ROS2 Introduction
The predecessor of ROS2 is ROS, and ROS is the Robot Operating System. But ROS itself is not an operating system, but a software library and toolset. The emergence of Ros solves the communication problem of various parts of the robot. Later, more and more robotic algorithms were integrated into ROS. ROS2 inherits ROS and is more powerful and easier to use than ROS.
1 Design goals and features of ROS2
ROS2 shoulders the historical mission of changing the era of intelligent robots. From the beginning of the design, it was considered to meet the needs of various robot applications.
Multi-robot system: In the future, robots are no longer independent individuals, and robots also need to communicate and collaborate with each other. ROS2 provides standard methods and communication mechanisms for the application of multi-robot systems.
Cross-platform: Depending on the robot application scenarios, the control platforms used will also be very different. In order to allow all robots to run ROS2, ROS2 can run cross-platform on Linux, Windows, MacOS, and RTOS.
Real-time: Robot motion control and many behavioral strategies require the robot to be real-time. For example, the robot must reliably detect a pedestrian ahead within 100 milliseconds, or complete kinematics and dynamics calculations within 1 millisecond. ROS2 provides basic requirements in real time like this.
Productization: A large number of robots have entered our lives, and there will be more and more in the future. ROS2 can not only be used in the robot research and development stage, but can also be directly installed in products and enter the consumer market. This also poses a huge challenge to the stability and robustness of ROS2.
Project Management: Robot development is a complex system engineering. Project management tools and mechanisms for the entire process of design, development, debugging, testing, and deployment will also be reflected in ROS2, making it easier for us to develop robots.
2 Release version
The corresponding release versions and maintenance cycles of ROS2 and Ubuntu.
| ROS2 Version | Release Date | Maintenance Period | Ubuntu Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dashing | 2019.5 | 2021.5 | Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver) |
| Eloquent | 2019.11 | 2020.11 | Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver) |
| Foxy | 2020.6 | 2023.5 | Ubuntu 20.04(Focal Fossa) |
| Galactic | 2021.5 | 2022.11 | Ubuntu 20.04(Focal Fossa) |
| Humble | 2022.5 | 2027.5 | Ubuntu 22.04(Jammy Jellyfish) |
3 Comparison between ROS and ROS2
ROS2 redesigns the system architecture. The architectural changes of the two generations of ROS are as follows:
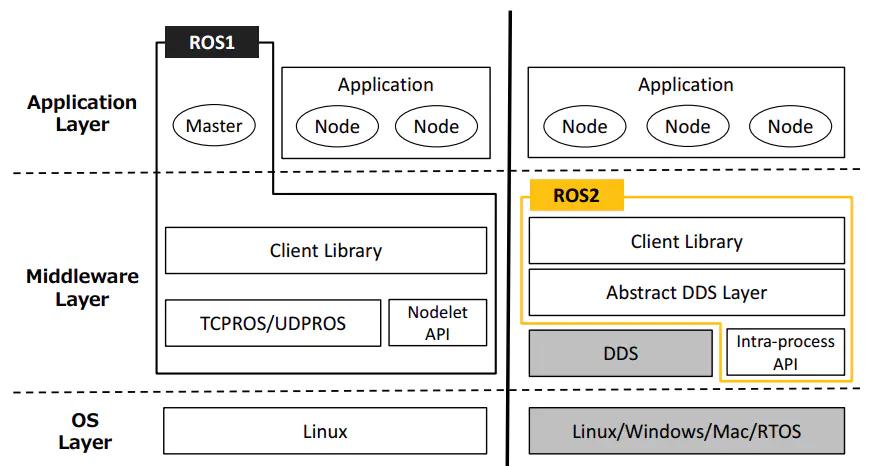
OS Layer: OS layer. In ROS2, it can be built on linux or other systems, or even bare metal without an operating system.
Middleware Layer: Middleware layer. The communication system of ROS1 is based on TCPROS/UDPROS, while the communication system of ROS2 is based on DDS. DDS is the standard solution for data publishing/subscription in distributed real-time systems.
Application Layer: Application layer. ROS1 relies on ROS Master, while in ROS2, a discovery mechanism called "Discovery" is used between nodes to help establish connections with each other.
ROS has designed a complete communication mechanism (topics, services, parameters, actions) to simplify robot development. Through this mechanism, the various parts of the robot can be connected. This mechanism designs a node called Ros Master, and all other component communications must pass through the master node. Once the master node hangs up, the communication of the entire robot system will collapse! Therefore, the instability of Ros cannot be used to build high-risk robots such as autonomous driving. Additionally, there are the following disadvantages:
- TCP-based communication has poor real-time performance and high system overhead
- Not friendly to python3 support
- The message mechanism is incompatible
- No encryption mechanism, low security
ROS2 first removes the master node existing in ROS. After removing the master node, each node can discover each other through the DDS node. Each node is equal and can achieve one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many communication. Reliability and stability are enhanced after using DDS for communication.
Compared with ROS which only supports Linux systems, ROS2 also supports windows, mac and even RTOS platforms.