Control and following of the robot arm
1 Slider Control
Open a command line and run:
# The default serial port name of 2022 mycobot 320-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to "/dev/ttyACM0".
roslaunch new_mycobot_320 mycobot_320_slider.launch port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 baud:=115200
# If the end is equipped with an adaptive gripper, run (only supports M5 version, serial port modification is the same as above):
roslaunch new_mycobot_320 mycobot_320_gripper_slider.launch port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 baud:=115200
rviz and a slider component will be opened, and you will see the following interface:
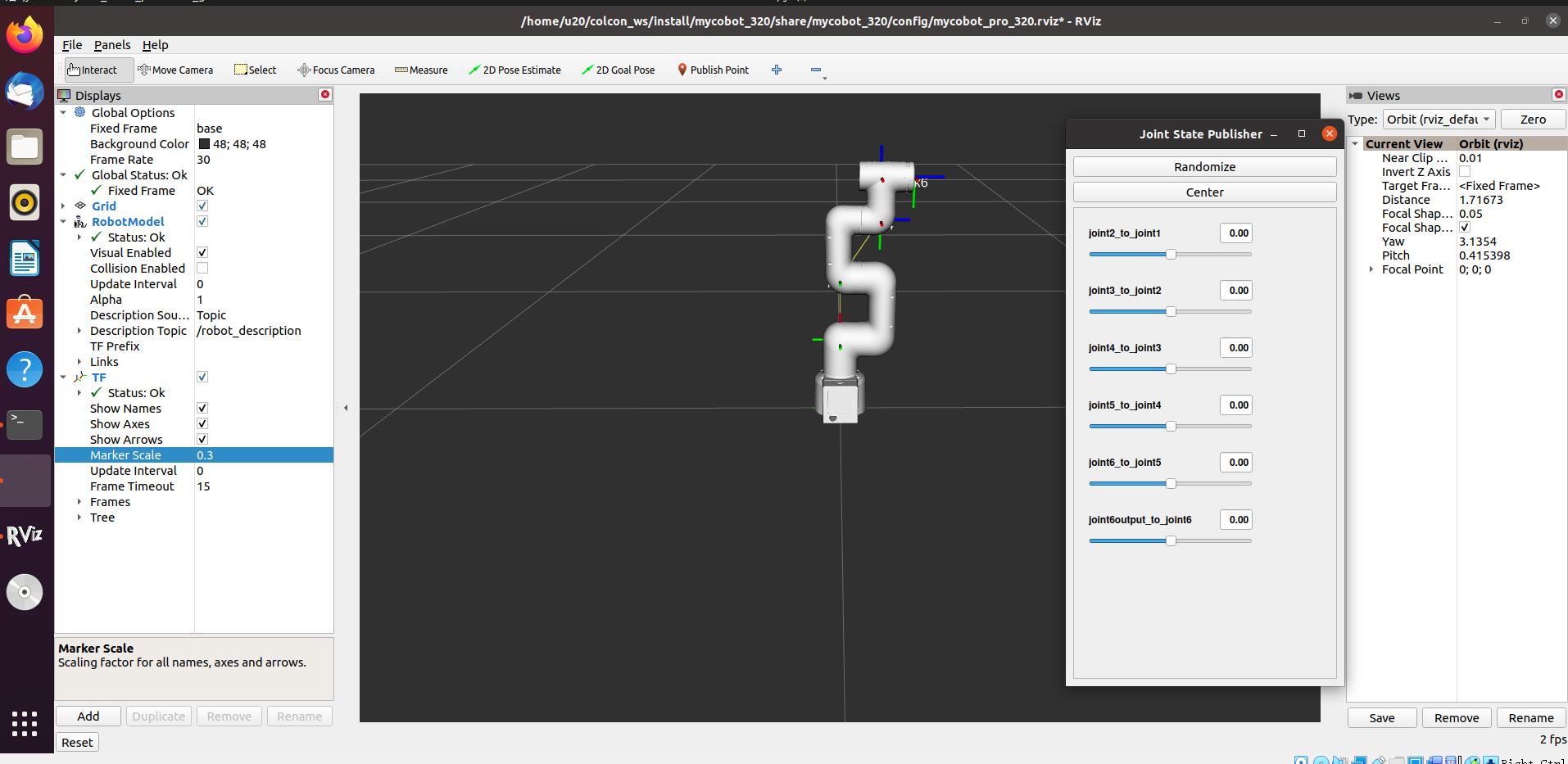
If the end is equipped with an adaptive gripper, you will see the following screen:

Then you can control the model in rviz to make it move by dragging the slider. If you want the real mycobot to move with the model, you need to open another command line and run:
# The default serial port name of 2022 mycobot 320-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to "/dev/ttyACM0".
rosrun new_mycobot_320 mycobot_320_slider.py _port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 _baud:=115200
# If the end is equipped with an adaptive gripper, run (only supports M5 version, serial port modification is the same as above):
rosrun new_mycobot_320 mycobot_320_gripper_slider.py _port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 _baud:=115200
Note: Since the robot arm will move to the current position of the model when the command is input, make sure that the model in rviz does not appear to be worn out before you use the command.
Do not drag the slider quickly after connecting the robot arm to prevent damage to the robot arm.
2 Model Following
In addition to the above controls, we can also let the model move by following the real robot arm.
Open a command line and run:
# The default serial port name of 2022 mycobot 320-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to "/dev/ttyACM0".
rosrun new_mycobot_320 mycobot_320_follow_display.py _port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 _baud:=115200
Then open another command line and run:
roslaunch new_mycobot_320 mycobot_320_follow_display.launch
It will open rviz to show the model following effect.
3 GUI control
On the basis of the previous contents, this package also provides a simple GUI control interface. This method is used for interaction between real robot arms. Connect to mycobot.
Open a command line:
# The default serial port name of 2022 mycobot 320-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to "/dev/ttyACM0".
roslaunch new_mycobot_320 mycobot_320_simple_gui.launch port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 baud:=115200
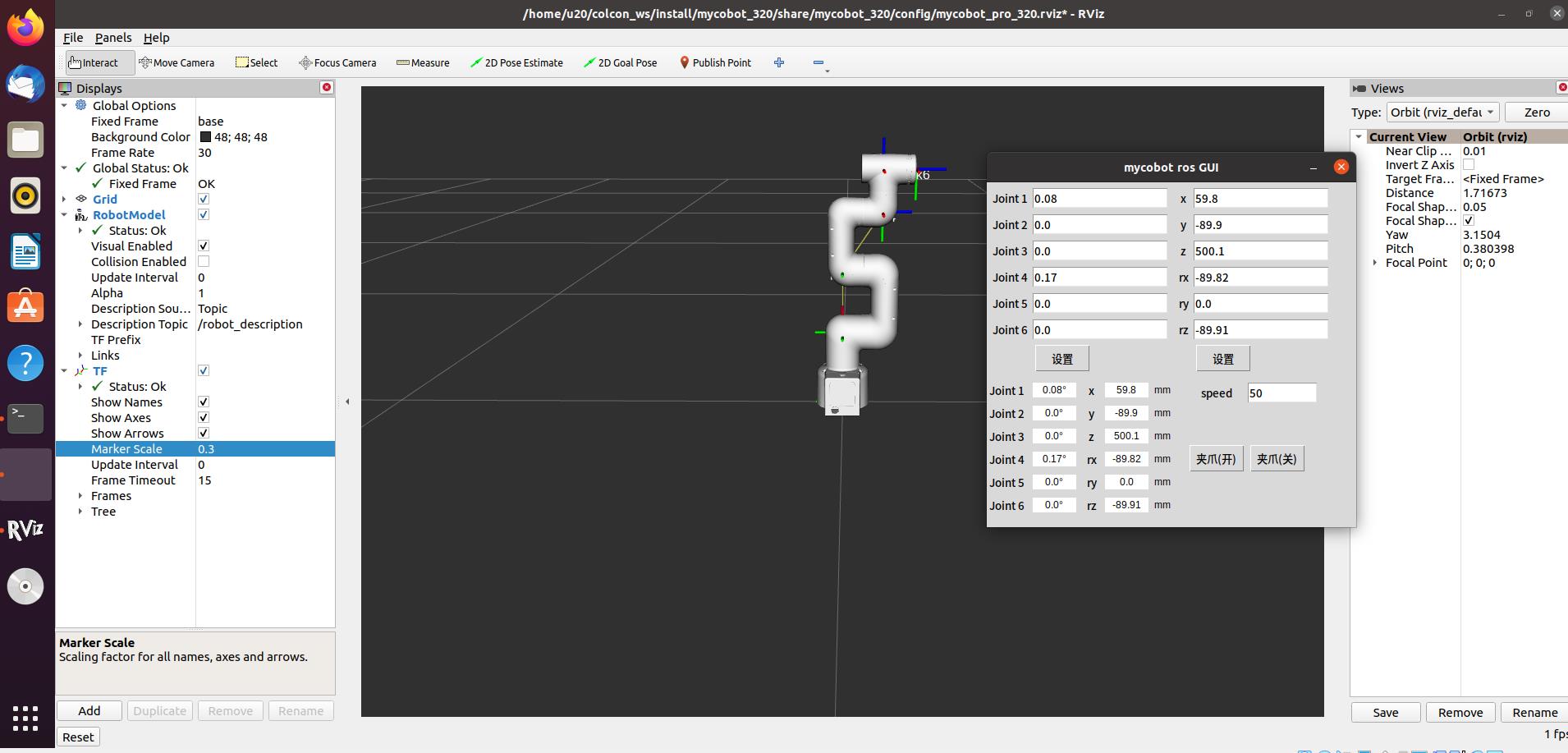
Note: Before using the gripper switch button, make sure the adaptive gripper is connected to the end of the robot arm.
4 Keyboard control
Keyboard control is added in new_mycobot_320 package, and real-time Synchronization is performed in rviz. This function depends on pythonApi, so be sure to connect with the real robot arm.
Open a command line and run:
# The default serial port name of 2022 mycobot 320-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to "/dev/ttyACM0".
roslaunch new_mycobot_320 mycobot_320_teleop_keyboard.launch port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 baud:=115200
Running effect is as follows:
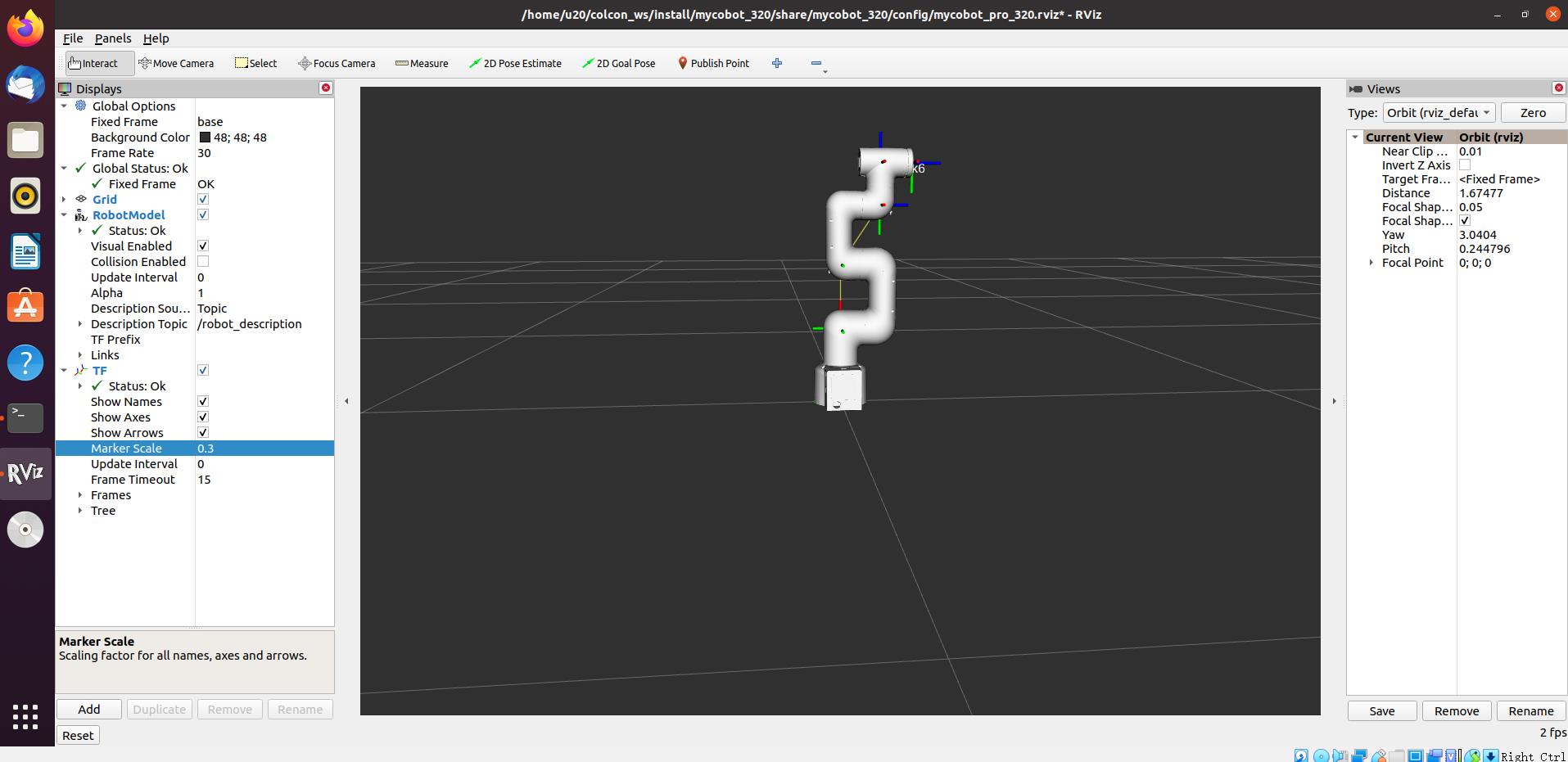
mycobot information will be output in the command line as follows:
SUMMARY
========
PARAMETERS
* /mycobot_services/baud: 115200
* /mycobot_services/port: /dev/ttyUSB0
* /robot_description: <?xml version="1....
* /rosdistro: kinetic
* /rosversion: 1.12.1.17
NODES
/
mycobot_services (new_mycobot_320/mycobot_services.py)
real_listener (new_mycobot_320/listen_real.py)
robot_state_publisher (robot_state_publisher/state_publisher)
rviz (rviz/rviz)
auto-starting new master
process[master]: started with pid [1333]
ROS_MASTER_URI=http://localhost:11311
setting /run_id to f977b3f4-b3a9-11eb-b0c8-d0c63728b379
process[rosout-1]: started with pid [1349]
started core service [/rosout]
process[robot_state_publisher-2]: started with pid [1357]
process[rviz-3]: started with pid [1367]
process[mycobot_services-4]: started with pid [1380]
process[real_listener-5]: started with pid [1395]
[INFO] [1620882819.196217]: start ...
[INFO] [1620882819.205050]: /dev/ttyUSB0,115200
MyCobot Status
--------------------------------
Joint Limit:
joint 1: -165 ~ +165
joint 2: -165 ~ +165
joint 3: -165 ~ +165
joint 4: -165 ~ +165
joint 5: -165 ~ +165
joint 6: -175 ~ +175
Connect Status: True
Servo Infomation: all connected
Servo Temperature: unknown
Atom Version: unknown
[INFO] [1620882819.435778]: ready
Then open another command line and run:
rosrun new_mycobot_320 mycobot_320_teleop_keyboard.py
You will see the following output in the command line:
Mycobot Teleop Keyboard Controller
---------------------------
Movimg options(control coordinations [x,y,z,rx,ry,rz]):
w(x+)
a(y-) s(x-) d(y+)
z(z-) x(z+)
u(rx+) i(ry+) o(rz+)
j(rx-) k(ry-) l(rz-)
Gripper control:
g - open
h - close
Other:
1 - Go to init pose
2 - Go to home pose
3 - Resave home pose
q - Quit
currently: speed: 50 change percent 5
In this terminal, you can control the state of the robot arm and move it using the keys in the command line.
Parameters supported by this script:
- _speed: the movement speed of the robot arm
- _change_percent: movement distance percentage
5 moveit use
mycobot_ros has integrated the MoveIt section.
Open the command line and run:
roslaunch new_mycobot_320_moveit mycobot320_moveit.launch
# If the end is equipped with an adaptive gripper, run (only M5 version is supported):
roslaunch new_mycobot_320_gripper_moveit mycobot320_gripper_moveit.launch
The operation effect is as follows:
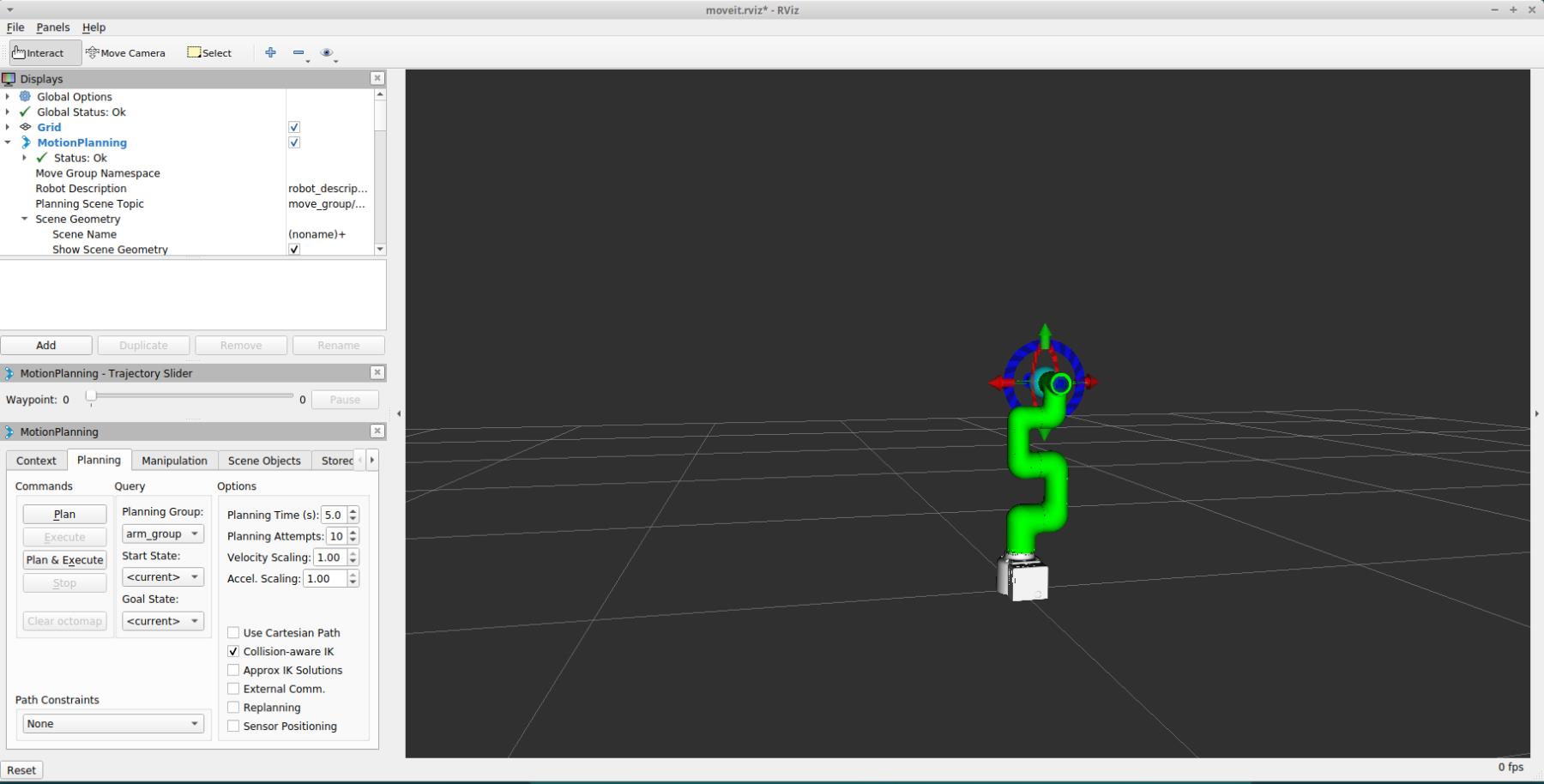
If the end is equipped with an adaptive gripper, the operation effect is as follows:
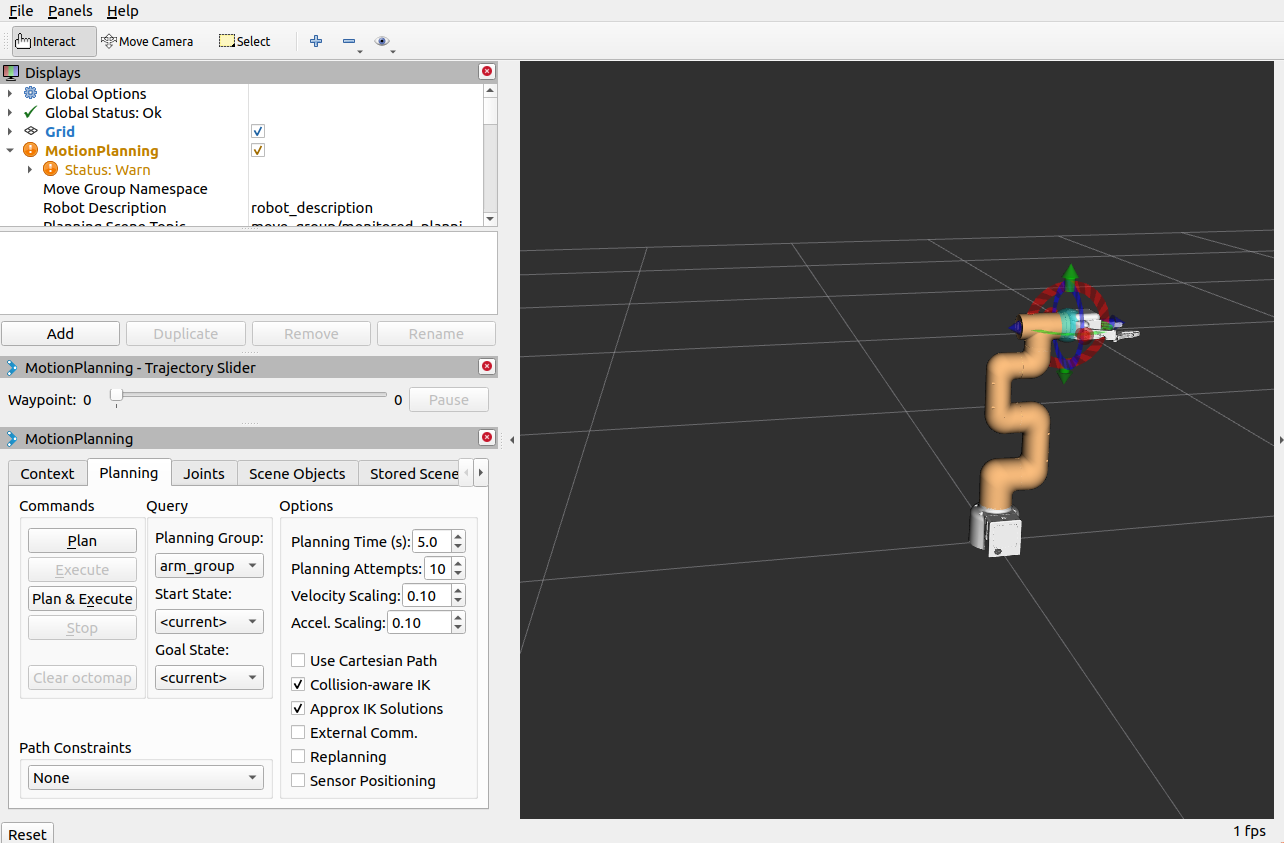 >
>
If you want a real robot arm to execute a plan synchronously, you need to open another command line and run:
# The default serial port name of 2022 mycobot 320-M5 version is "/dev/ttyUSB0", and the baud rate is 115200. The serial port name of some models is "dev/ttyACM0". If the default serial port name is wrong, you can change the serial port name to "/dev/ttyACM0".
rosrun new_mycobot_320_moveit sync_plan.py _port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 _baud:=115200
# If the end is equipped with an adaptive gripper, run (only supports M5 version, serial port modification is the same as above):
rosrun new_mycobot_320_gripper_moveit sync_plan.py _port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 _baud:=115200
Note: If the end is equipped with an adaptive gripper, and you need to plan the gripper, you need to switch the planning group to the planning group of the gripper.
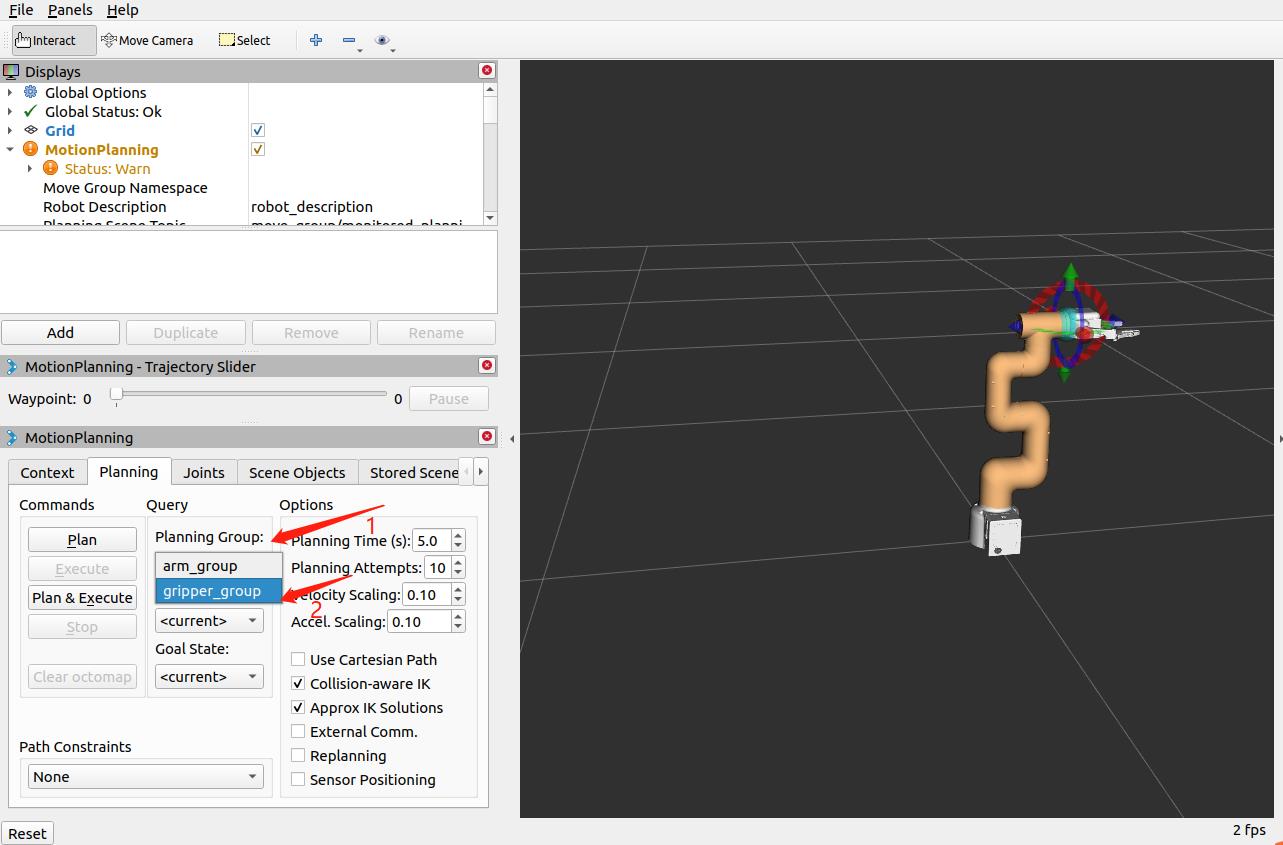 >
>
Modify motion speed
In order to prevent the joints from shaking during the movement of the real robotic arm, the movement speed of the joints needs to be reduced.
In the
sync_plan.pyfile, modify the speed parameter of the robot arm Python API, here it is changed to 25.... def callback(data): # rospy.loginfo(rospy.get_caller_id() + "%s", data) data_list = [] for index, value in enumerate(data.position): radians_to_angles = round(math.degrees(value), 2) data_list.append(radians_to_angles) rospy.loginfo(rospy.get_caller_id() + "%s", data_list) mc.send_angles(data_list, 25) # Change speed to 25 ...In the Moveit RViz interface, modify the scaling ratio of speed and acceleration. Here, change it to 0.5, and then save the current configuration.
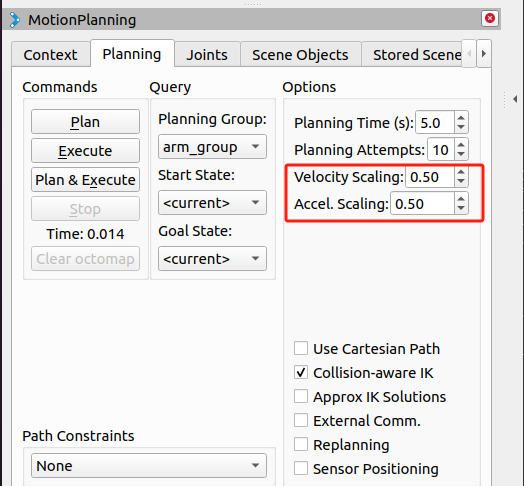 >
>