Communication Protocol
Notice: The communication protocol is used to directly control the machine, and the serial port assistant software is needed for communication
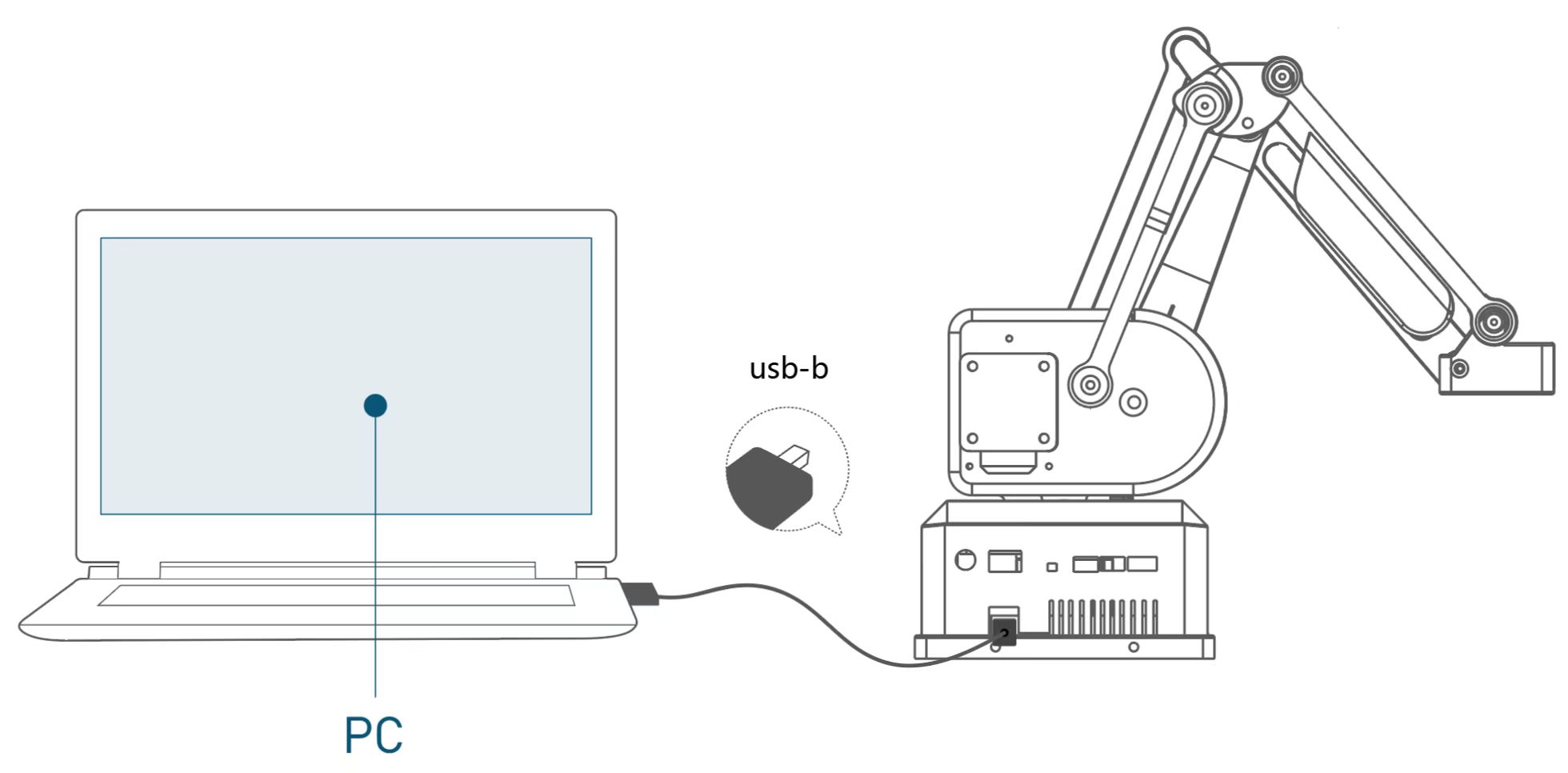
1 Settings of USB Communication
Make sure the following settings are prepared:
- Interface of mainline: USB Type-B connect
- Port ratio: 11520
- Data bit: 8
- Parity bit: none
- Stop bit: 1
2 Introduction to Command Frame & Sole Instruction
The PC sends data to the robot arm, which is analyzed after receiving the data from the robot arm. The command containing the return value will be returned to the PC within 20ms
3 Formats of Message Commands' Sending and Receiving
All commands are in string format. When sending commands, '\r' must be added at the end of the command. Commands comply with Gcode naming rules
- 1 Header: G / M
- 2 Serial number 00 ~ 120
- Corresponding number of developed commands
- You may leave it blank
- 3 Content:
- You may leave it blank
- 4 End: \r
- Invariable
- Indispensable
4 Explanation for Commands
The PC sends data to the robot arm. After receiving the data, the robot arm analyzes it. The command containing the return value will be returned to the host within 20ms.
| Type | Data | Length | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Header | Header | 1 | G / M |
| Serial number | 1-3 | 00 ~ 120 | |
| Content | Content | 0 ~ | The command comes with data, depending on the command |
| End | End | 1 | \r |
5 Explanation for Sole-Instruction Commands
coordinate control
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] | Data[3] | Data[4] | Data[5] | Data[6] | Data[7] | Data[8] | Data[9] | Data[10] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | End |
| Data | G | 0 | X | X.Value | Y | Y.Value | Z | Z.Value | F | F.Value | \r |
Make the robot arm move to the coordinate position at the speed of 100 [200,0,0]
Serial port sending example:G0 X200 Y0 Z0 F100\r
X.Value:-260~300 mm
Y.Value:-300~300 mm
Z.Value:-130~135 mm
F.Value:0-200 mm/s
wait (seconds)
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] | Data[3] | Data[4] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | Parameter frame | Parameter value | End |
| Data | G | 4 | S | S.Value | \r |
Make the robot wait 1 second
Serial port sending example:G4 S1\r
back to zero point
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | G | 28 | \r |
Serial port sending example:G28\r
Return:DATA: [ok]
set absolute cartesian mode
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | G | 90 | \r |
Serial port sending example:G90\r
set relative cartesian mode
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | G | 91 | \r |
Serial port sending example:G91\r
set point (current position)
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] | Data[3] | Data[4] | Data[5] | Data[6] | Data[7] | Data[8] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | End |
| Data | G | 92 | X | X.Value | Y | Y.Value | Z | Z.Value | \r |
Set the current position to [0,0,0]
Serial port sending example:G92 X0 Y0 Z0\r
Set the current position to [100,50,10]
Serial port sending example:G92 X100 Y50 Z10\r
X.Value:-260~300 mm
Y.Value:-300~300 mm
Z.Value:-130~135 mm
turn on the laser
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 3 | \r |
turn on the laser
Serial port sending example:M3\r
turn off the laser
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 5 | \r |
turn off the laser
Serial port sending example:M5\r
set PWM duty cycle
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] | Data[3] | Data[4] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | Parameter frame | Parameter value | End |
| Data | M | 21 | P | P.Value | \r |
Set the laser PWM to 200
Serial port sending example:M21 P200\r
P.Value:0~255, The higher the number, the stronger the laser frequency
set suction pump off
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 22 | \r |
Turn off the pump
Serial port sending example:M22\r
set suction pump on
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 23 | \r |
Turn on the pump
Serial port sending example:M23\r
set gripper calibration
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 24 | \r |
Gripper moves to the specified position, setting the current position as gripper zero point
Serial port sending example:M24\r
Notice: The zero position of the gripper has been set before delivery. Do not change the zero position of the gripper arbitrarily, which may cause damage to the gripper
set gripper open state
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] | Data[3] | Data[4] | Data[5] | Data[6] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | End |
| Data | M | 25 | A | A.Value | F | F.Value | \r |
Move the gripper to 50% position at 200 speed
Serial port sending example:M25 A50 F200\r
A.Value:0~100 0-close 100-open
F.Value:0~1500 RPM/s
release gripper
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 26 | \r |
Set gripper release
Serial port sending example:M26\r
set fan on
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 27 | \r |
set fan on
Serial port sending example:M27\r
Notice:The fan in the robot arm is enabled by default
set fan off
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 28 | \r |
set fan off
Serial port sending example:M28\r
Notice:Turning off the fan decreases the heat dissipation effect of the robot arm. To avoid operating experience, do not turn off the fan at will
single joint angle control
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] | Data[3] | Data[4] | Data[5] | Data[6] | Data[7] | Data[8] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | End |
| Data | M | 10 | J | J.Value | A | A.Value | F | F.Value | \r |
Move joint 1 to 90° position at the speed of 100
Serial port sending example:M10 J1 A90 F100\r
J.Value:1/2/3
A.Value: J1:-150°~170° J2:-20°~90° J3:-5°~60°
F.Value:0~200 mm/s
all angle control
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] | Data[3] | Data[4] | Data[5] | Data[6] | Data[7] | Data[8] | Data[9] | Data[10] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | End |
| Data | M | 11 | X | X.Value | Y | Y.Value | Z | Z.Value | F | F.Value | \r |
Make the robot arm move to position [90,30,30] at the speed of 100
Serial port sending example:M11 X90 Y30 Z30 F100\r
X.Value:-150°~170°
Y.Value:-20°~90°
Z.Value:-5°~60°
F.Value:0~200 mm/s
get current joint angle information
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 12 | \r |
Serial port sending example:M12\r
Return:DATA: ANGLES[0.00 ,0.00 ,90.00 ,0.00]
jog angle move
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] | Data[3] | Data[4] | Data[5] | Data[6] | Data[7] | Data[8] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | End |
| Data | M | 13 | J | J.Value | D | D.Value | F | F.Value | \r |
Keep joint 1 moving in the positive direction at the speed of 10
Serial port sending example:M13 J1 D0 F10\r
J.Value:1/2/3
D.Value:0-Positive direction 1-Negative direction
F.Value:0~200 mm/s
jog coord move
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] | Data[3] | Data[4] | Data[5] | Data[6] | Data[7] | Data[8] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | Parameter frame | Parameter value | End |
| Data | M | 14 | J | J.Value | D | D.Value | F | F.Value | \r |
Keep the robot arm moving in the positive direction of X axis at the speed of 10
Serial port sending example:M14 J1 D0 F10\r
J.Value:1/2/3 1-X-axis 2-Y-axis 3-Z-axis
D.Value:0-Positive direction 1-Negative direction
F.Value:0~200 mm/s
jog stop
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 15 | \r |
The robot arm stops moving in the direction
Serial port sending example:M15\r
release all motors
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 17 | \r |
release all joints
Serial port sending example:M17\r
power on all motors
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 18 | \r |
power on all joints
Serial port sending example:M18\r
get current cartesian coordinate information
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 114 | \r |
Obtain the current coordinate position of the robot arm
Serial port sending example:M114\r
Return:DATA : COORDS[204.00,0.00,120.00,0.00]
get the status of all current homing switches
| Domain | Data[0] | Data[1] | Data[2] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanation | Recognition frame | Recognition frame | End |
| Data | M | 119 | \r |
get the status of all current homing switches
Serial port sending example:M119\r
Return:DATA : ENDSTOP[1 ,1 ,1]