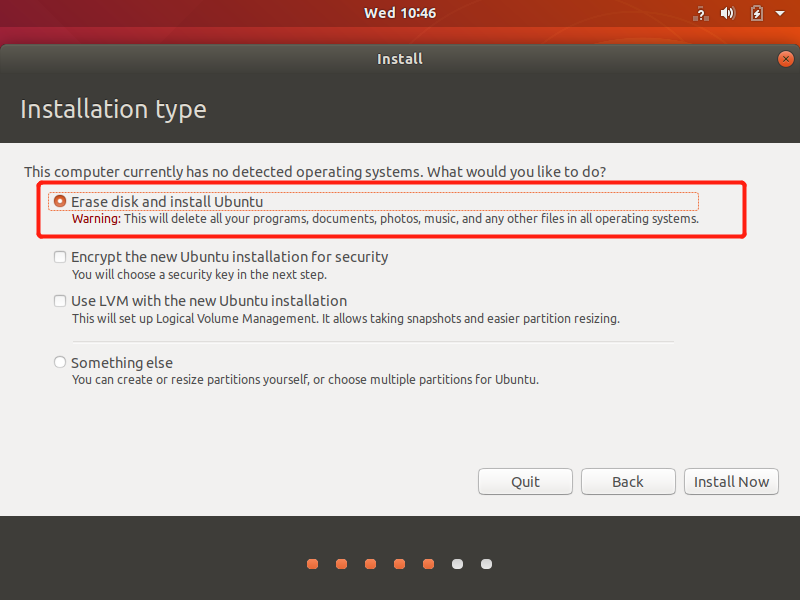
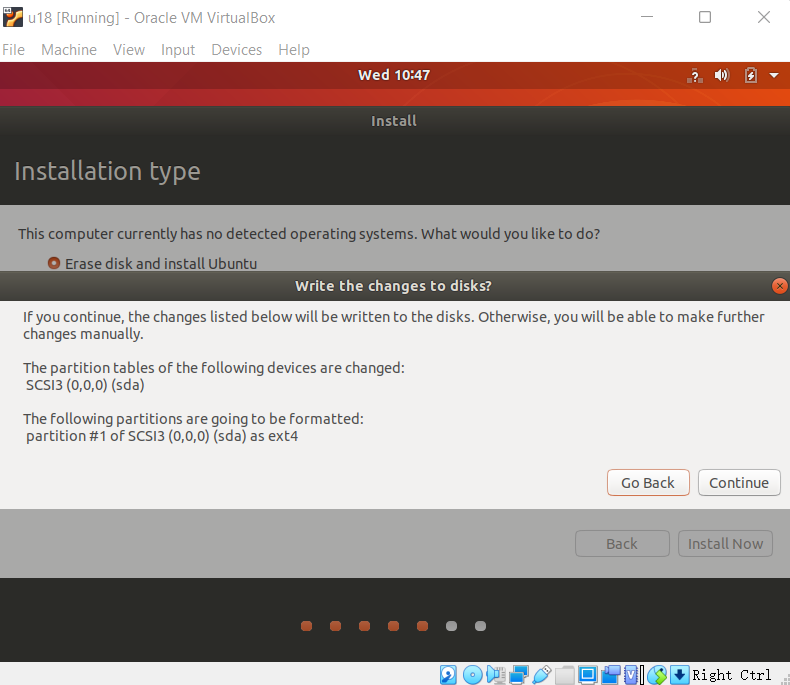
Click the "Continue" button in the pop-up dialog box;
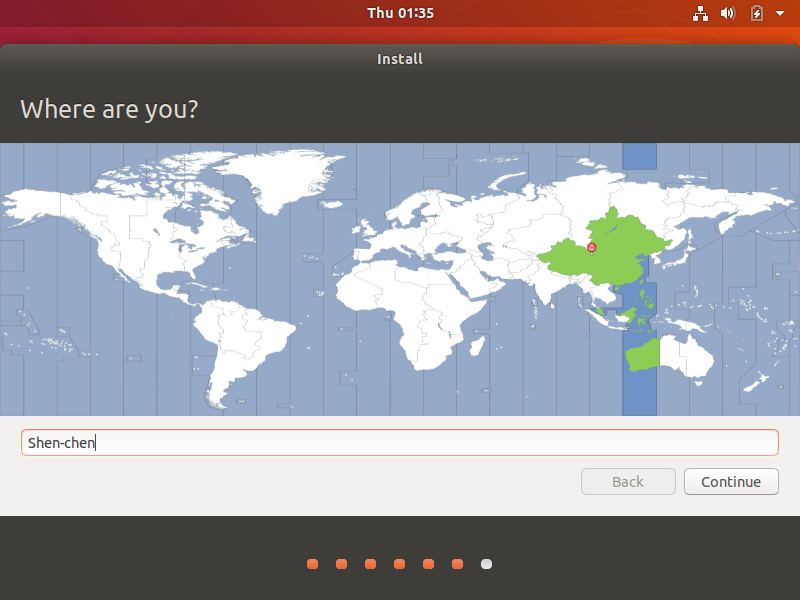
Set the geographical location and click the "Continue" button;
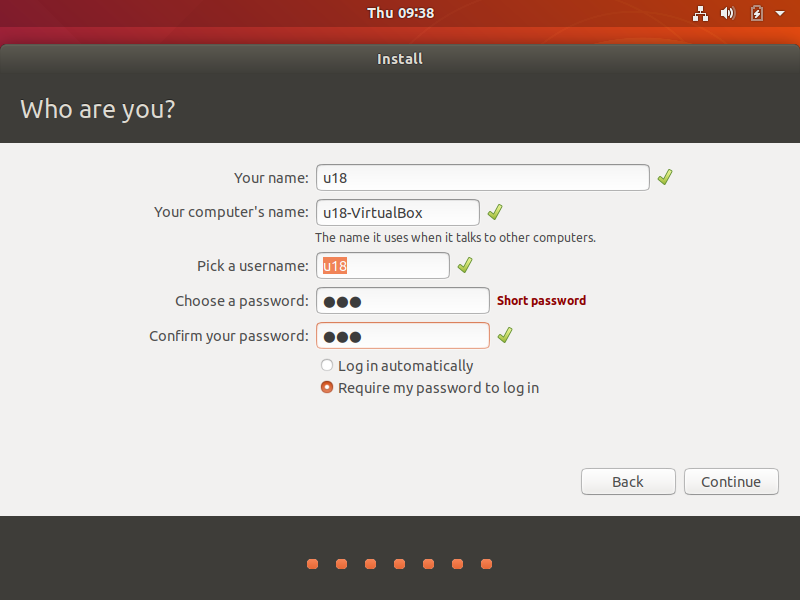
Set the username and password and click the "Continue" button;
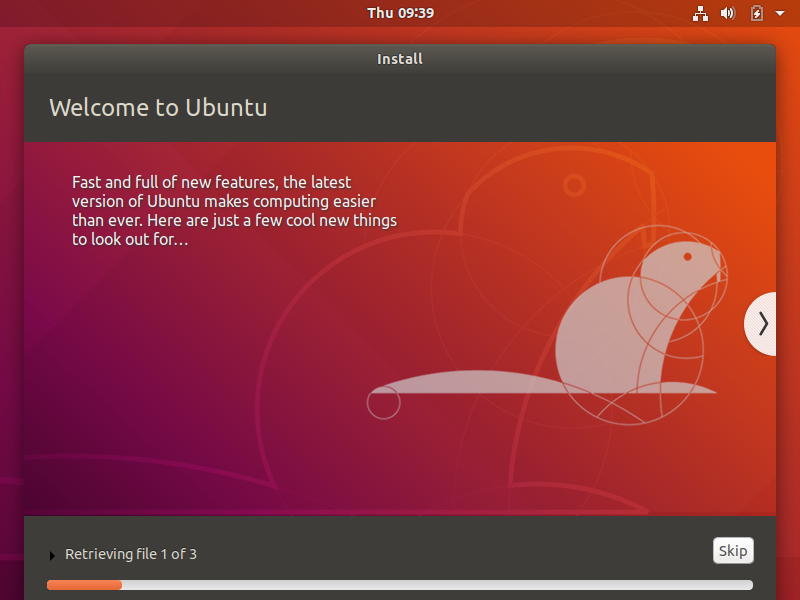
Enter the system installation interface, please wait patiently;
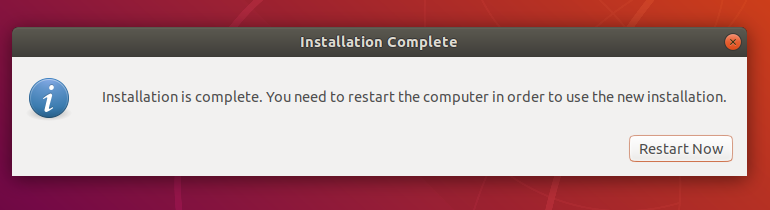
After the installation is completed, click the "Restart now" button in the pop-up dialog box to complete the installation.
3 ROS environment construction
3.1 ROS installation
To build a basic development environment, you need to install the robot operating system ROS, MoveIt, and git version manager. The installation methods and processes are introduced below.
3.1.1 Version selection
There is a one-to-one correspondence between ROS and ubuntu. Different versions of ubuntu correspond to different versions of ROS. The reference website is as follows: http://wiki.ros.org/Distributions
- Here are the ROS versions supported by Ubuntu:
- Ubuntu 16.04/ROS Kinetic
- Ubuntu 18.04/ROS Melodic
- Ubuntu 20.04/ROS Noetic
Please install the corresponding ROS version according to the Ubuntu version you installed
If the versions are different, the download will fail. The system we selected here is Ubuntu 18.04, and the corresponding ROS version is ROS Melodic
NOTE: Currently we do not provide any reference for installing ROS on windows. If necessary, please refer to https://www.ros.org/install/
3.1.2 Start installation
1 Add source
There is no ROS software source in Ubuntu's own software source list, so you need to first configure the ROS software source into the software list warehouse before you can download ROS. Open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T) and enter the following command:
- Official source:
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
- If the download speed is slow, it is recommended to choose a nearby mirror source to replace the above command. For example, Tsinghua University is:
sudo sh -c '. /etc/lsb-release && echo "deb http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ros/ubuntu/ `lsb_release -cs` main" > /etc/apt/sources.list .d/ros-latest.list'
You will be asked to enter the user password here. Just enter the user password set when installing Ubuntu.
2 Set the secret key
Configure the public network key. This step is to let the system confirm that our path is safe, so that there will be no problem downloading the file, otherwise it will be deleted immediately after downloading:
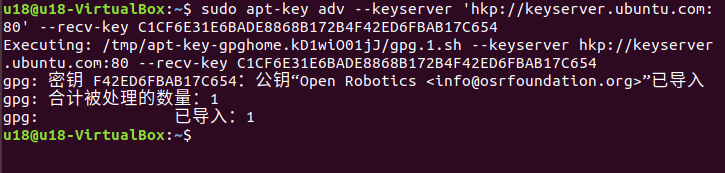
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver 'hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80' --recv-key C1CF6E31E6BADE8868B172B4F42ED6FBAB17C654
The execution results are shown as follows:
3 Installation
After adding a new software source, you need to update the software source list and open a console terminal (shortcut keys Ctrl+Alt+T< /kbd>), enter the following command:
sudo apt-get update
Execute Install ROS, open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T), please follow your own Ubuntu version Choose to enter the following commands:
#Ubuntu 16.04
sudo apt install ros-kinetic-desktop-full
#Ubuntu 18.04
sudo apt install ros-melodic-desktop-full
#Ubuntu 20.04
sudo apt install ros-noetic-desktop-full
It is recommended to install complete ROS to prevent missing libraries and dependencies.
The installation process takes a long time, so you need to wait patiently
- If the following error message appears on the console terminal during the installation process, you need to replace the software source list in /etc/apt/sources.list.
- Open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T) and enter the following command:
sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list
- Replace all official software sources in sources.list with the following Alibaba Cloud software sources:
Ubuntu 16.04 version:
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial main
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial main
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-updates main
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-updates main
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial universe
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial universe
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-updates universe
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-updates universe
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-security main
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-security main
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-security universe
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-security universe
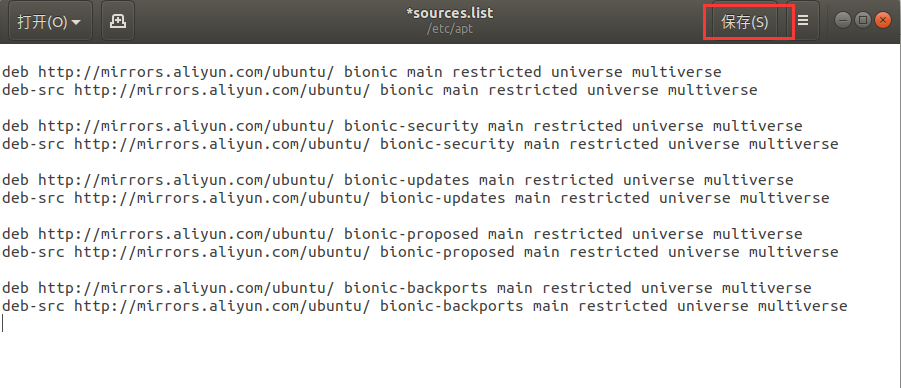
Ubuntu 18.04 version:
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-backports main restricted universe multiverse
Ubuntu 20.04 version:
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
- After the configuration is completed, the contents of the sources.list file are as follows, click Save and exit.
- To update the software source list, enter: in the console terminal:
sudo apt-get update
- Enter the instructions to install ROS in the console terminal:
#Ubuntu 16.04
sudo apt install ros-kinetic-desktop-full
#Ubuntu 18.04
sudo apt install ros-melodic-desktop-full
#Ubuntu 20.04
sudo apt install ros-noetic-desktop-full
The installation process takes a long time, so you need to wait patiently
4 Configure the ROS environment to the system
rosdep allows you to easily install the source code you want to compile, or the system dependencies required by some ROS core components. Execute the following commands in the terminal to open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl +Alt+T).
If rosdep is not installed on your system, please use the command sudo apt install python-rosdep to install it.
If the Ubuntu system you installed is version 20.04, please use the command sudo apt install python3-rosdep to install it. After completion, execute the rosdep initialization command.
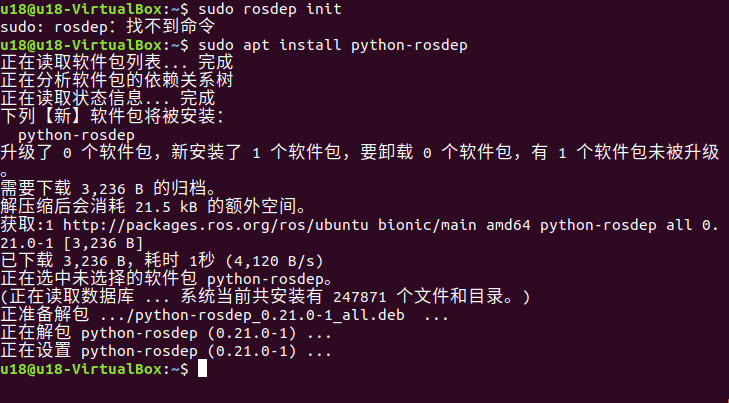
Initialize rosdep:
sudo rosdep init
If an error message appears as shown below:
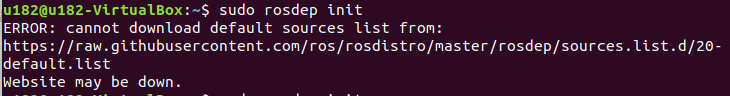
Solution: Modify the hosts file and enter the following command in the console terminal:
sudo gedit /etc/hosts
At the end of the file content, add the IP addresses of the following two URLs to achieve access:
199.232.28.133 raw.githubusercontent.com
151.101.228.133 raw.github.com
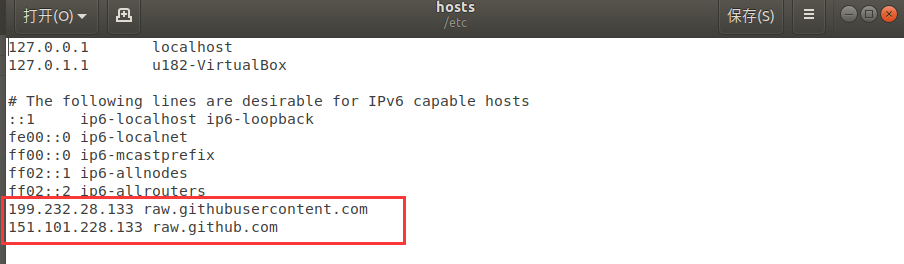
After the modification is completed, execute in the console terminal:
sudo rosdep init
rosdep update
After the initialization is completed, in order to avoid the need to re-validate the ROS function path every time the terminal window is closed, we can configure the path into the environment variable so that the ROS function can be automatically valid every time a new terminal is opened. path Execute the following commands in the terminal to open a console terminal (shortcut keys Ctrl+Alt+T):
3.1.3 Set up ros environment
1 Bash
Execute the following command:
#Ubuntu 16.04
# Add the ros environment to the environment variables of the current console
echo "source /opt/ros/kinetic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
#Ubuntu 18.04
echo "source /opt/ros/melodic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
#Ubuntu 20.04
echo "source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
2 Install dependencies
Enter the following command in the terminal Install ROS additional dependencies and open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T) :
sudo apt-get install python-rosinstall python-rosinstall-generator python-wstool build-essential
If your Unbutu system is version 20.04, please execute the following command to install:
sudo apt install python3-rosdep python3-rosinstall python3-rosinstall-generator python3-wstool build-essential
#Ubuntu 16.04
sudo apt install ros-kinetic-joint-state-publisher-gui
#Ubuntu 18.04
sudo apt install ros-melodic-joint-state-publisher-gui
#Ubuntu 20.04
sudo apt install ros-noetic-joint-state-publisher-gui
3.1.4 Verify installation
The startup of the ROS system requires a ROS Master, which is the node manager. We can enter the roscore command in the terminal to start the ROS Master.
In order to verify whether ROS is installed successfully, open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T) and execute the following command in the terminal:
roscore
When the following interface is displayed, it means that the ROS installation is successful.
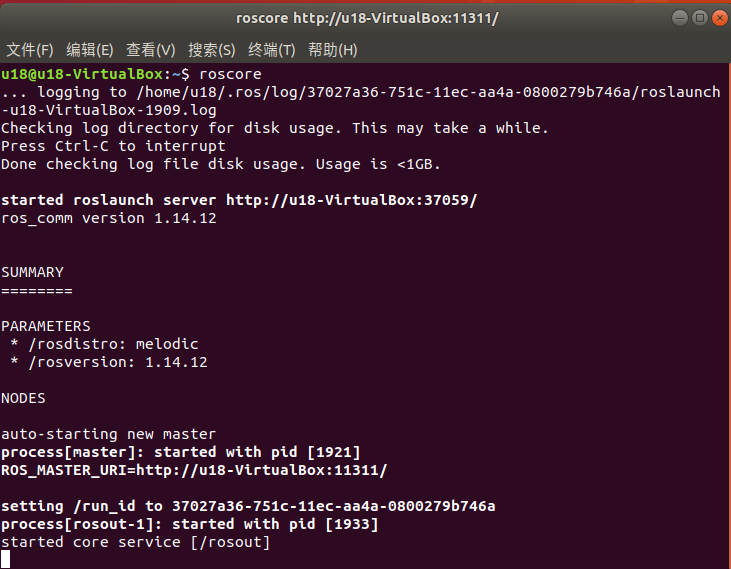
The roscore command starts a node manager, which is used for node management. In a ros system, there is only one. It is the prerequisite for the running of the ros node. Therefore, the first step needs to be executed before starting the ros node. roscore.
For more detailed installation instructions, please refer to the official installation instructions, URL: http://wiki.ros.org/ROS/Installation
3.2 MoveIt installation
MoveIt is a series of functional packages for mobile operations in ros, which mainly include motion planning, collision detection, kinematics, 3D perception, operation control and other functions.
1 Update software source list
Open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T) and enter the following command in the terminal window to update the software source list **:
sudo apt-get update
2 Install MoveIt
Open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T), enter the following command in the terminal window to execute *MoveIt installation *:
#Ubuntu16.04
sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-moveit
#Ubuntu 18.04
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-moveit
#Ubuntu20.04
sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-moveit
3.3 Git installation
1 Add software source
Add the software source installed by git to the ubuntu software source list, open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T< /kbd>), enter the following command in the terminal window:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:git-core/ppa
2 Update software source list
Open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T) and enter the following command in the terminal window to update the software source list **:
sudo apt-get update
3 Install git
Open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T), enter the following command in the terminal window, *execute git installation *:
sudo apt-get install git
4 Verify installation
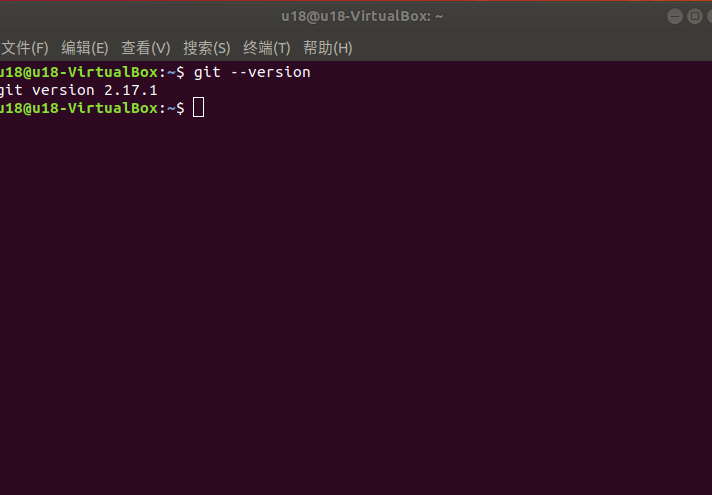
Read the git version, open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T), enter the following in the terminal window Order:
git --version
The git version number can be displayed in the terminal, as shown below, which means the installation is successful.
5 Use
You need to use git to download the ros package later. For the use of git, please refer to the following link:
4.4 mycobot_ros installation
mycobot_ros is a ROS package launched by ElephantRobotics that is adapted to its desktop six-axis robotic arm mycobot series.
Project address: http://github.com/elephantrobotics/mycobot_ros
1 Prerequisite
Before installing the package, make sure you have a ros workspace.
Here we give sample command to create a workspace, the default is catkin_ws, open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt+T), enter the following command on the command line:
mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src # Create folder
cd ~/catkin_ws/src # Enter the folder
catkin_init_workspace # Initialize the current directory into a ROS workspace
cd ~/catkin_ws # Return to workspace
catkin_make # Build the code in the workspace.
Add workspace environment
The official default ROS1 workspace is catkin_ws.
#Ubuntu 16.04
echo "source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
#Ubuntu 18.04
echo "source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
#Ubuntu 20.04
echo "source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
2 Installation
NOTE:
- This package depends on ROS and MoveIT. Make sure ROS and MoveIT are successfully installed before use.
- The interaction between this package and the real robot arm relies on PythonApi -
pymycobot - The Api project location is: https://github.com/elephantrobotics/pymycobot
Quick installation:
pip install pymycobot --upgradeWhen executing the pip install pymycobot --upgrade command, if the following error message appears:
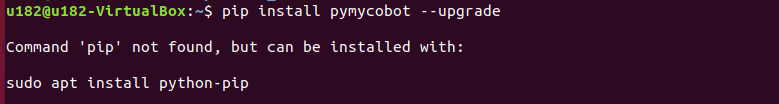
Enter the following command according to the prompts to install pip
sudo apt install python-pipIf your Ubuntu system is version 20.04, please execute the command
sudo apt install python3-pipto install pip After the pip installation is completed, execute it again in the terminalpip install pymycobot --upgradeThe installation method depends on Git, please make sure Git is installed in the virtual machine system.
The official default ROS1 workspace is catkin_ws.
cd ~/catkin_ws/src # Enter the src folder in the workspace
# Clone the code on github
git clone https://github.com/elephantrobotics/mycobot_ros.git
cd ~/catkin_ws # Return to the workspace
catkin_make # Build the code in the workspace
cd..
source devel/setup.bash #Add environment variables
Import Linux system image
Note: In order to reduce the difficulty of setting up the environment, we will provide Linux system image (Ubuntu 20.04), Virtual Box installation package and its expansion package. Next, we will teach you how to install Virtual Box and import the Linux system image (the default password is 123). Built-in environment: ROS1 + Moveit + Git + pymycobot + mycobot_ros
1 Install virtual machine
Go to the official website to download the virtual machine Virtual Box Or go to the official website to download the virtual machine VM ware
VirtualBox installation package: Windows hosts
VirtualBox Extension Pack: VirtualBox 7.0.10 Oracle VM VirtualBox Extension Pack
Of course, if you already have your virtual machine, you can skip this step.
We chose to download Virtual box because it is free.


2 Download Linux system image
Click to download: Linux ubuntu20.04
3 Import Linux system image
In the Virtual Box interface, click Management -> Import virtual computer -> Select virtual image -> Select the installation path and import it. Install as follows.
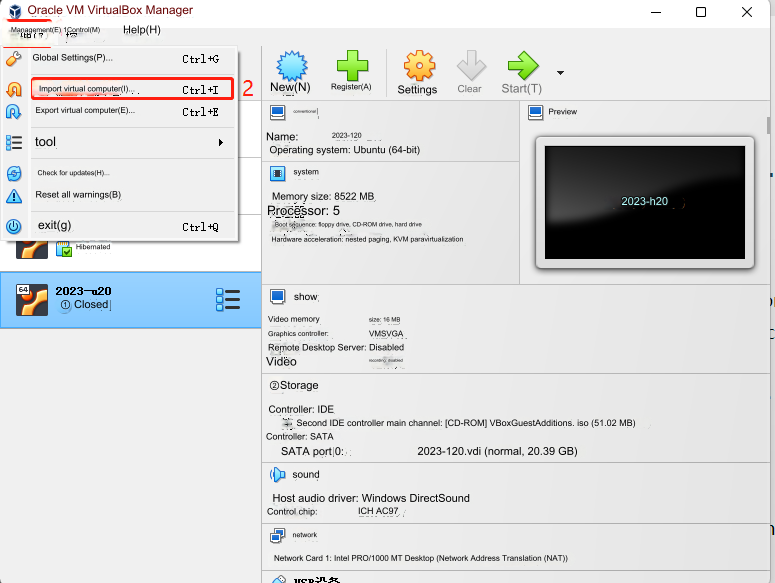

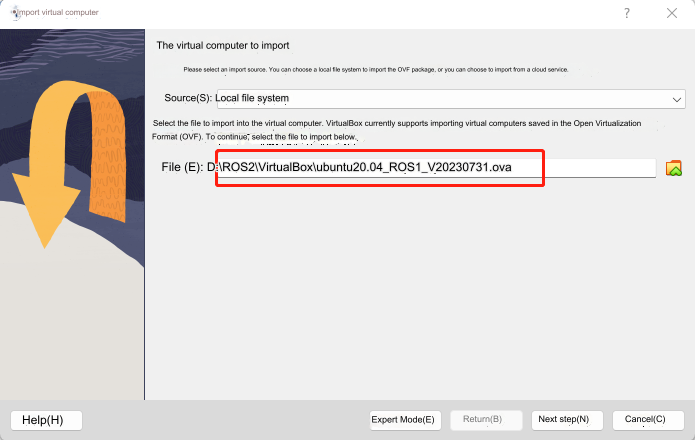
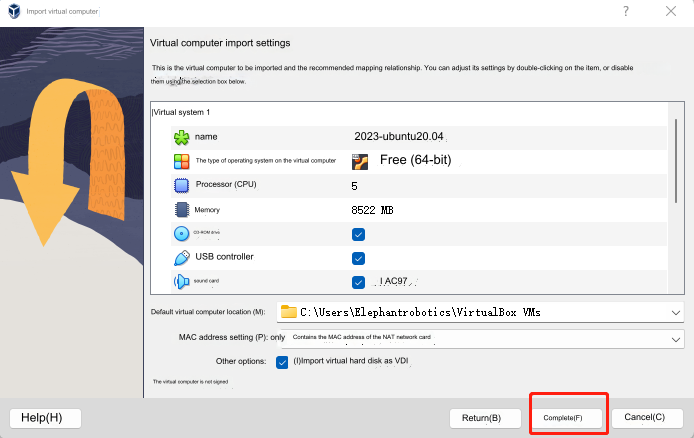
Just wait for the image to be imported. As shown below, the installation is successful.
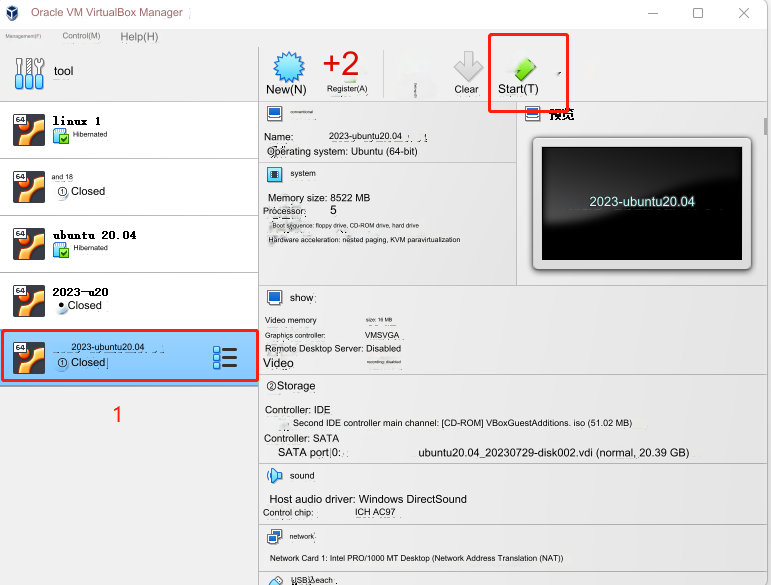
Then start the system, the default password is 123
3 Update mycobot_ros package
In order to ensure that users can use the latest official packages in a timely manner, you can enter the ~/catkin_ws/src folder through the file manager and open a console terminal (shortcut key Ctrl+Alt</ kbd>+T), enter the command on the command line to update:
# Clone the code on github
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/elephantrobotics/mycobot_ros.git # Please check the note below before deciding whether to execute this command
cd ~/catkin_ws # Return to the workspace
catkin_make # Build code in the workspace
source devel/setup.bash #Add environment variables
Note: If the mycobot_ros folder already exists in the ~/catkin_ws/src directory, you need to delete the original mycobot_ros first and then execute the above command.
At this point, the ROS1 environment is set up. You can learn Basic knowledge of ROS or ROS use cases.