1. What is mybuddy?
mybuddy is a fully visual modular programming software, belongs to the graphical programming language. mybuddy is similar in function/design to Scratch, MIT's children's programming language. With mybuddy, users can build code logic by dragging and dropping modules, much like building blocks. From a user perspective, mybuddy is an easy-to-use visual tool for generating code. From the developer's point of view, mybuddy is a text box containing the user-typed code. The process of generating the code to the text box is the process of the user dragging and dropping in the mybuddy.
mybuddy installation
mybuddy interface

download mybuddy No download link, later online to supplement
applicable equipment:
- mybuddy 280
Use the premise
- Pi version needs to be added
- Configure the Python environment and install the latest pymycobot library
2. Basic applicability of mybuddy
2.1 MyBuddy interface introduction
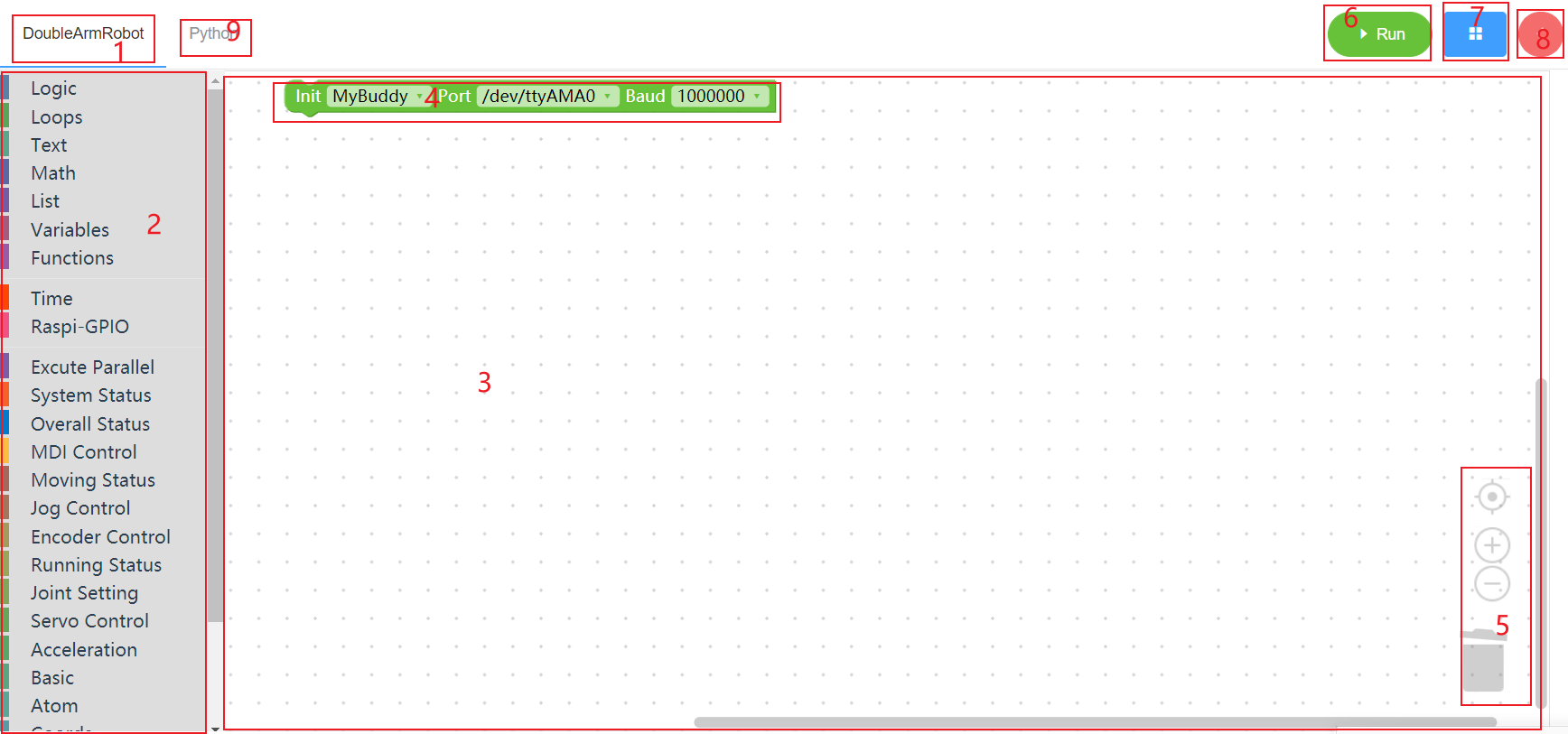
As shown above, mybuddy is divided into nine parts:
- area 1 is the page where the main functions of MyBuddy are located. Users will spend most of their time on this page.
- area 2 is the toolbar where the building block is located. A corresponding menu can be opened by clicking the label of the toolbar. Users can place the building block in the workspace by dragging the corresponding building block.
area 3 is the software workspace, which contains all the building blocks selected by the user.
Mark 4 initializes the building blocks for the machines, the default do not delete, click the first drop-down box can switch to other models (temporarily only mybuddy a model), the second drop-down box for a serial port list, click can show on the system after all the serial port, users need to select the initialization of the machine corresponds to a serial port (each system shows the serial port name, The third drop-down box is the baud rate required to initialize the robot. Mybuddy is 115200.
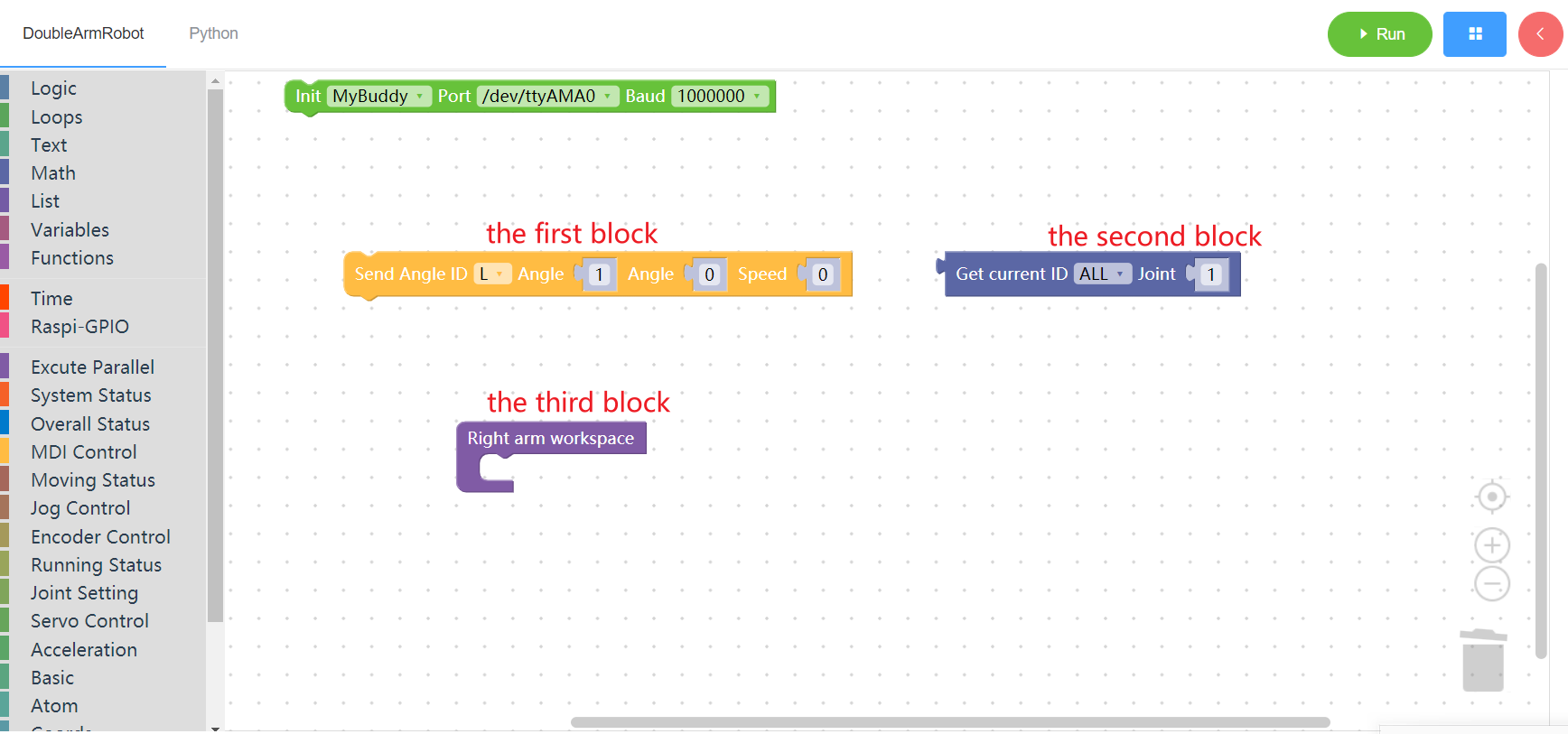
Note: In this software, there are three main shapes of building blocks. The first one is that the joint is in the form of upper and lower buckles, which can be placed arbitrarily according to requirements. The second for the button on the left side of the card, the building blocks in general is the return value type, if you want to put the blocks in the other building blocks, need to make sure that their type is consistent, this within the software already has to deal with, of course, the result of the performance on the user side is if the type is not consistent, cannot be put into the building blocks. The third type is less common. The blocks themselves have no clasp, only internal joints.
Examples of the three blocks are as follows:
area 5 is the workspace control module
- The dustbin is the first one from bottom to top, which stores the blocks deleted by the user. When the user wants to delete a block in the work area, he can drag the block to the dustbin and release the mouse to delete the block, or press del to delete the block. To restore the deleted blocks, click open trash and drag them out.
- The second button is the shrink button. When the user feels that the workspace block is relatively large, he can click the minus button to shrink the workspace scale, or use the mouse pulley to shrink the workspace
- The third is the enlarge button, click can enlarge the work area, also can enlarge the operation through the mouse pulley
The fourth button is to restore and locate the current workspace. When the user feels that the workspace is too large or too small, he can click this button to restore the workspace to its initial state and locate it to the center of the workspace
Note: The size of the workspace will affect the blocks in the toolbar, so you need to choose a proper scale to avoid blocks blocking the screen
- area 6 is the run button. Clicking on the button will convert the user's workspace code into Python code and execute it. At the same time, a pop-up window will print out the running results of the program
- area 7 For the software setup button, click to save workspace to file, load file to current workspace, set software language, theme, and view current software version information and the version required by PyMycobot
area 8 for fast moving toolbar, which contains mybuddy control arm around the waist of the coordinate and Angle, speaking, reading and writing, and the user to select machine, serial port and baud rate (keep pace with the workspace of the initialization data) and then click the open button to connect the robot, and then click add and subtract Numbers coordinates from the Angle of control arm movements. Note:The Python button cannot run when Quick Move is enabled because the serial port is occupied. If you need to run Python code, please turn off quick Move first.
area 9 is the Python code area. Users can click to view the Python code corresponding to the building blocks in the workspace
3. Building block API introduction
3.1 system information
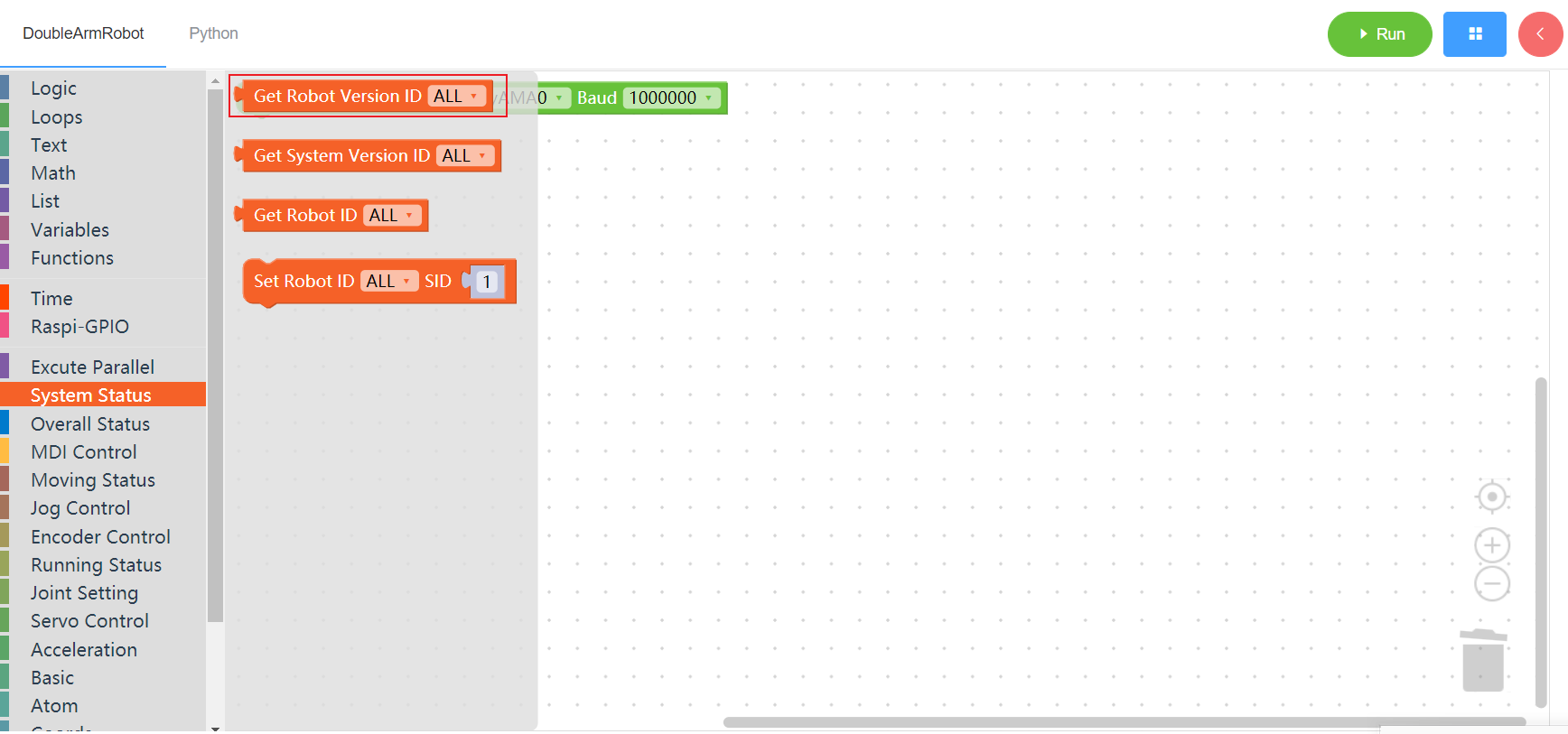
3.1.1 Get the Robot version
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get robot version information
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waist
- Return : Robot version information
2. Block display
3.1.2 Checking the Software Version
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:get software version
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waist
- Return :version information
2. Block display

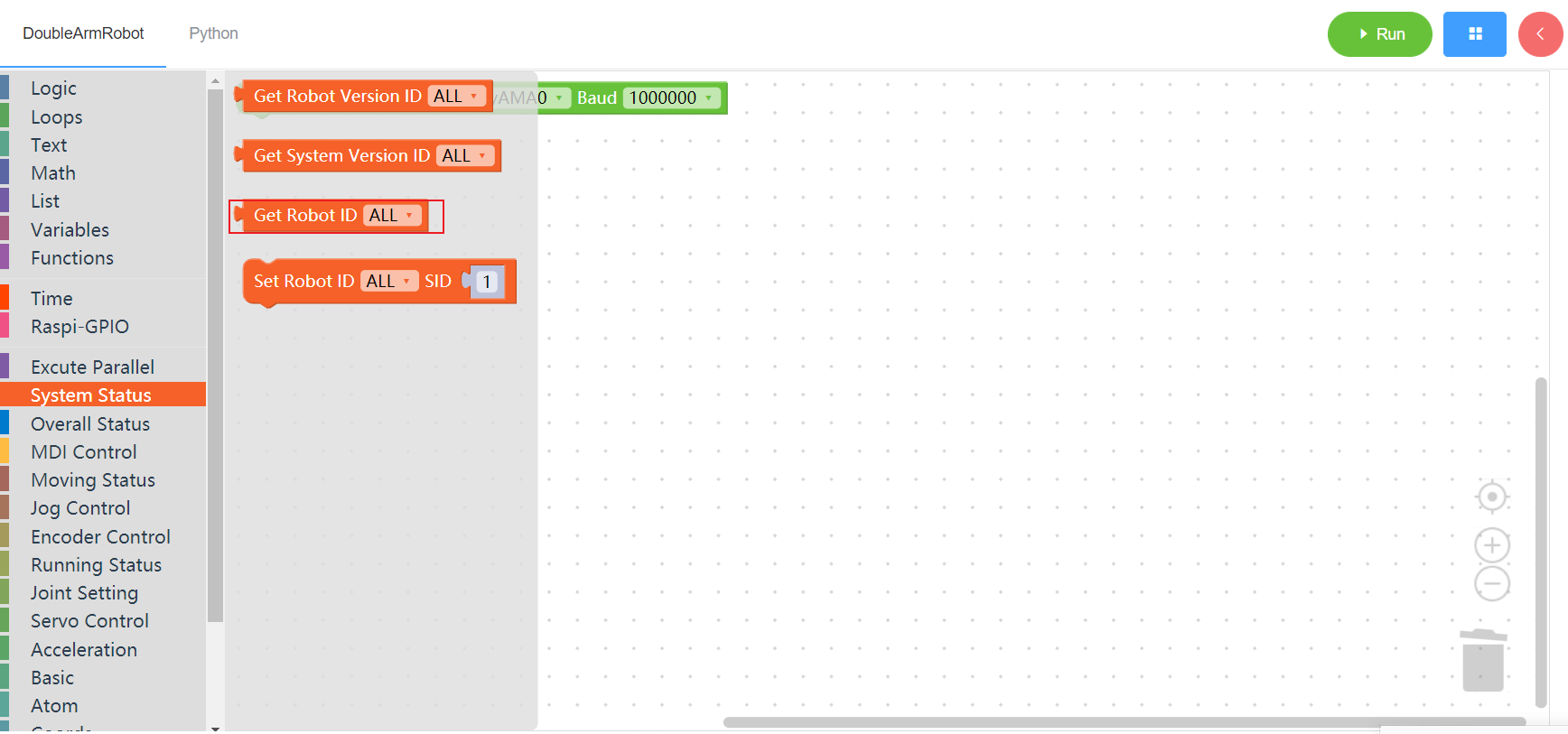
3.1.3 Get Robot ID
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get Robot ID
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waist
- Return :ID
2. Block display
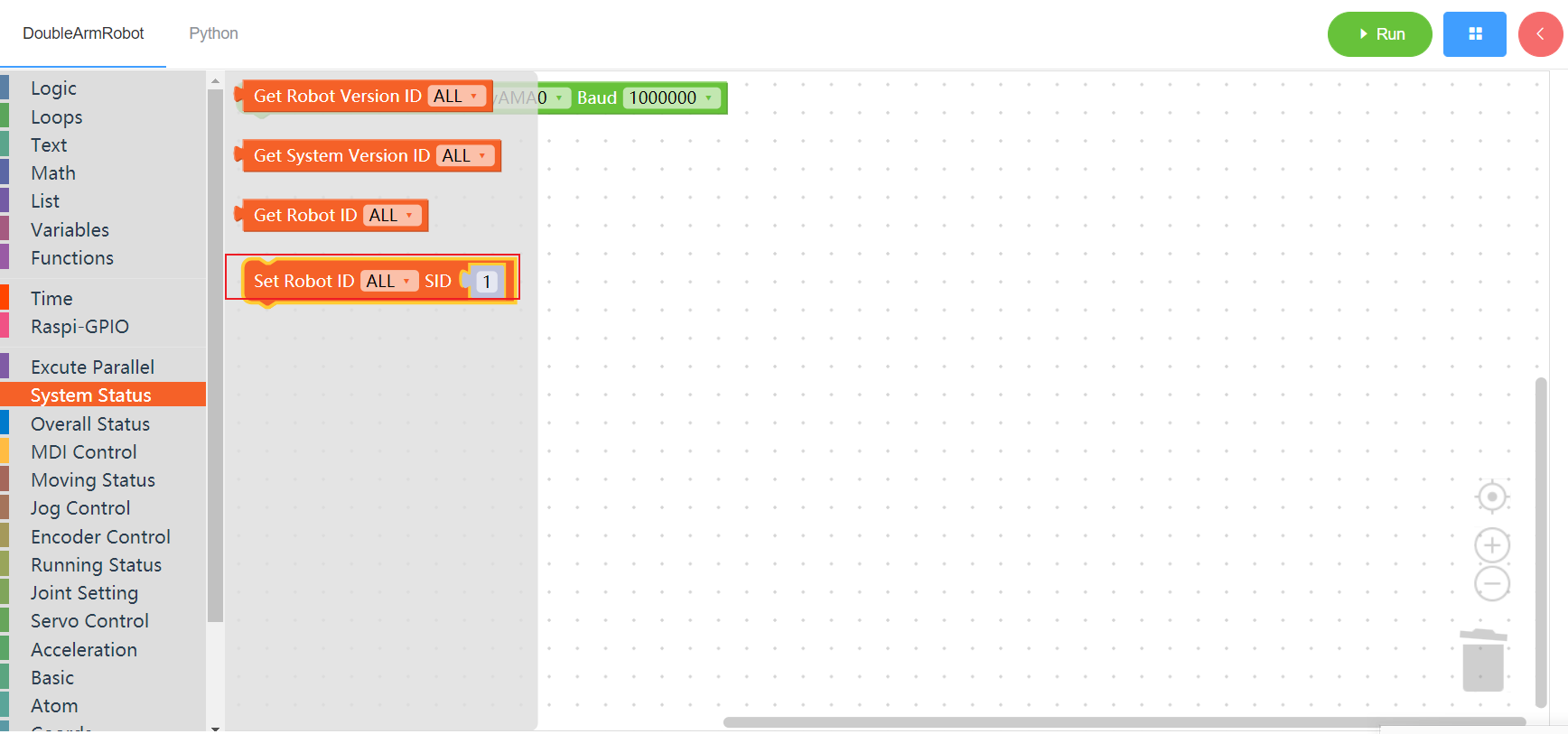
3.1.4 Set Robot ID
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set Robot ID
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waistNUM:integer(1~253)
- Return :none
2. Block display
3.2 The overall state of the manipulator
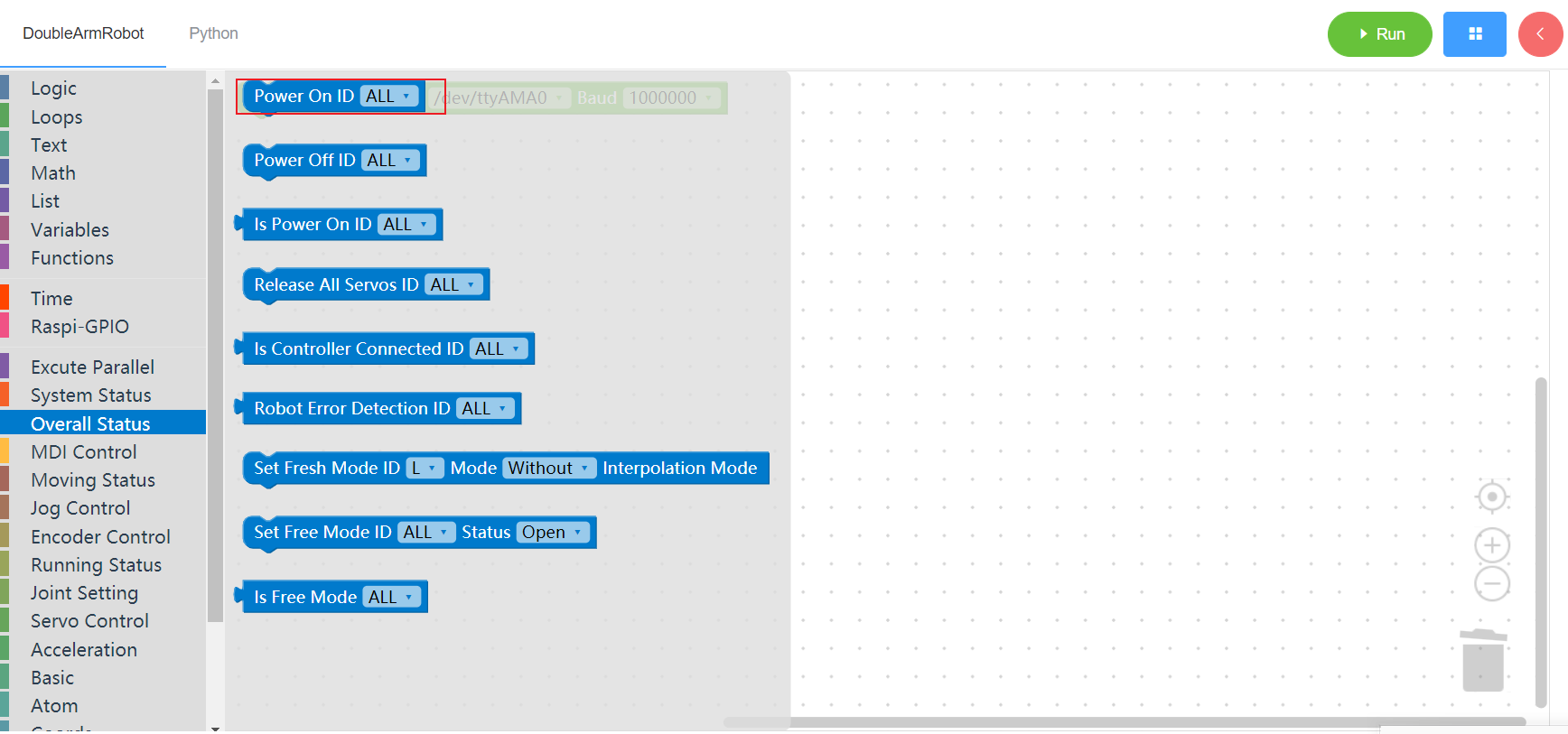
3.2.1 Power on
1. Runtime API Reference
Function:Power on the manipulator
Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waist
- Return :none
2. Block display
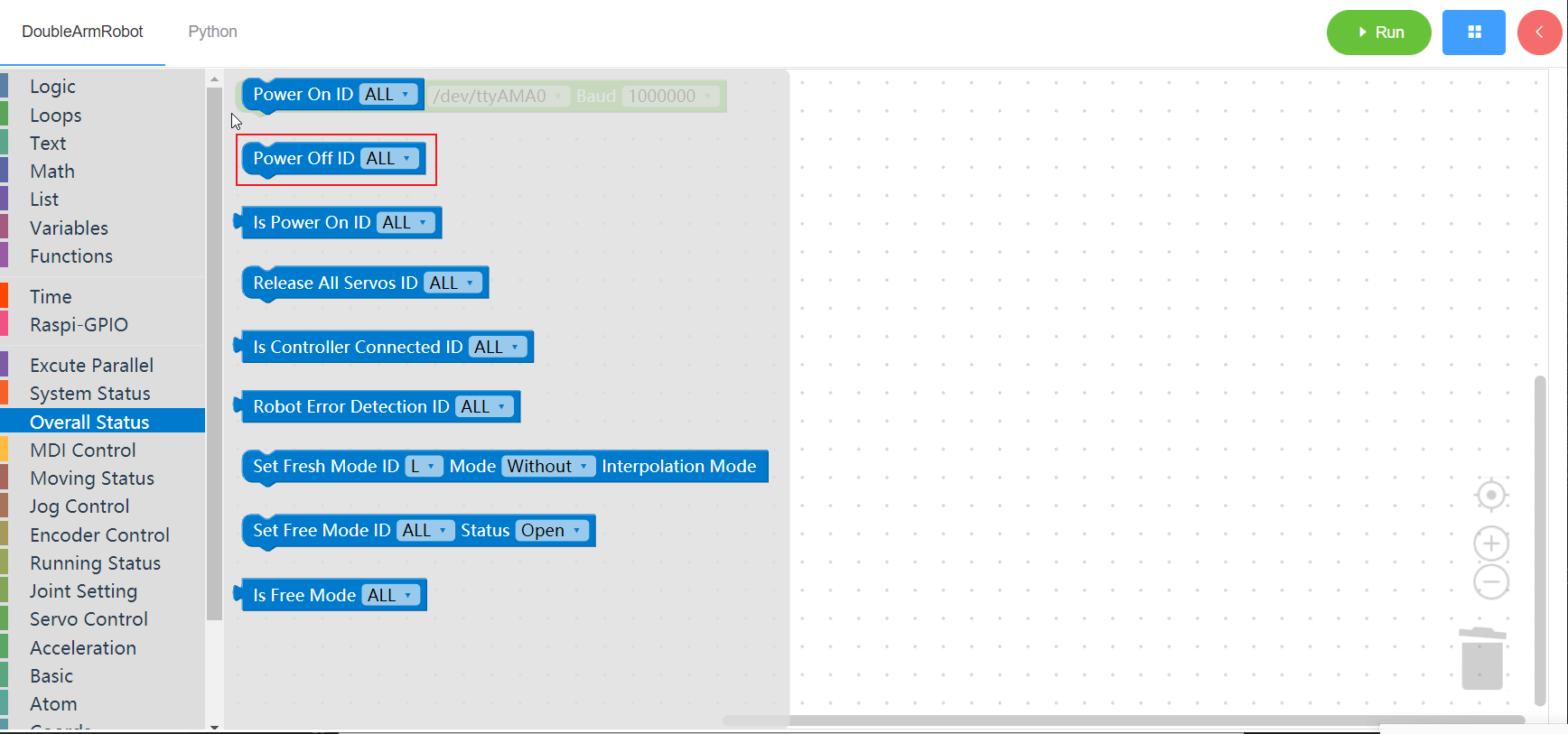
3.2.2 Power iff
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Power off the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waist
2. Block display
3.2.3 Check whether the mechanical arm is powered on
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Check whether the mechanical arm is powered on
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waist
- Return :
- 1 power on
- 0 power down
- -1 error
2. Block display
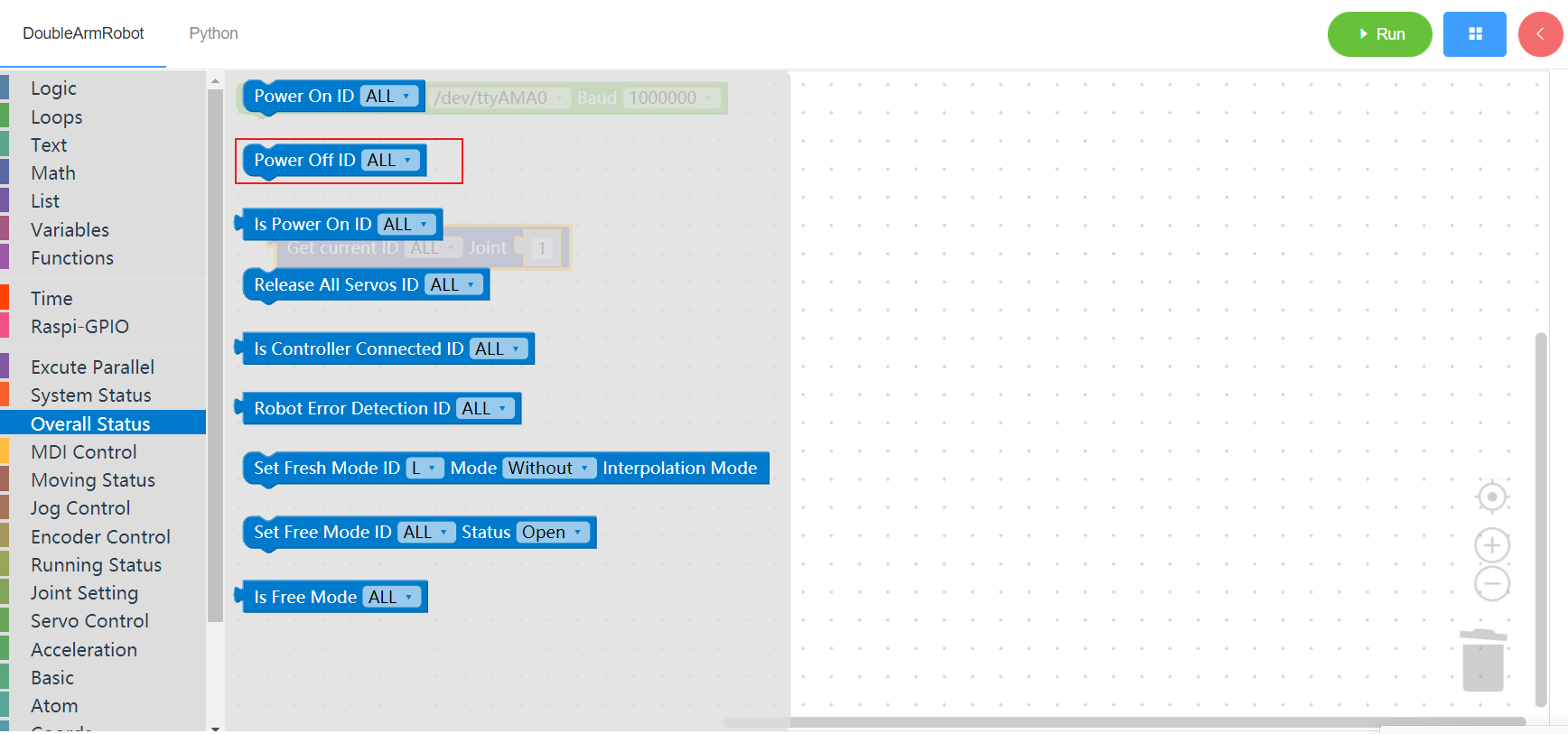
3.2.4 Release all servos
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Release all servos
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waist
- Return :none
2. Block display
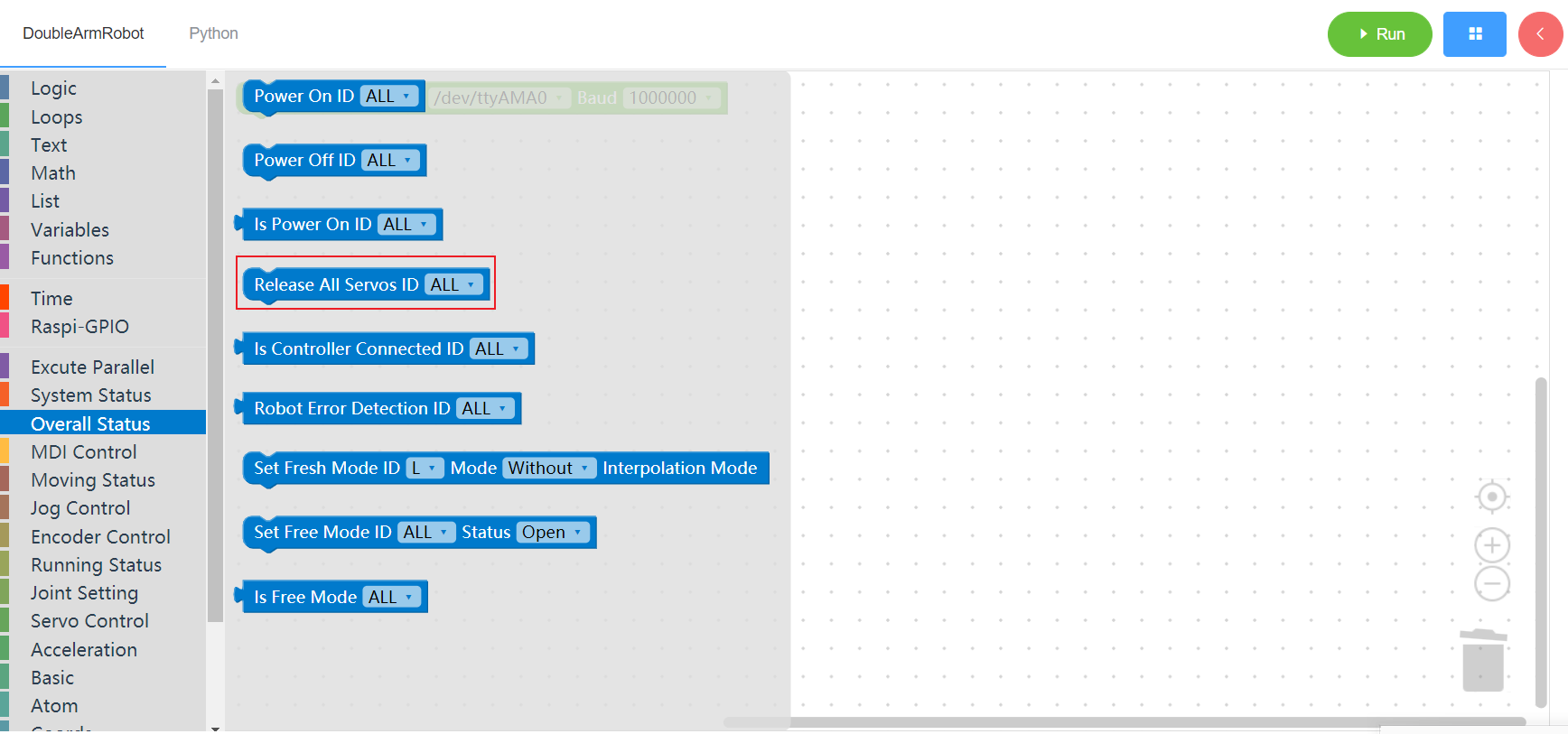
3.2.5 check control connection
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Check whether the manipulator control is connected
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waist
- Return :unknown
2. Block display
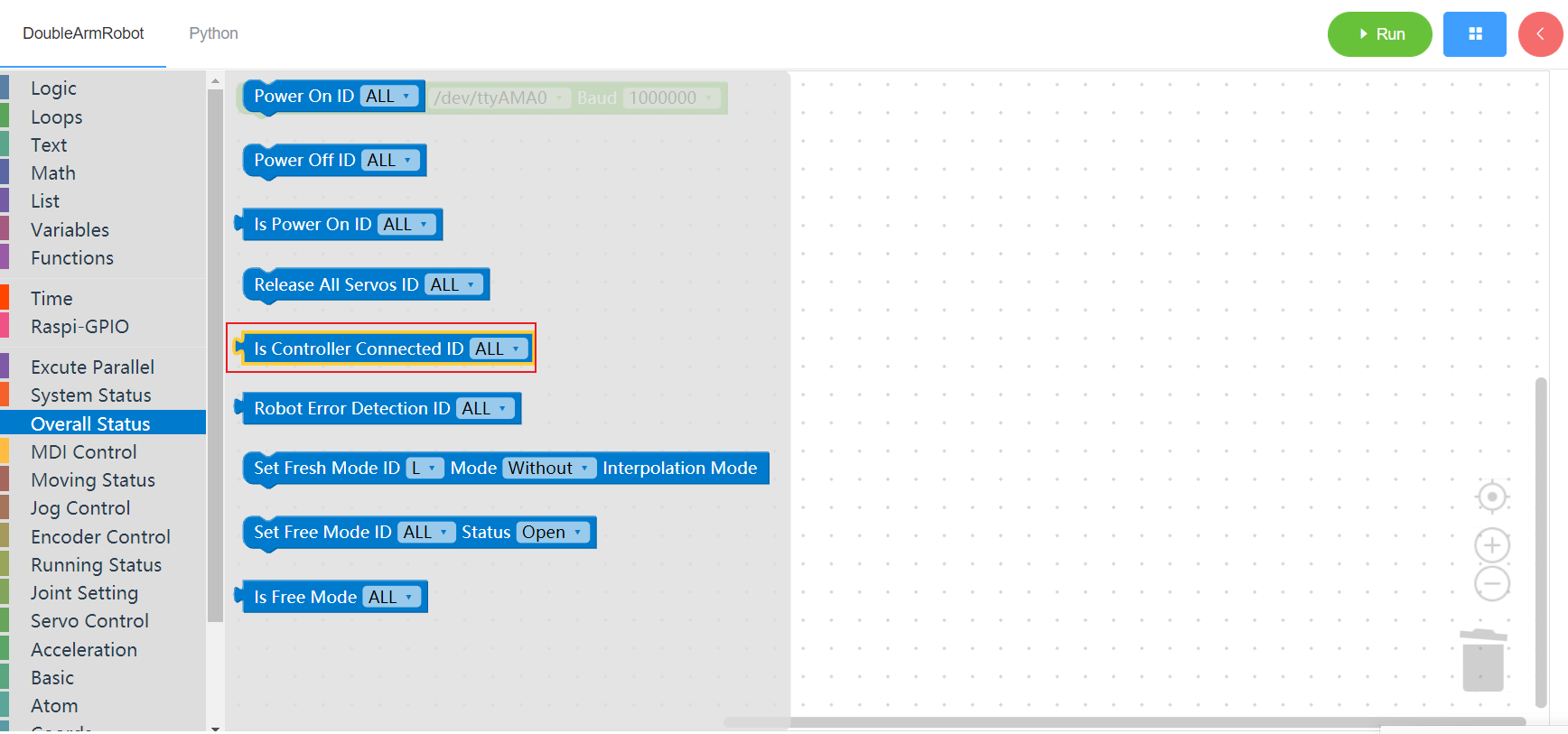
3.2.6 Robot error detection
1. Runtime API Reference
Function:Robot error detection
Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waist
- Return :none
2. Block display
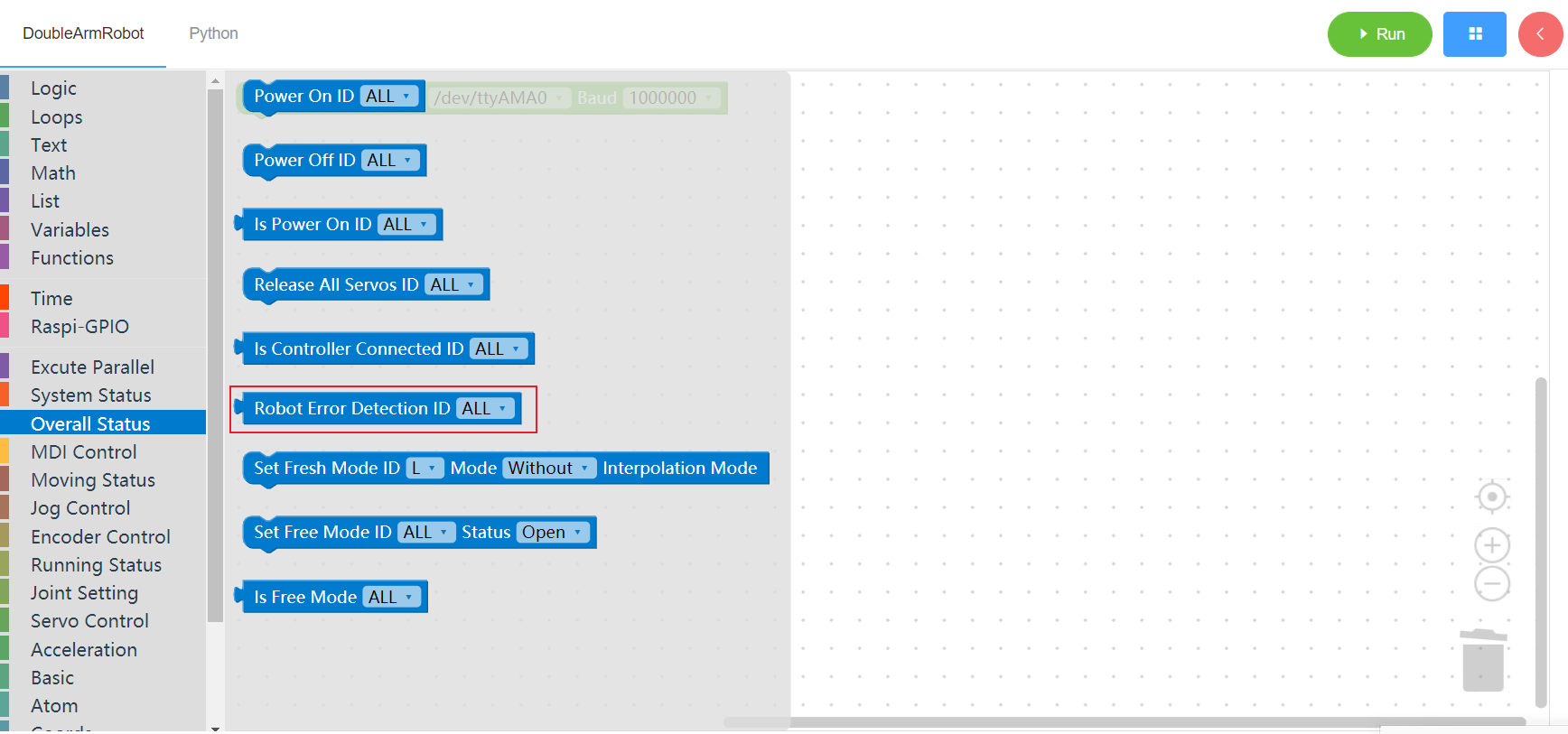
3.2.7 Set instruction refresh mode
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set instruction refresh mode
Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armMODE: Interpolation mode, non-interpolation mode (default)
Return :none
2. Block display
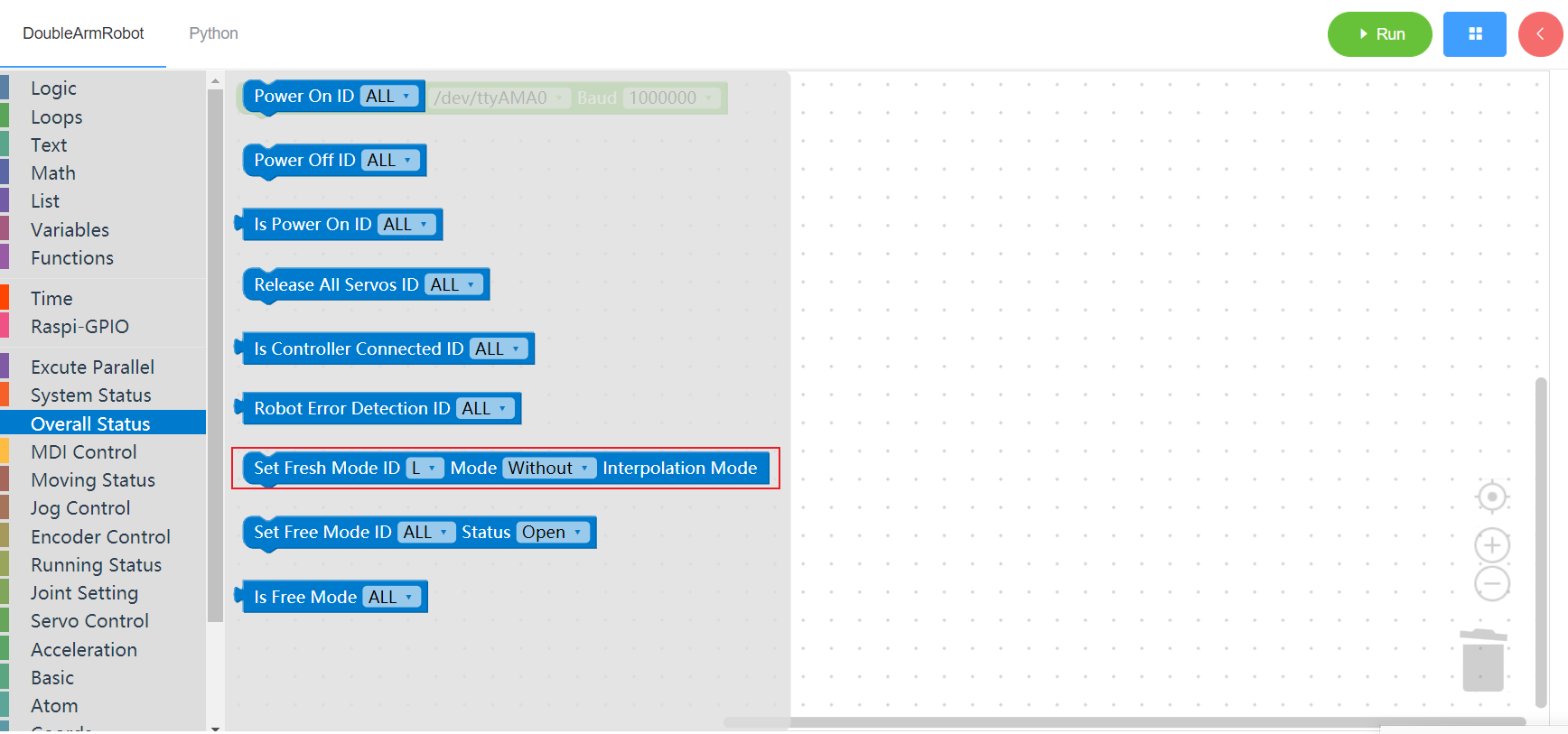
3.2.8 Free mode state
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the free mode state of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waistSTATUS:status(open/close)
- Return* :none
2. Block display
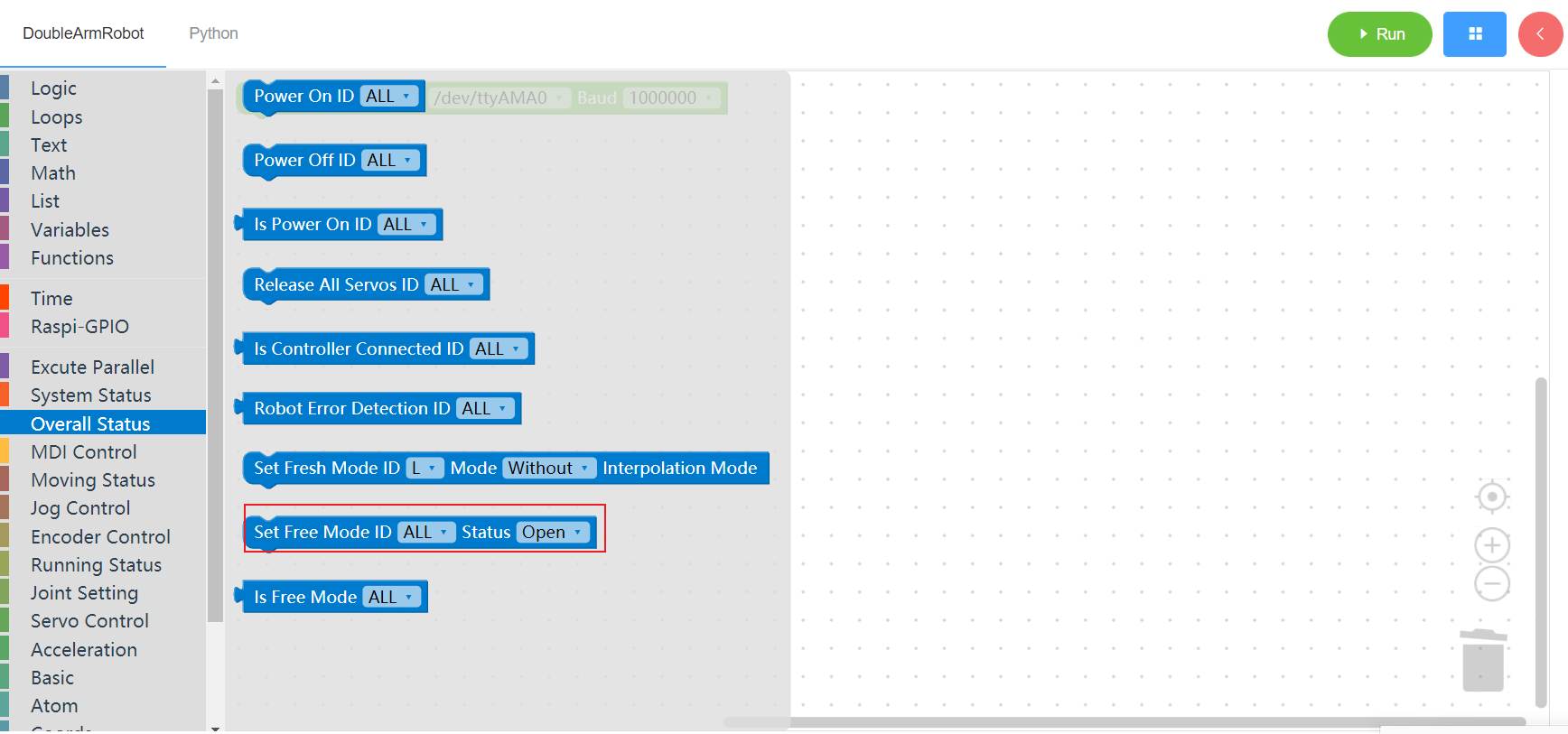
3.2.9 Check whether it is in free mode
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Check whether the manipulator is in free mode
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): ALL for ALL manipulator arms, L for left arm, R for right arm, W for waist
- Return :
- 0 no
- 1 yes
2. Block display
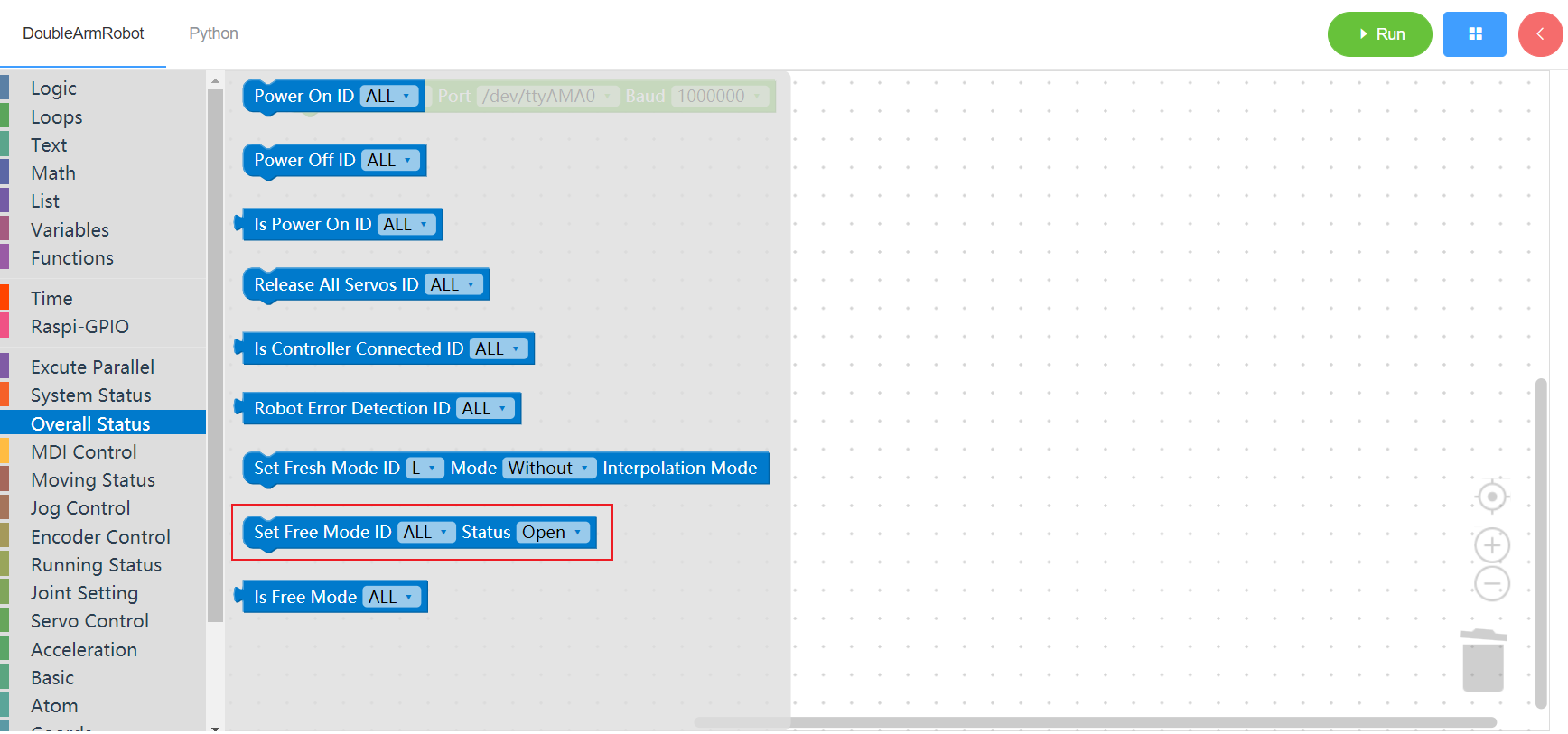
3.3 MDI control
3.3.1 Read single Angle
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Read single Angle
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint id(1~6)
- Return :single angle
2. Block display
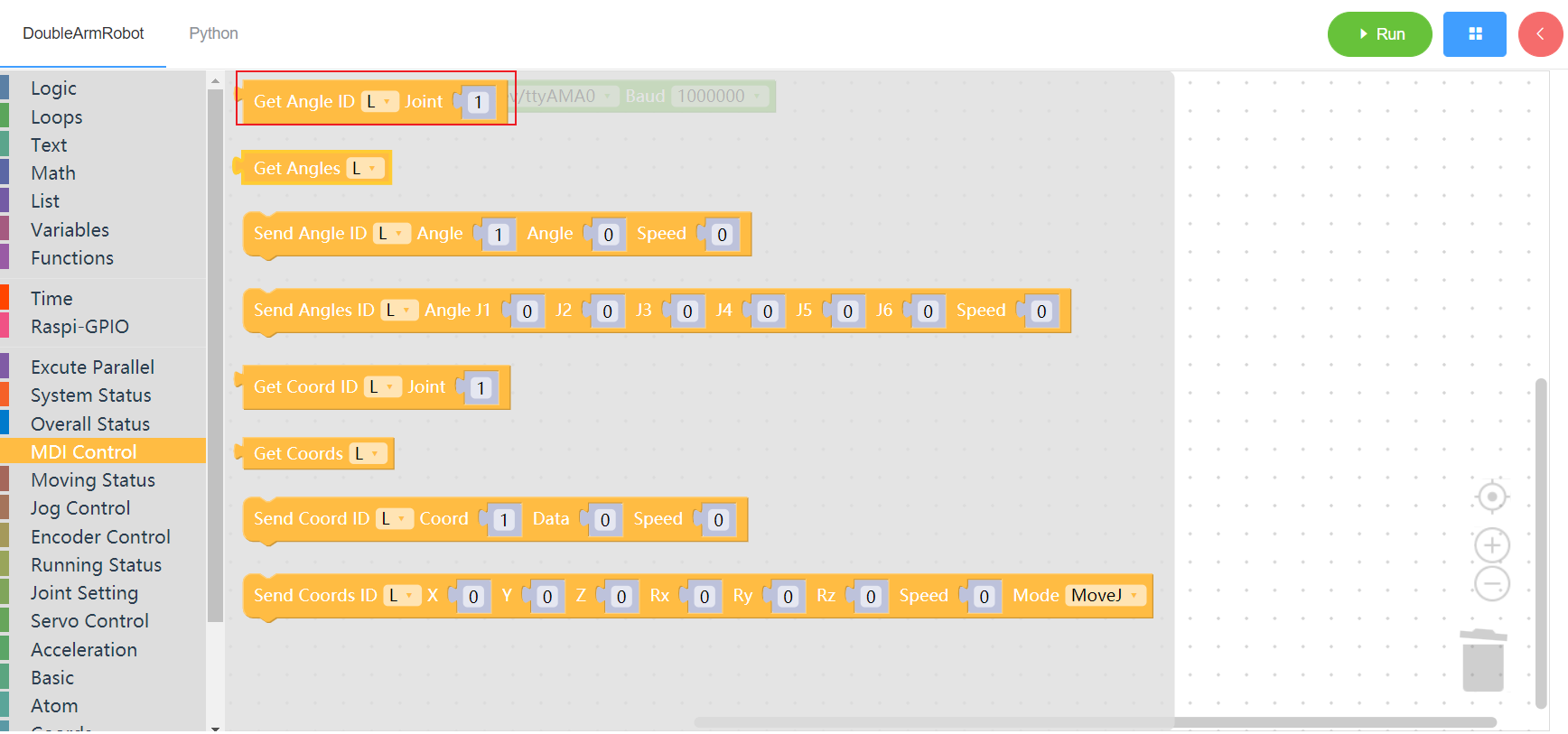
3.3.2 Read all angles
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Read all angles of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right arm
- Return :
ANGLES:List of joint angles corresponding to the manipulator (including the angles from joint 1 to joint 6)
2. Block display
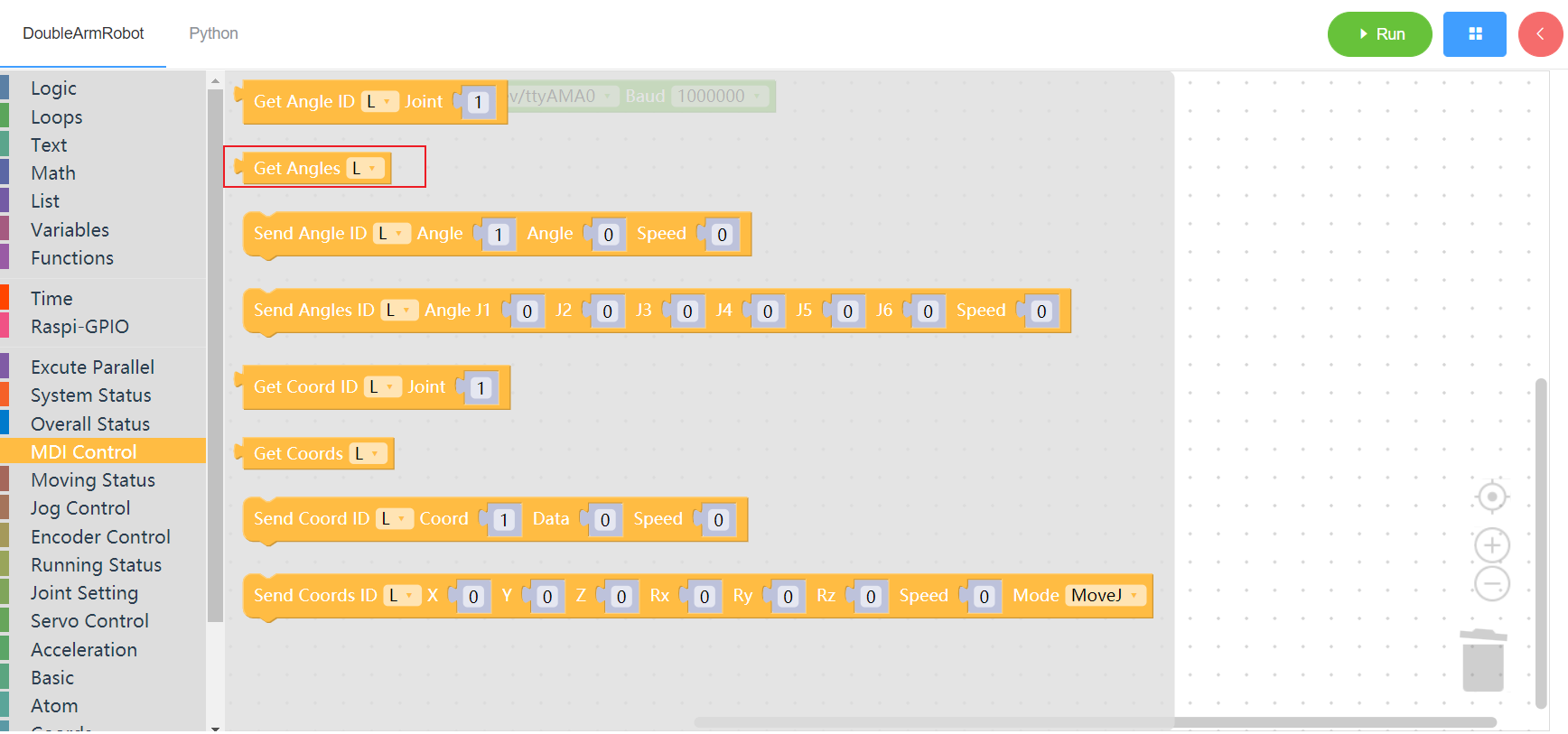
3.3.3 Send single angle
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the single Angle of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT_ID:joint1~6ANGLE:angleSPEEDspeed(0~100)
- Return :none
2. Block display
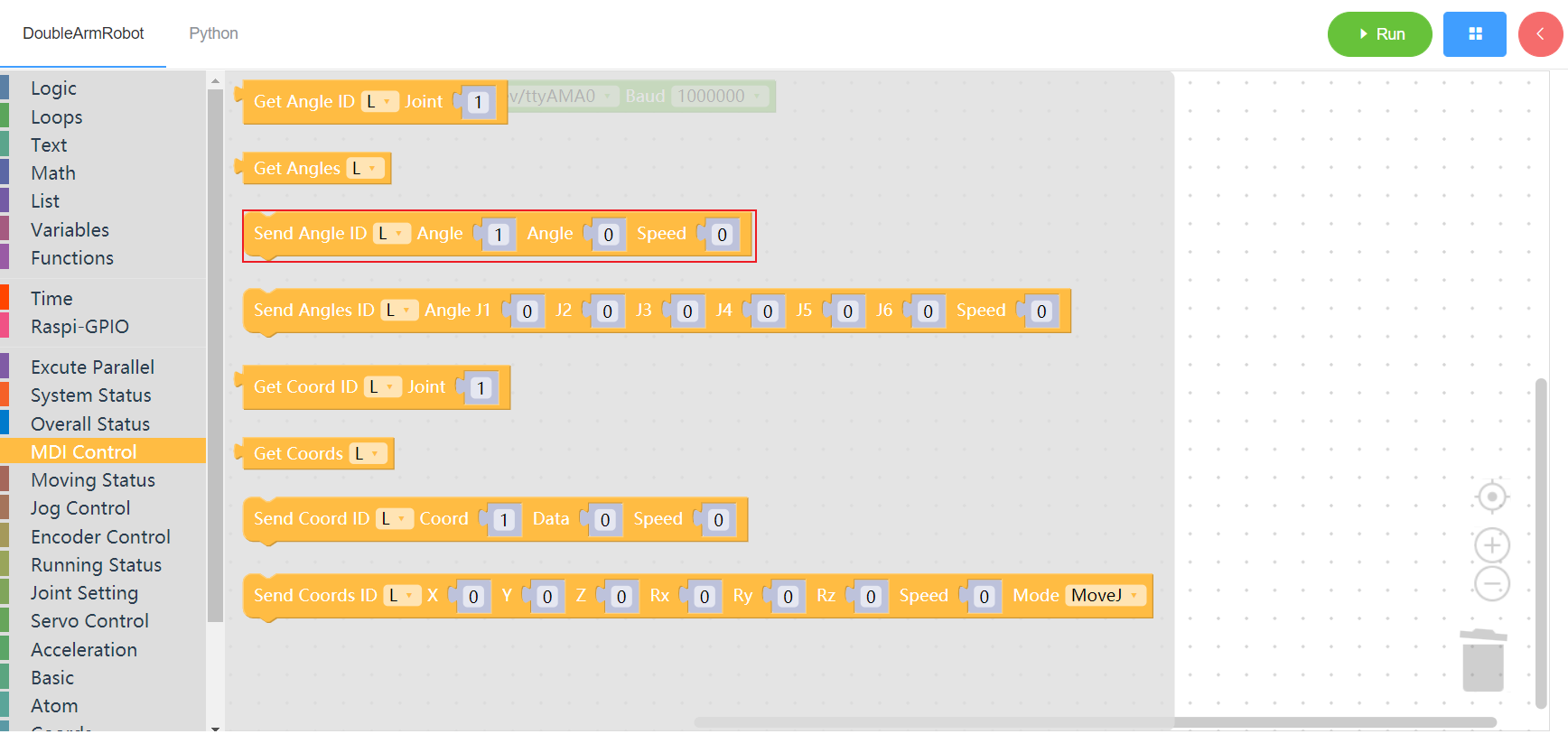
3.3.4 Send all angles
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set all the angles of the manipulator
Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armANGLES: Angle from joint 1 to joint 6SPEED:Moving speed of mechanical arm (0~100)
Return :none
2. Block display
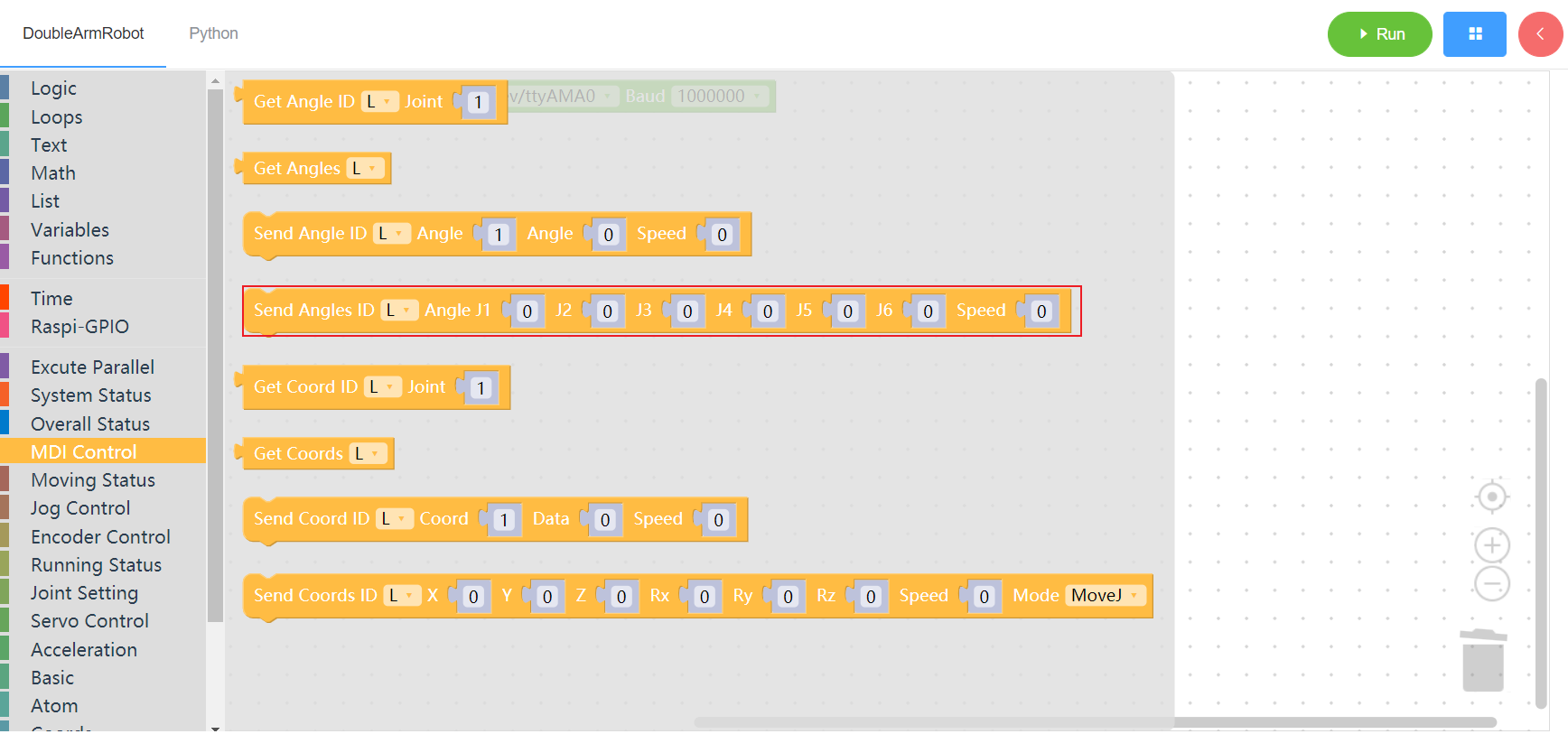
3.3.5 Read single coordinate
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Read the coordinates of a single joint of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for the waistCOORD:1~6(x/y/z/rx/ry/rz)SPEED: speed(0~100)
- Return : single coordinate
2. Block display

3.3.6 Read all coordinates
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Read all coordinates of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right arm
- Return :
COORDS: All joint coordinates of the manipulator
2. Block display

3.3.7 Send single coordinate
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set a single coordinate of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistCOORD:Coordinate ID, range 1~6(x/y/z/rx/ry/rz)DATA:coordinate dataSPEED: speed(0~100)
- Return :none
2. Block display

3.3.8 Send all coordinates
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set all coordinates of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armCOORDS: Coordinates of joints 1 to 6SPEED: The moving speed of the manipulator(0~100)MODE: 0 - moveJ, 1 - moveL, 2 - moveC
- Return :none
2. Block display

3.4 Motion control
3.4.1 Pause
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Suspend the movement of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W): All for all arms , for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :none
2. Block display
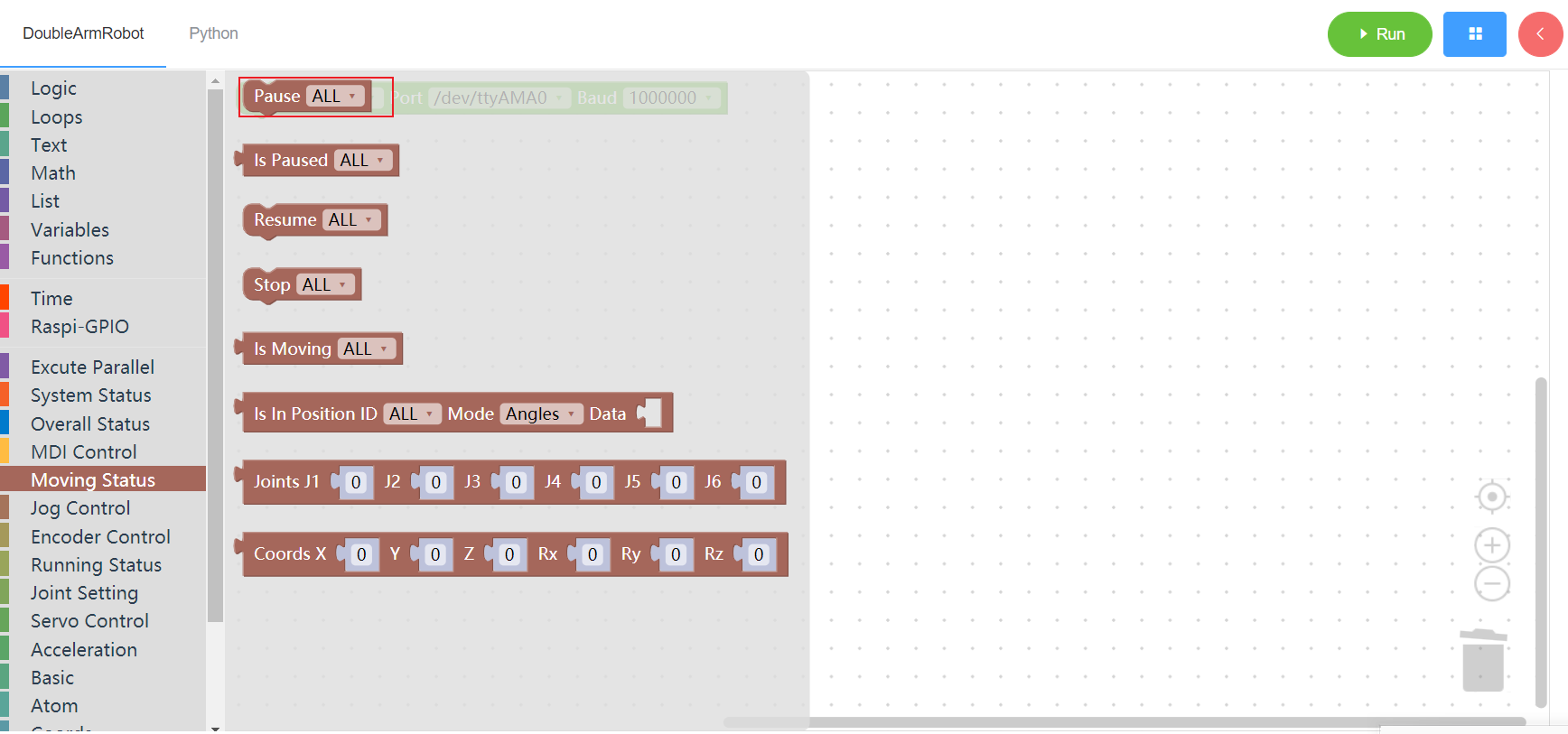
3.4.2 Is paused
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Check whether the manipulator is suspended
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :
- 1 paused
- 0 did not pause
- -1 error
2. Block display
3.4.3 Resume
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Restore the movement of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :none
2. Block display
3.4.5 Is moving
1. Runtime API Reference
Function:Check if the arm is moving
Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :
- 1 moving
- 0 did not move
- -1 error
2. Block display
3.4.6 Whether to reach the specified position
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Check whether the manipulator reaches the specified position
Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistDATA: Data list: 13 data for ALL, 6 data for L/R, and 1 data for WMODE: Mode (Angles/Coords)
Return :
- 1 yes
- 0 no
- -1 error
2. Block display
3.4.7 Angles list
1. Runtime API Reference
Function: for 3.4.6 Whether to reach the specified position separately set the list, can be filled in 6 angles
Arguments:
DATA:Data list, fill in 6 angles
Return :
ANGLES: Angle list (length 6)
2.Block display
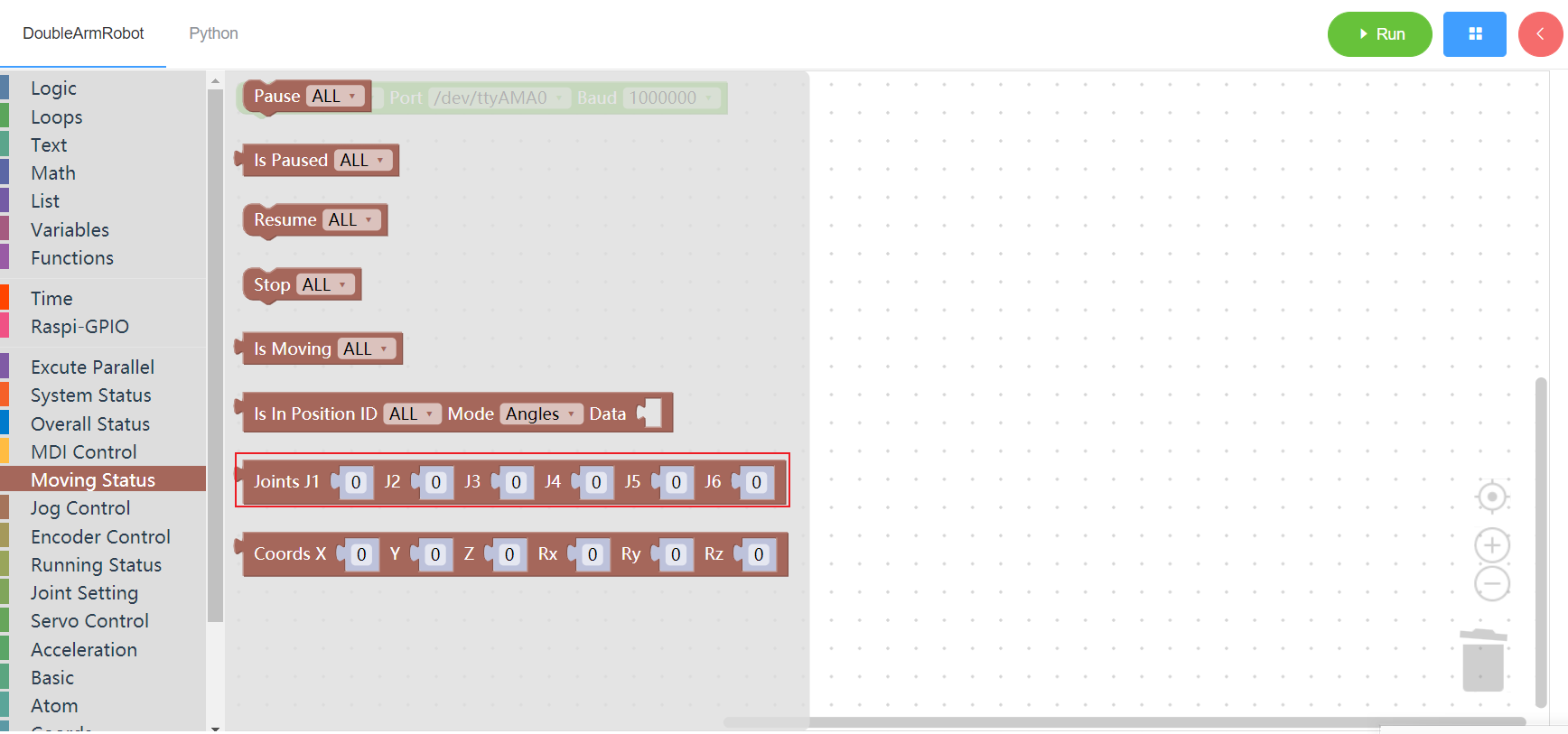
3.4.8 Coordinates list
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function: for 3.4.6 Whether to reach the specified location separately set the list, can be filled in 6 coordinates
Arguments:
DATA: Data list, fill in 6 coordinates
Return :
COORDS:Coordinate list (length 6)
2.Block display
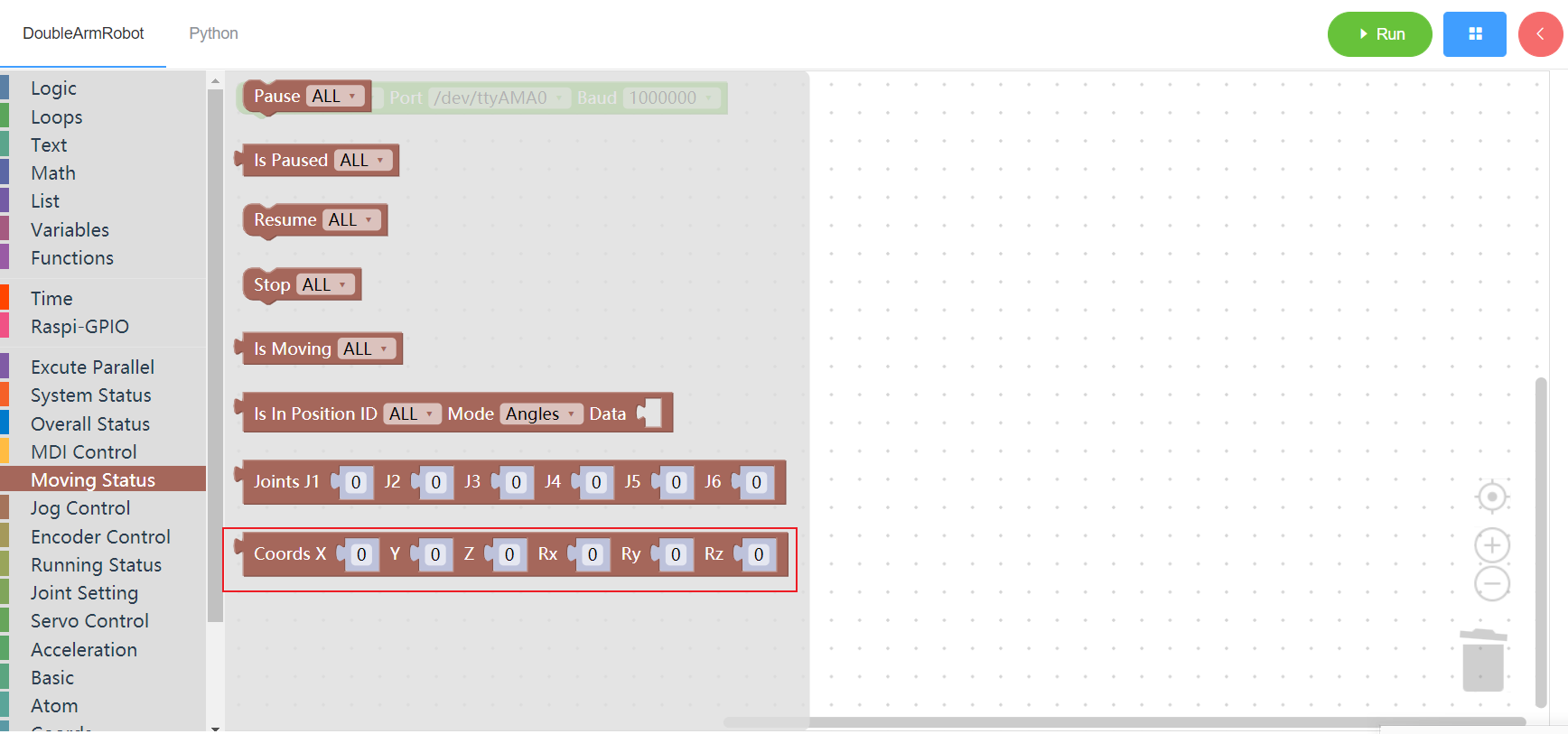
3.5 Jog control
3.5.1 Jog angle
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Jog angle
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint id,1~6DIRECTION:0-decrease 1-increaseSPEED:speed(0~100)
Return :none
2.Block display
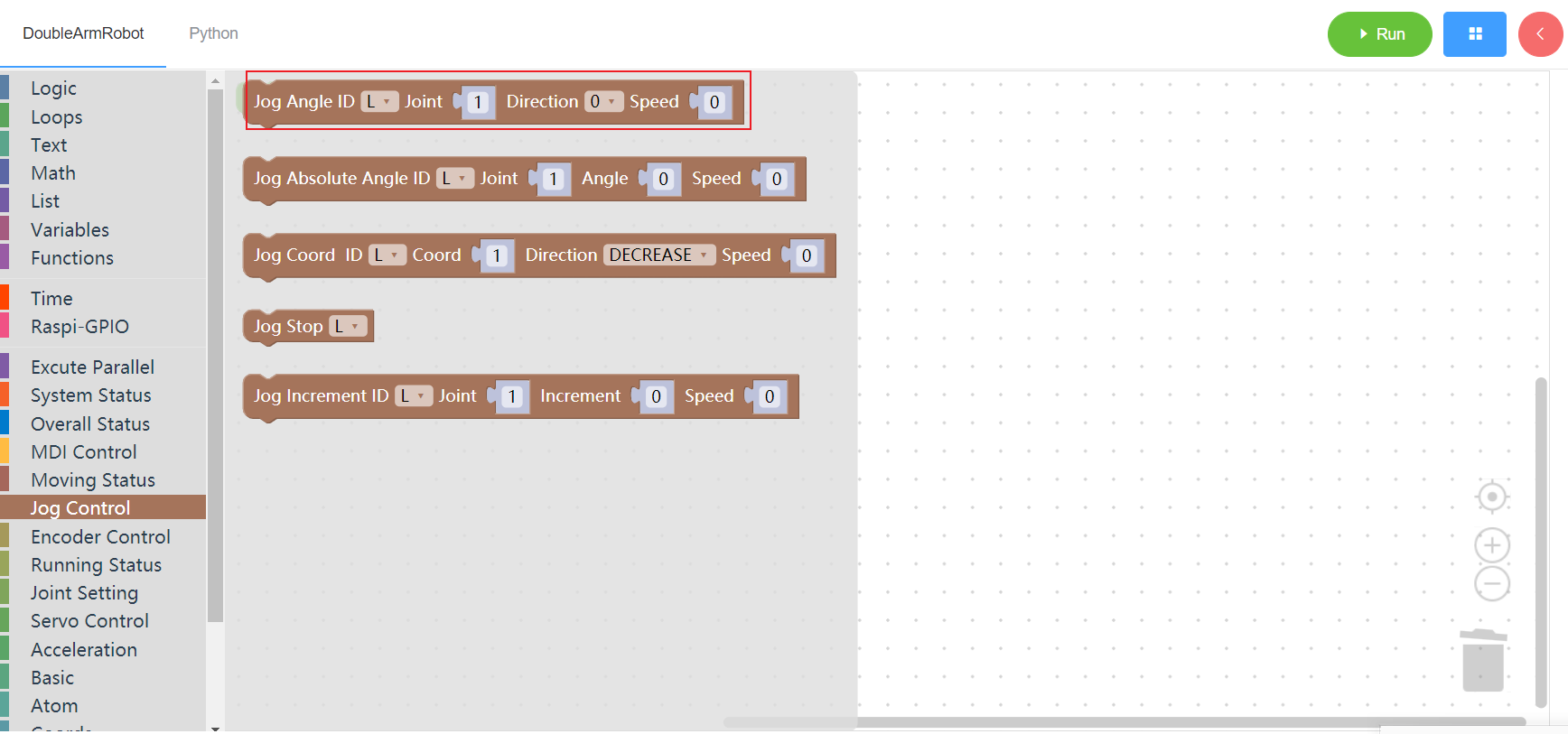
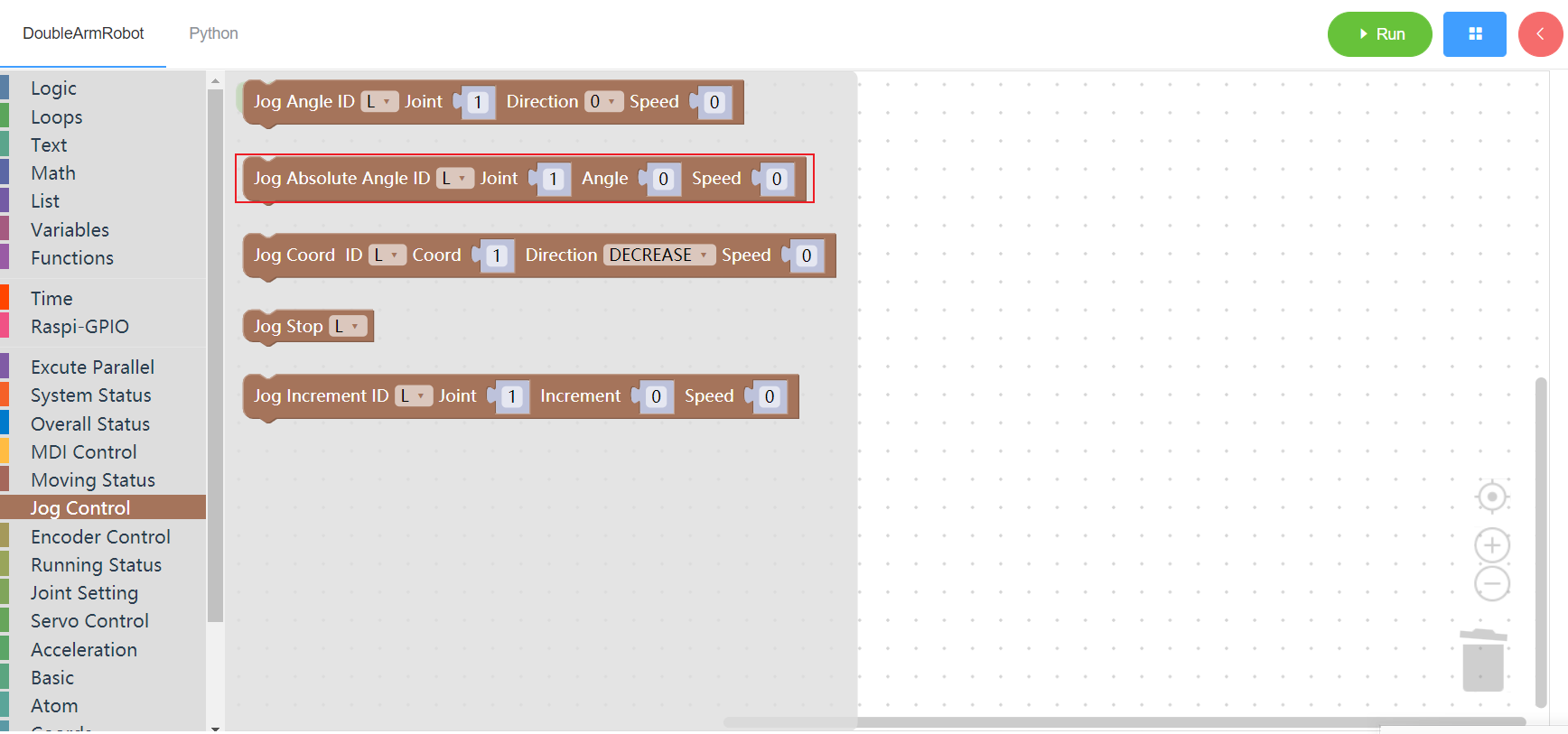
3.5.2 Jog absolute
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Jog absolute
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint id,1~6AGNLE:angleSPEED:speed(0~100)
Return :none
2.Block display
3.5.3 Jog coordinate
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Jog coordinate
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistCOORD:coordinate 1~6(x/y/z/rx/ry/rz)DIRECTION:0-decrease 1-increaseSPEEDspeed (0~100)
Return :none
2.Block display
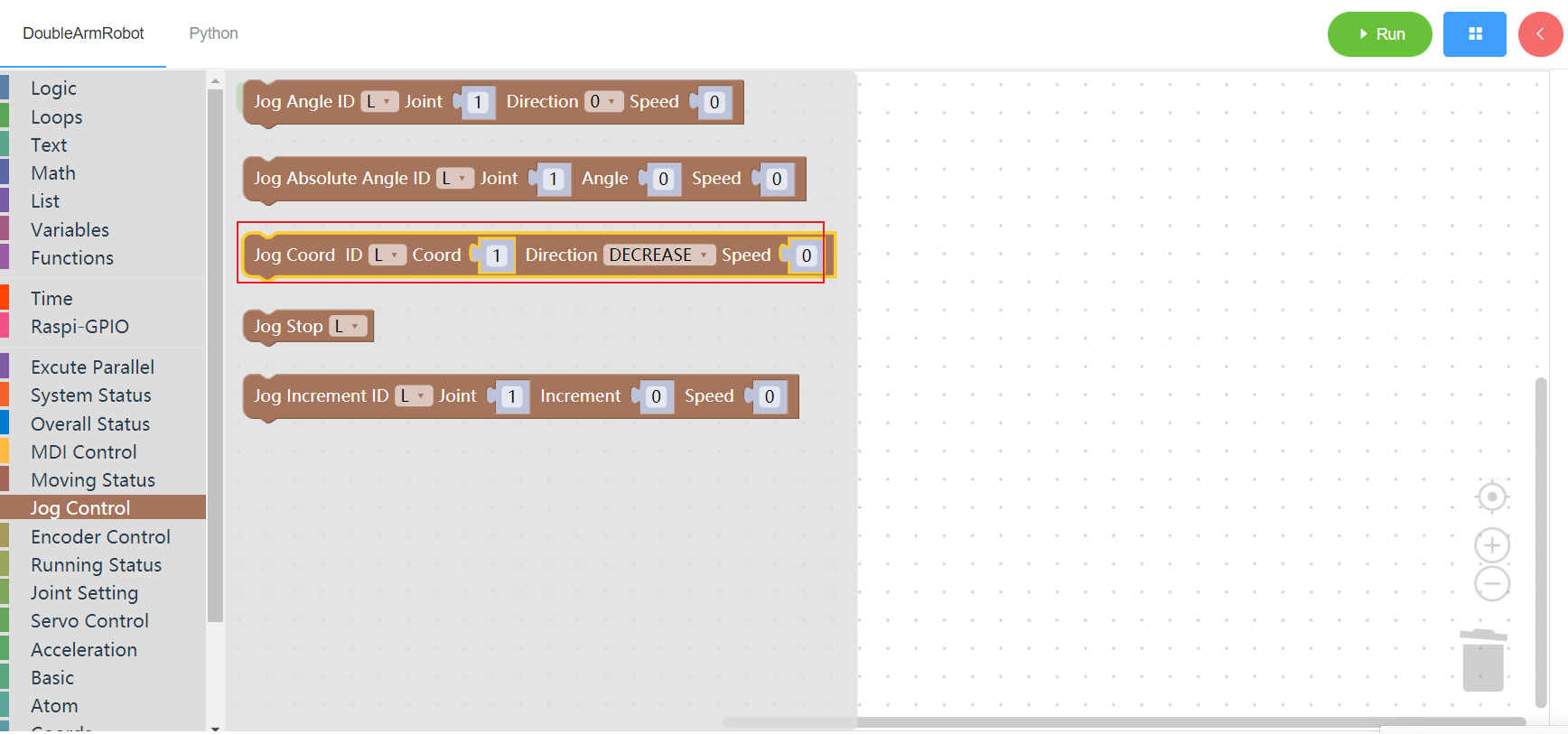
3.5.4 Jog stop
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Jog stop
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
Return :none
2.Block display
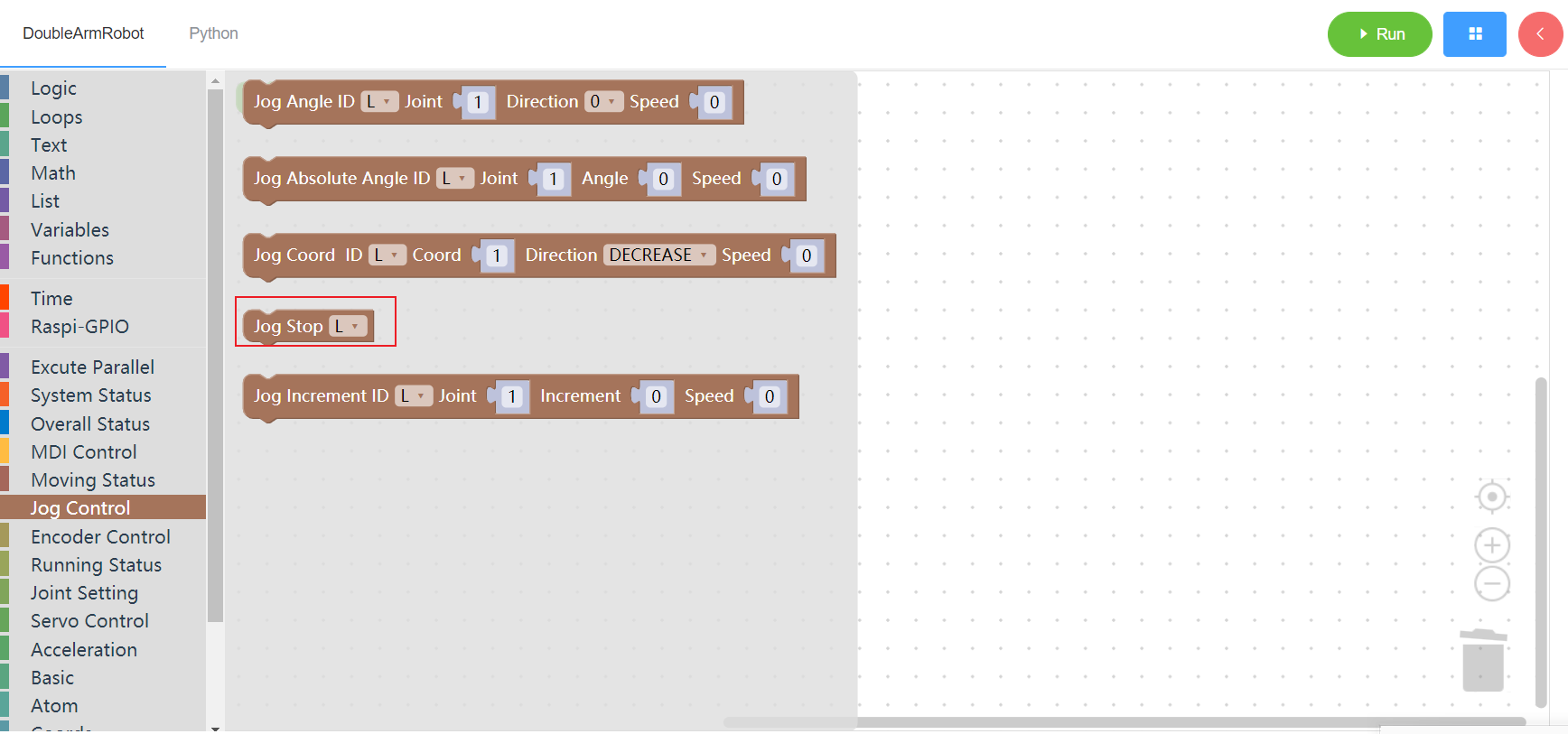
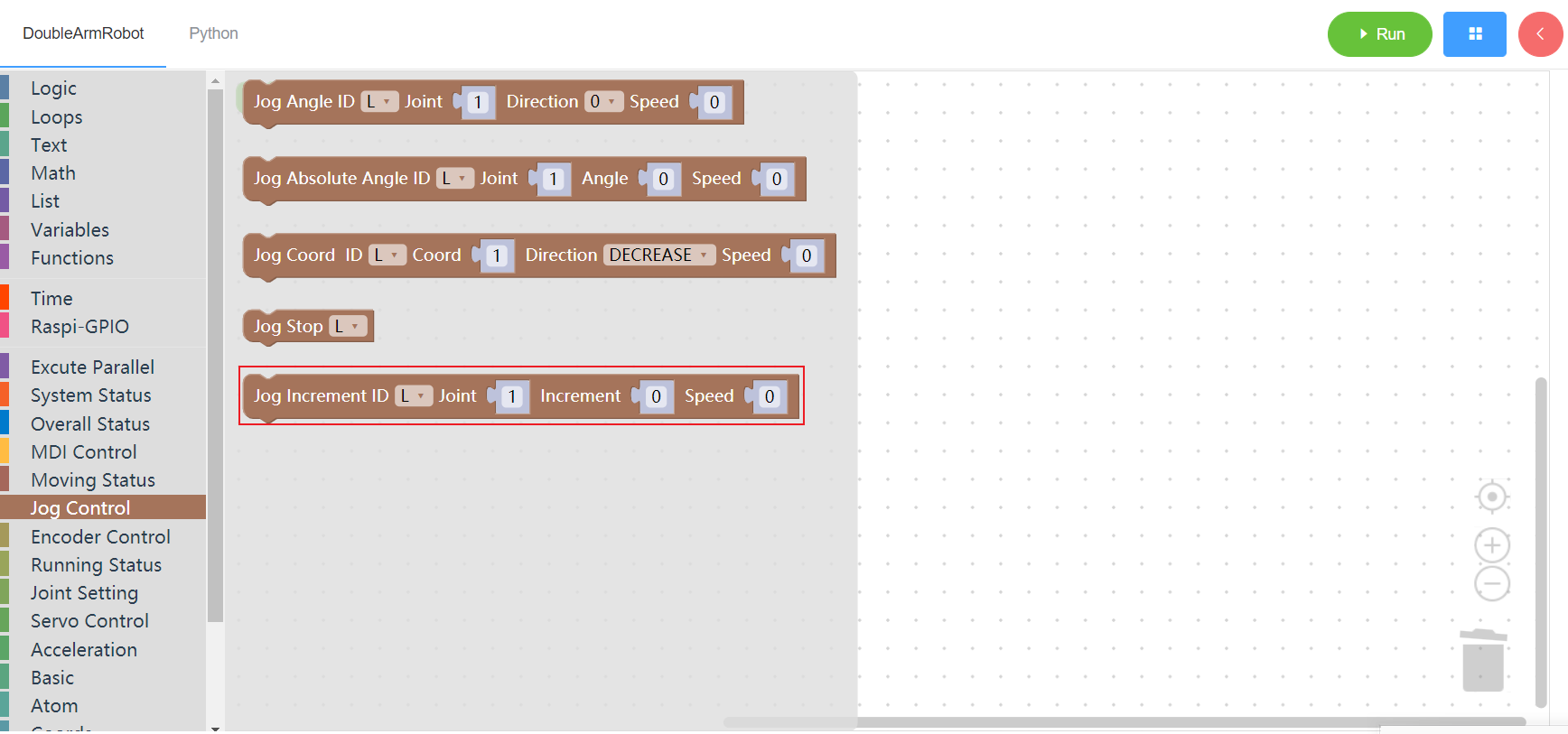
3.5.5 Jog increment
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set jog increment
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint id(1~6)INCREMENTincrement (integer)SPEEDspeed (0~100)
Return :none
2.Block display
3.6 Encoder
3.6.1 Set encoder
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the potentiometer code of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint 1~6ENCODER:value (integer)
Return :none
2.Block display

3.6.2 Get encoder
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Obtain the potentiometer code of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint 1~6
Return :
ENCODER: value(0 ~ 4096)
2.Block display
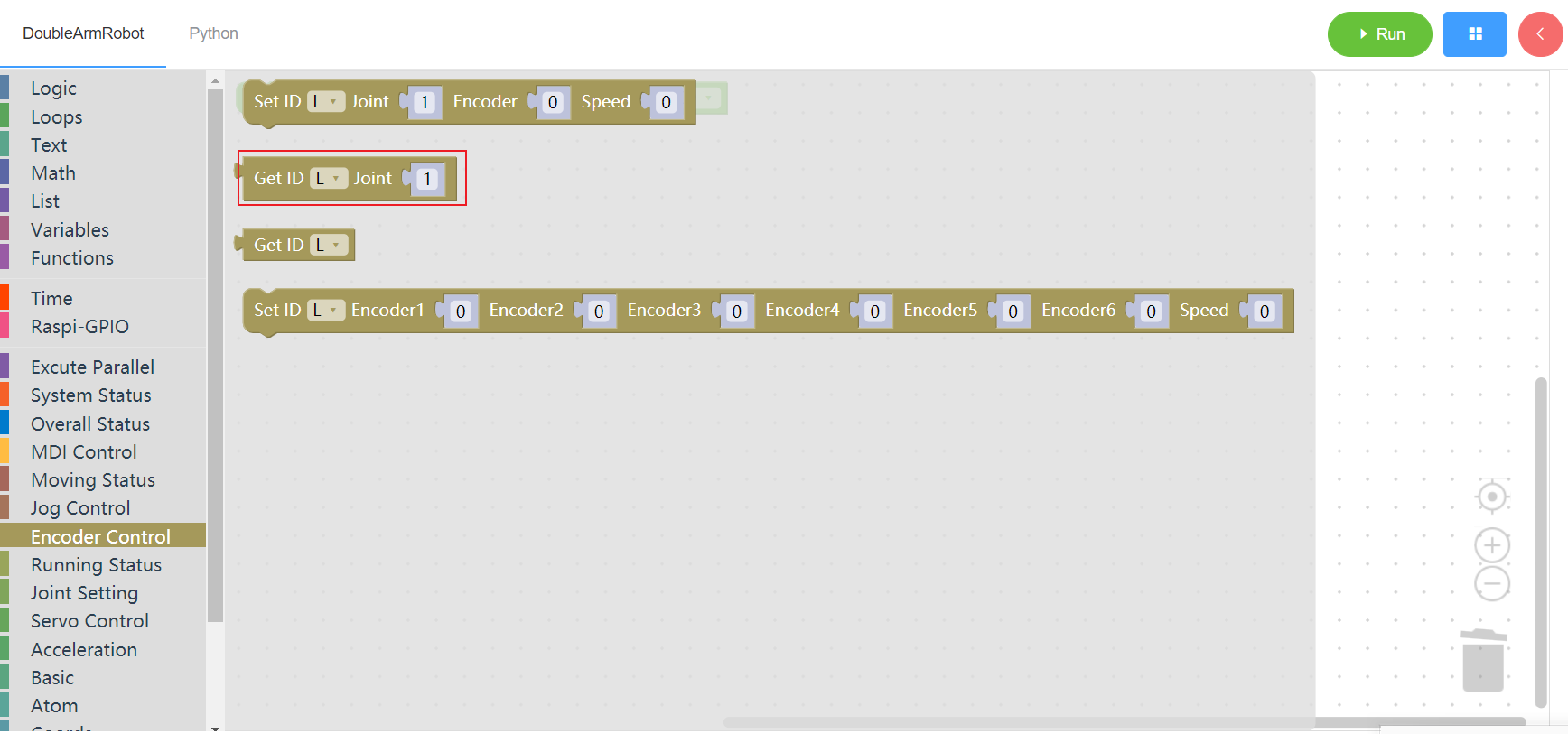
3.6.3 Get encoders
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Obtain all potentiometer codes of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right arm
Return :
ENCODERS: encoders list
2.Block display

3.6.4 Set encodes
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Obtain all potentiometer codes of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armENCODERS:encodes list(lenth 6)SPEEDspeed(0~100)
Return :none
2.Block display
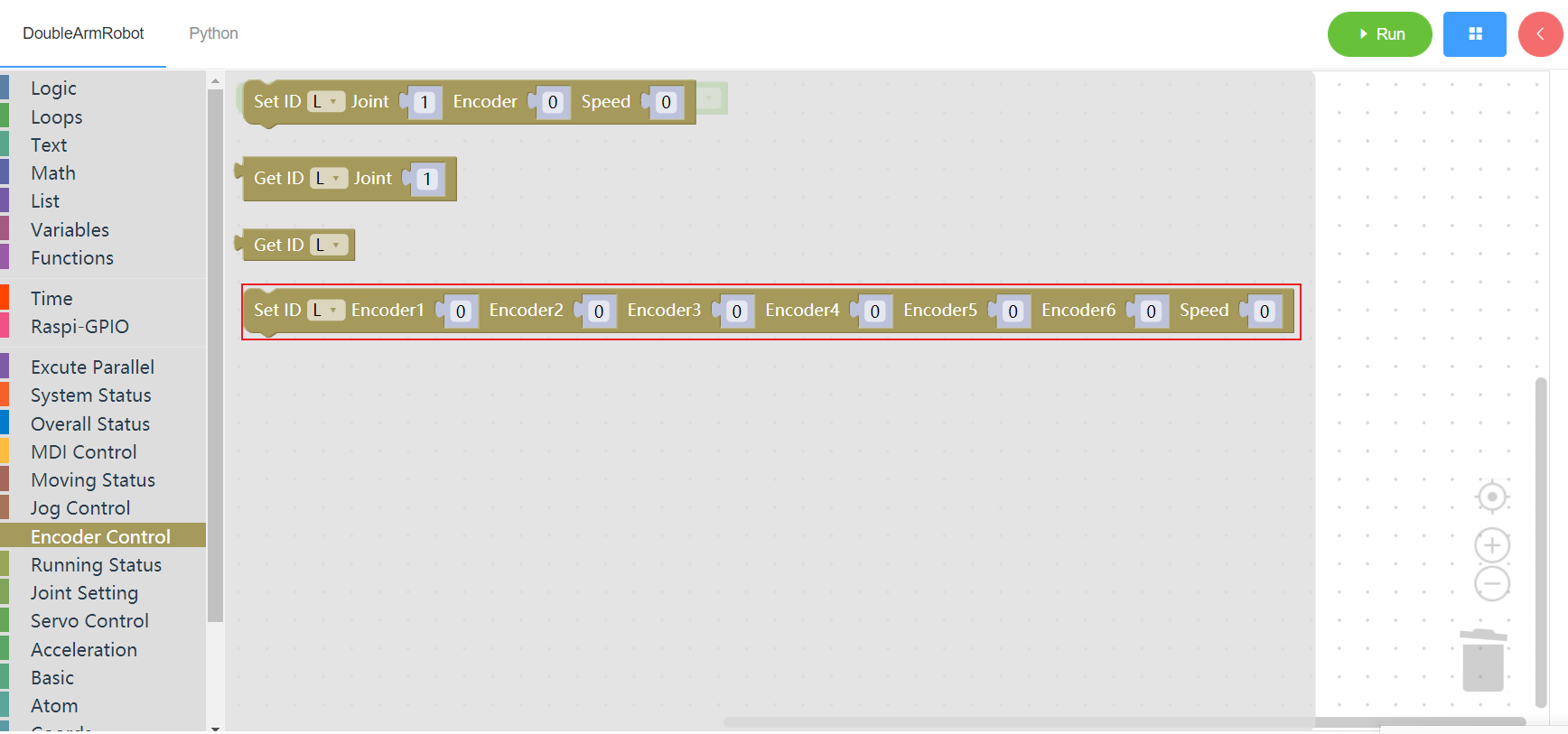
3.7.1 Running status
3.7.1 Get speed
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get the speed of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
Return :
SPEEDspeed(0~100)
2.Block display
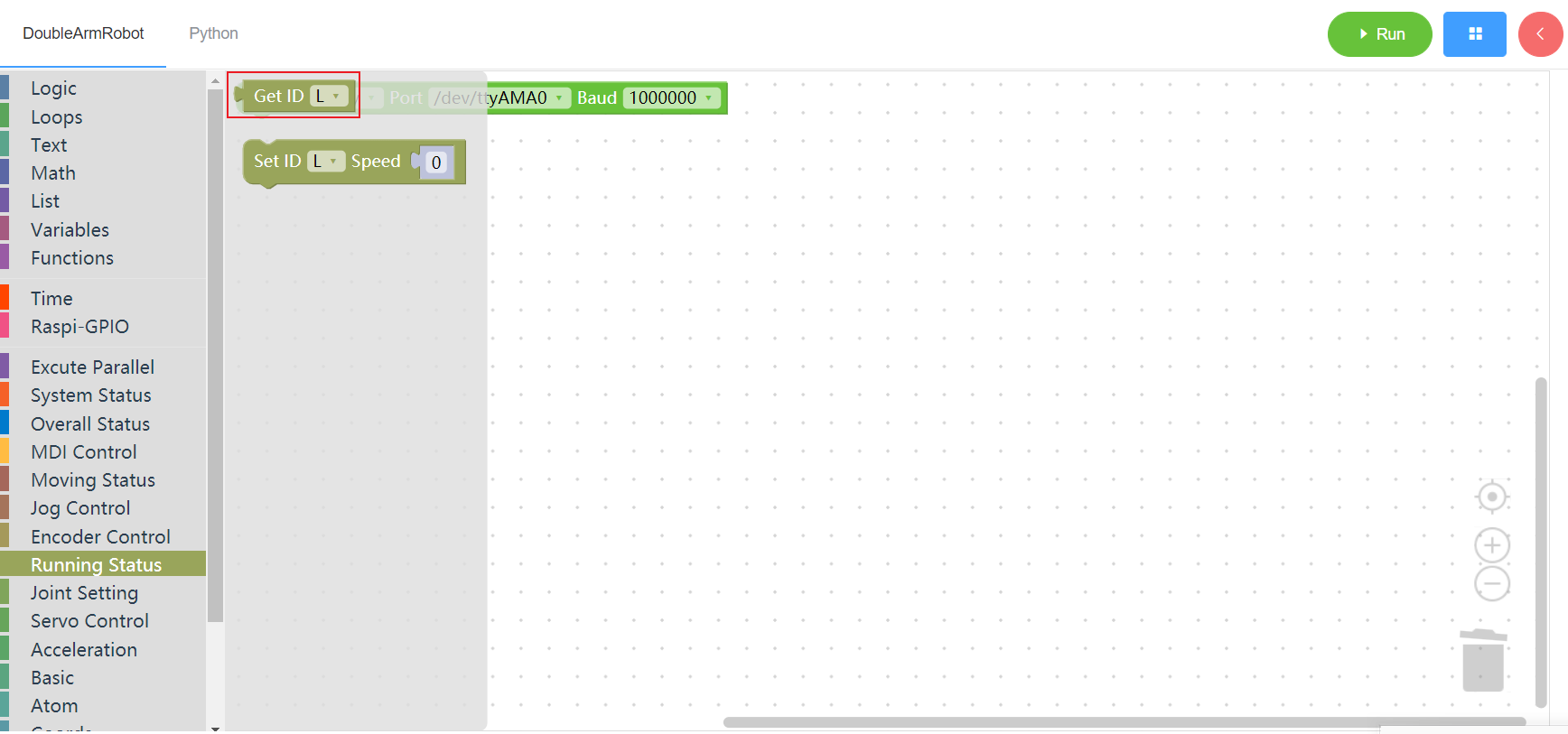
3.7.2 Set speed
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the speed of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistSPEED:speed(0~100)
Return :none
2.Block display
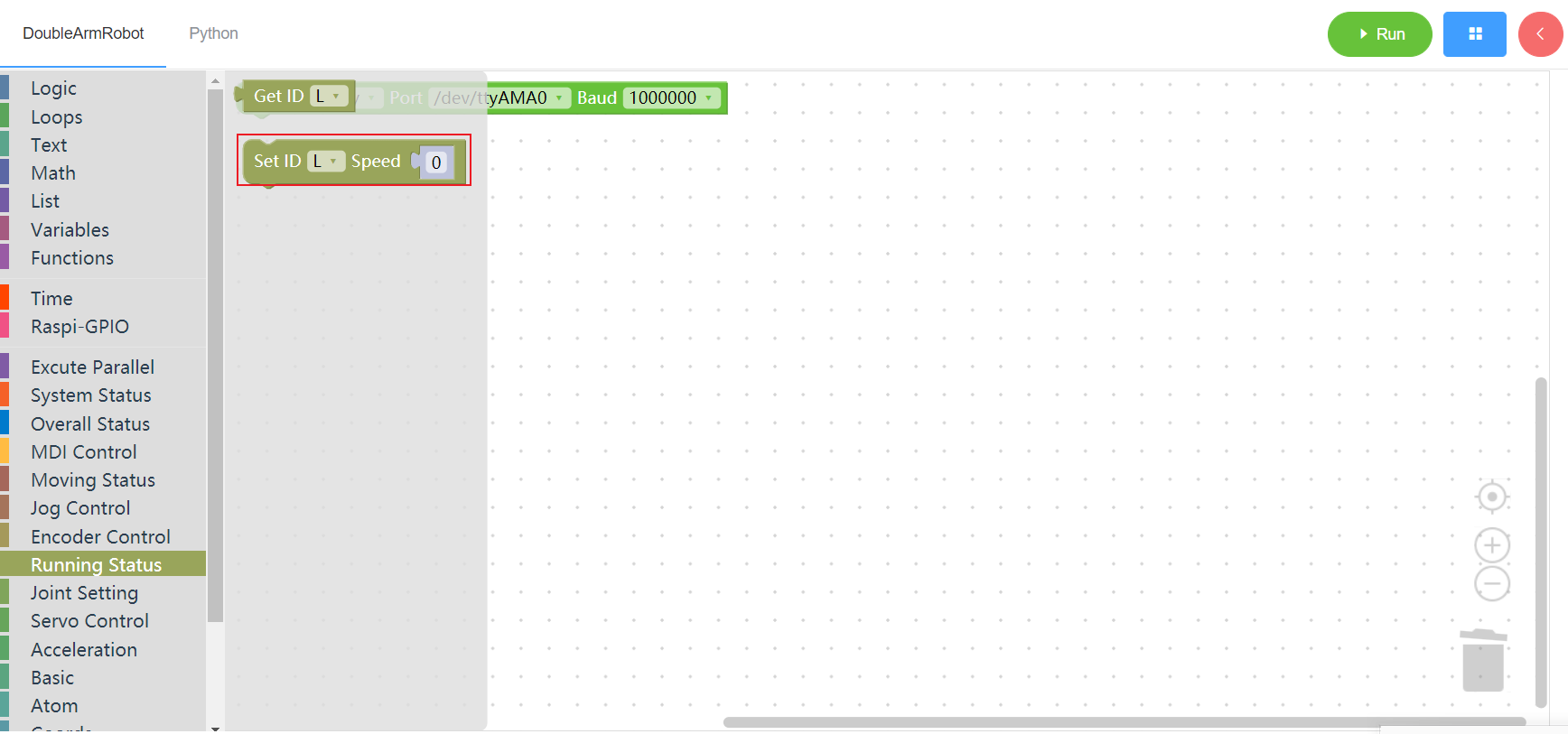
3.8 Joint limit
3.8.1 Read the minimum joint Angle
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Read the minimum joint Angle of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint id(1~6)
Return :
ANGLE:angle
2.Block display
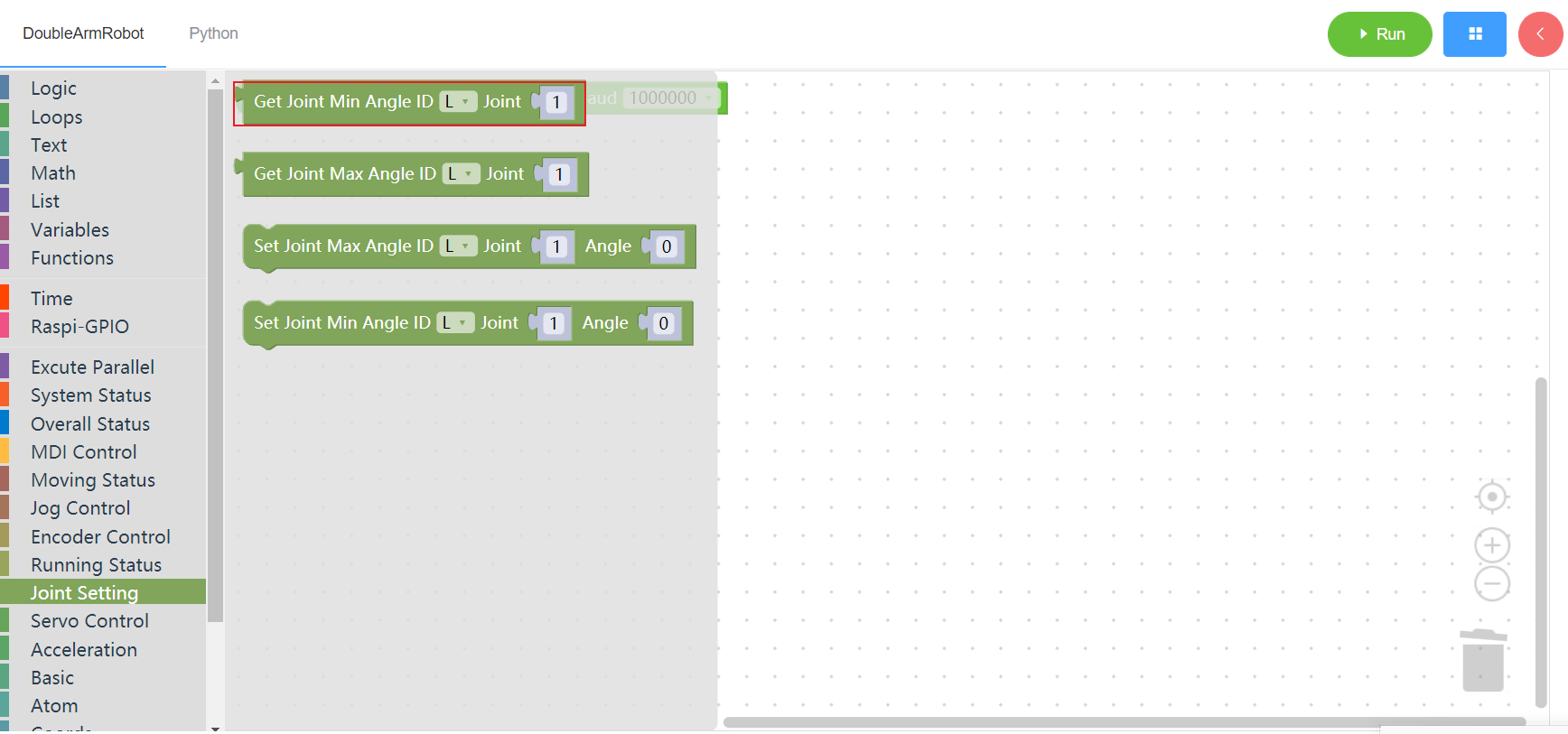
3.8.2 Read the maximum joint Angle
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Read the maximum joint Angle of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint id(1~6)
- Return :
ANGLE: angle
2.Block display
3.8.3 Set the maximum joint Angle
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the maximum joint Angle of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint id(1~6)ANGLE: angle
- Return :none
2.Block display
3.8.4 Set the minimum joint Angle
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the minimum joint Angle of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint id(1~6)ANGLE:angle
- Return :none
2.Block display
3.9 Servo settings
3.9.1 Joint state
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Check whether the specified joint of the manipulator is connected
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistSERVOID:servo id(1~6)
- Return :
- 0 disenable
- 1 enable
- -1 error
2.Block display
3.9.2 Status of all joint connections
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Check whether all joints of the manipulator are connected
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :
- 0 disenable
- 1 enable
- -1 error
2.Block display
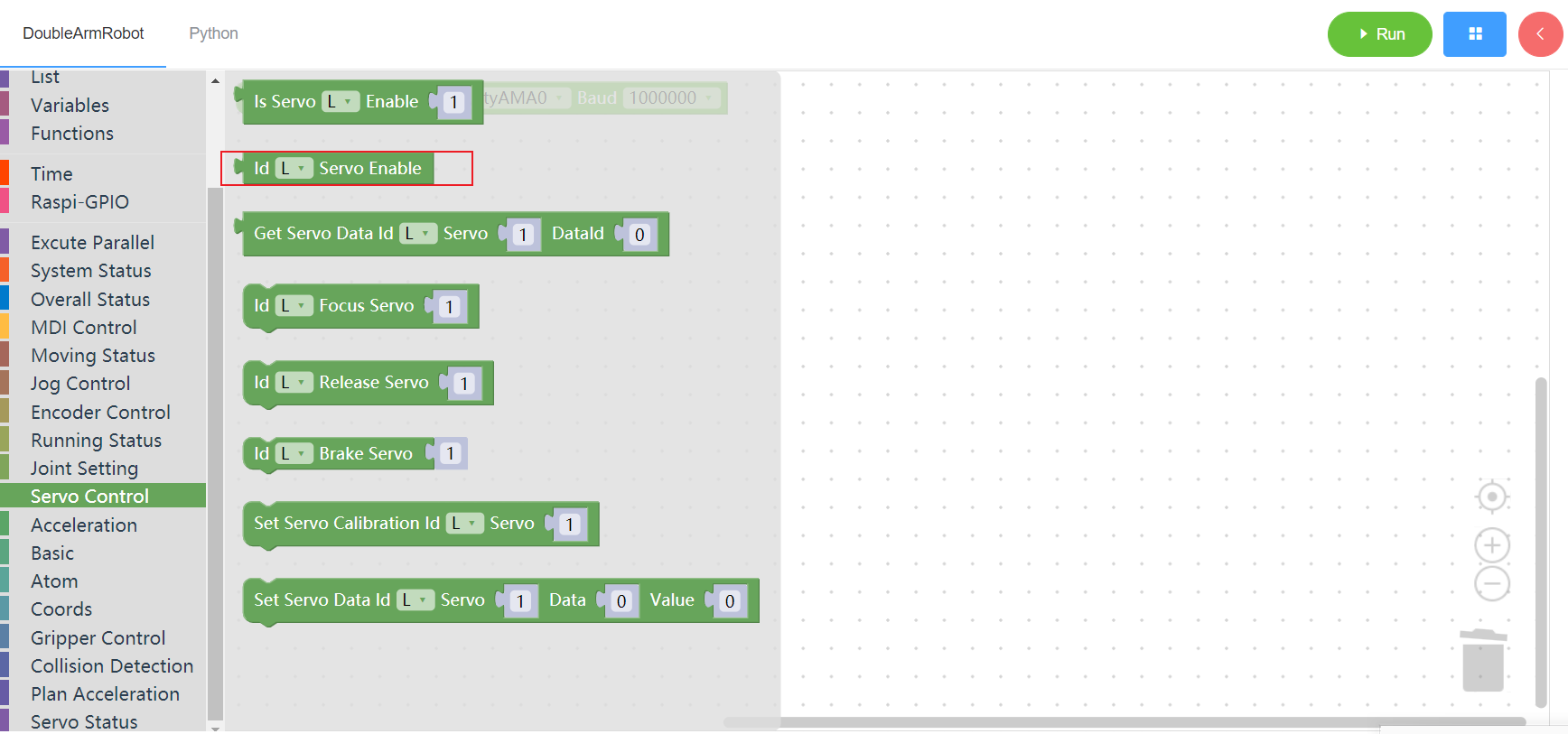
3.9.3 Get servo data
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get servo data of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistSERVOID:servo id(1~6)DATA_ID: address
- Return :
- 0 disenable
- 1 enable
- -1 error
2.Block display
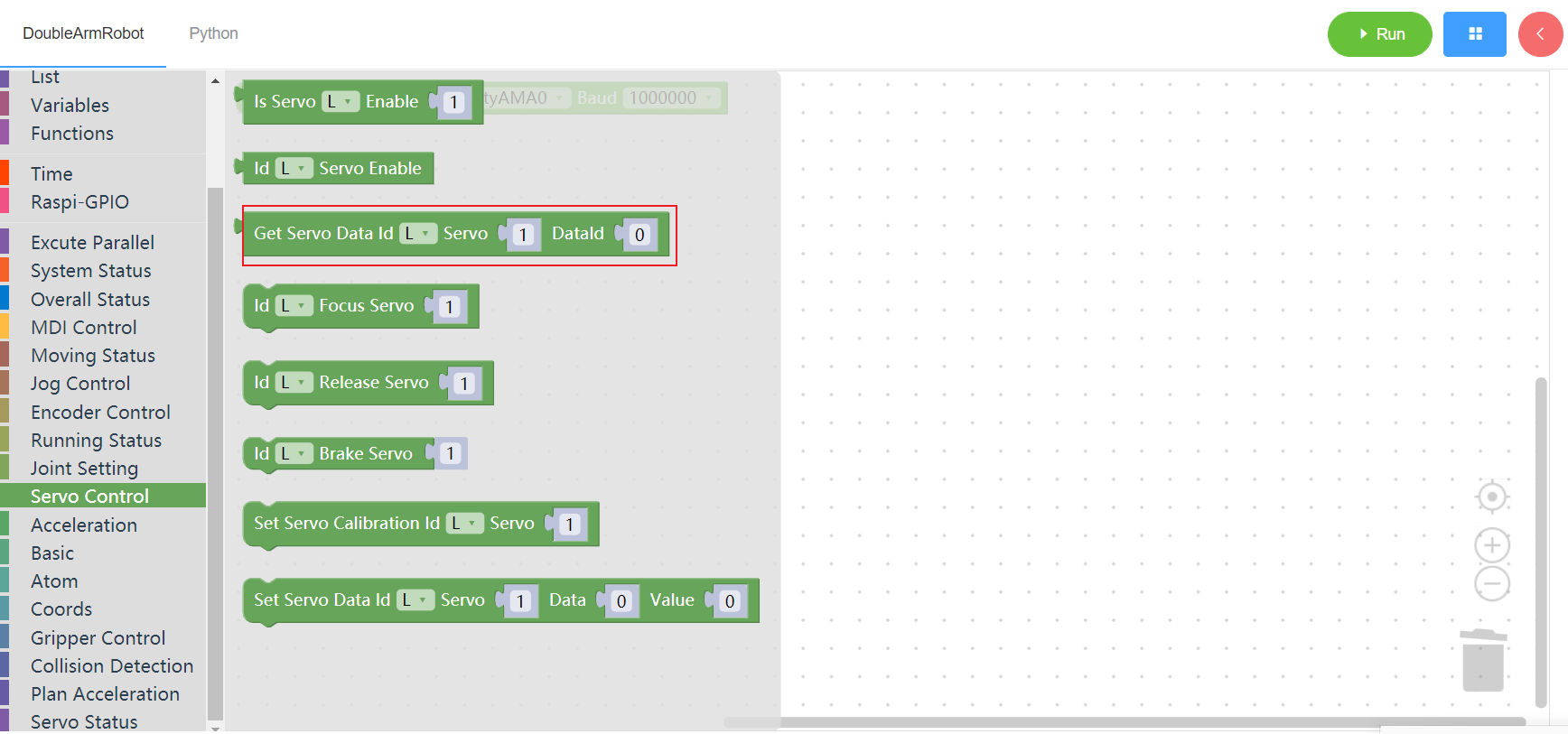
3.9.4 Power on a single motor
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Power on a single motor of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistSERVOID:servo id(1~6)
- Return :none
2.Block display

3.9.5 Power off a single motor
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Power off a single motor of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistSERVOID:servo id(1~6)
- Return :none
2.Block display
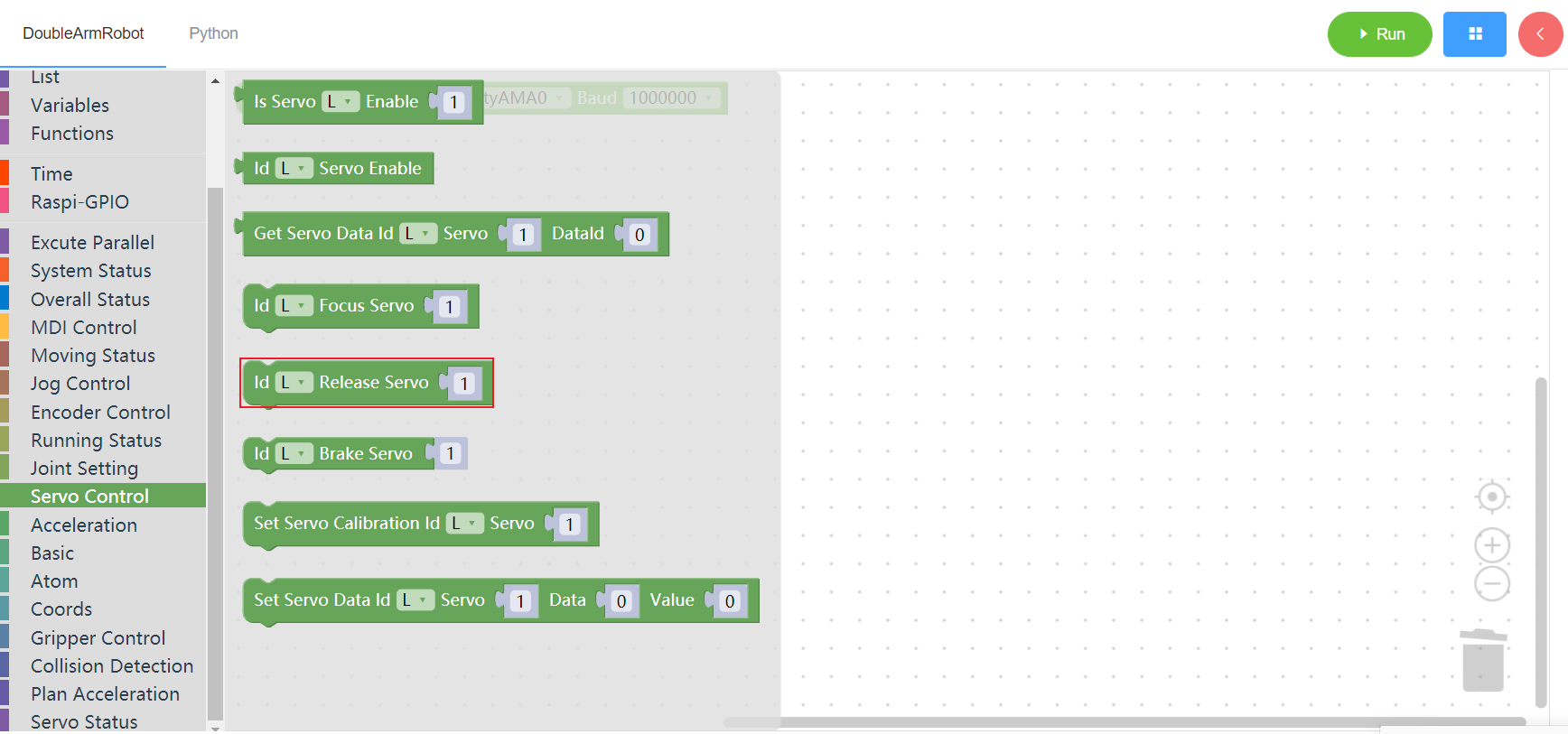
3.9.6 Single joint brake
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:The manipulator brakes on a single joint
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint id(1~6)
- Return :none
2.Block display
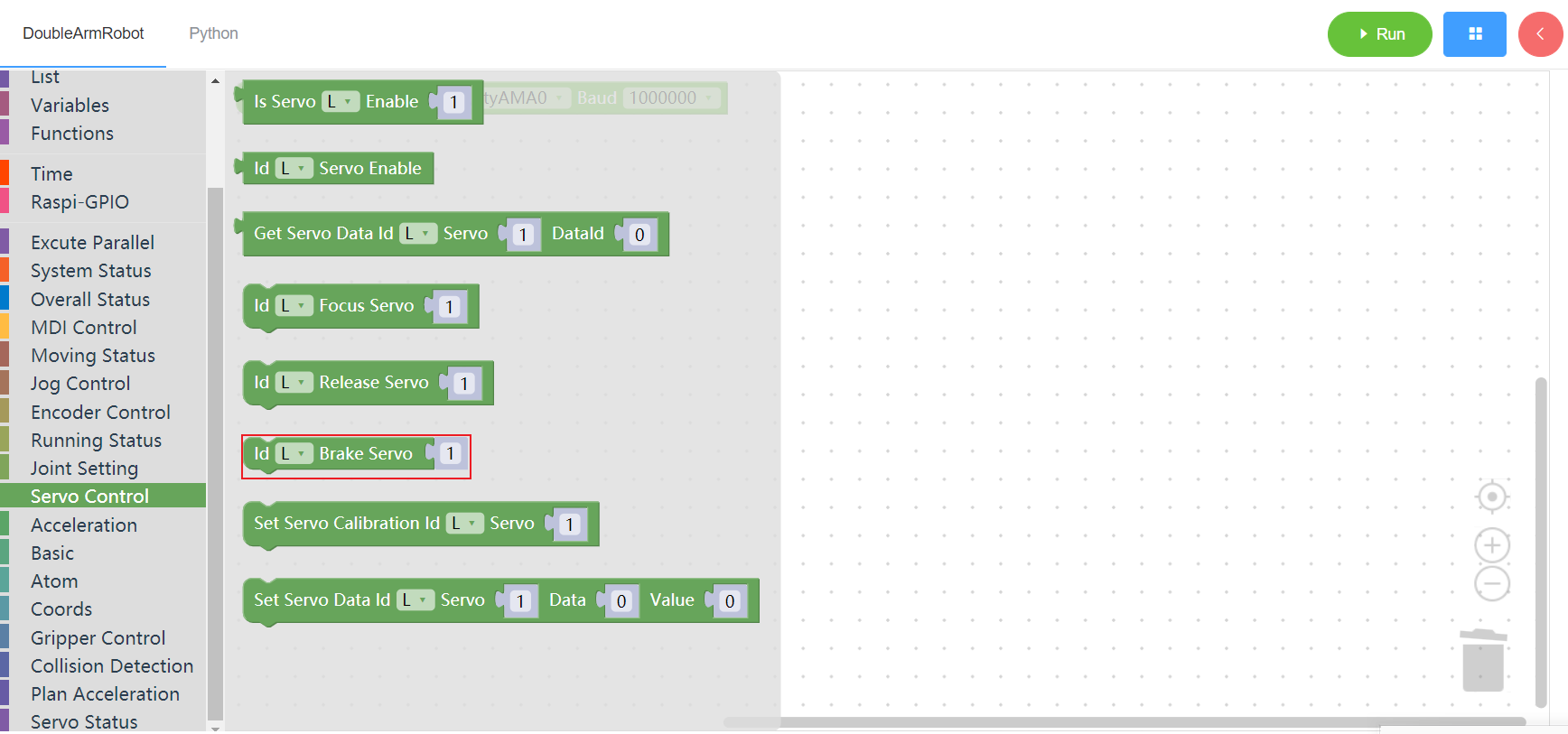
3.9.7 Set motor zero
1. Runtime API Reference
Function:Set motor zero
Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistJOINT:joint id(1~6)
- Return :none
2.Block display
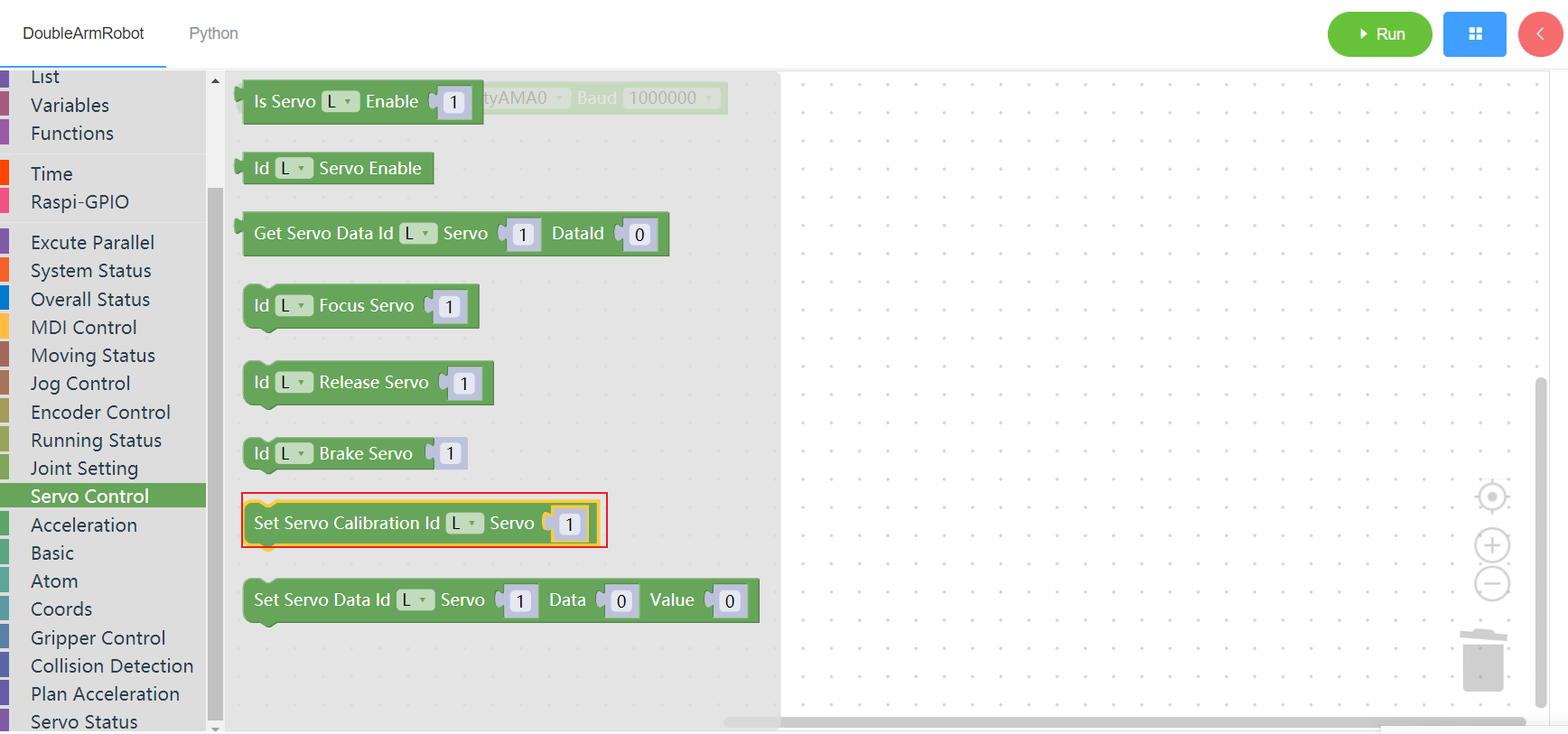
3.9.8 Set servo data
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set servo data
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistSERVO_ID:servo id(1~6)DATA: data addressVALUE:value
- Return :none
2.Block display

3.10 Acceleration settings
3.10.1 Get acceleration
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Read the acceleration of all movements
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :
SPEED:speed
2.Block display

3.10.2 Set movement acceleration
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set movement acceleration
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistACC:integer(1~100)
- Return :none
2.Block display

3.11 Basic
3.11.1 Get basic input
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get basic input
- Arguments:
PIN_NO:integer(0~20)
- Return :unknown
2.Block display
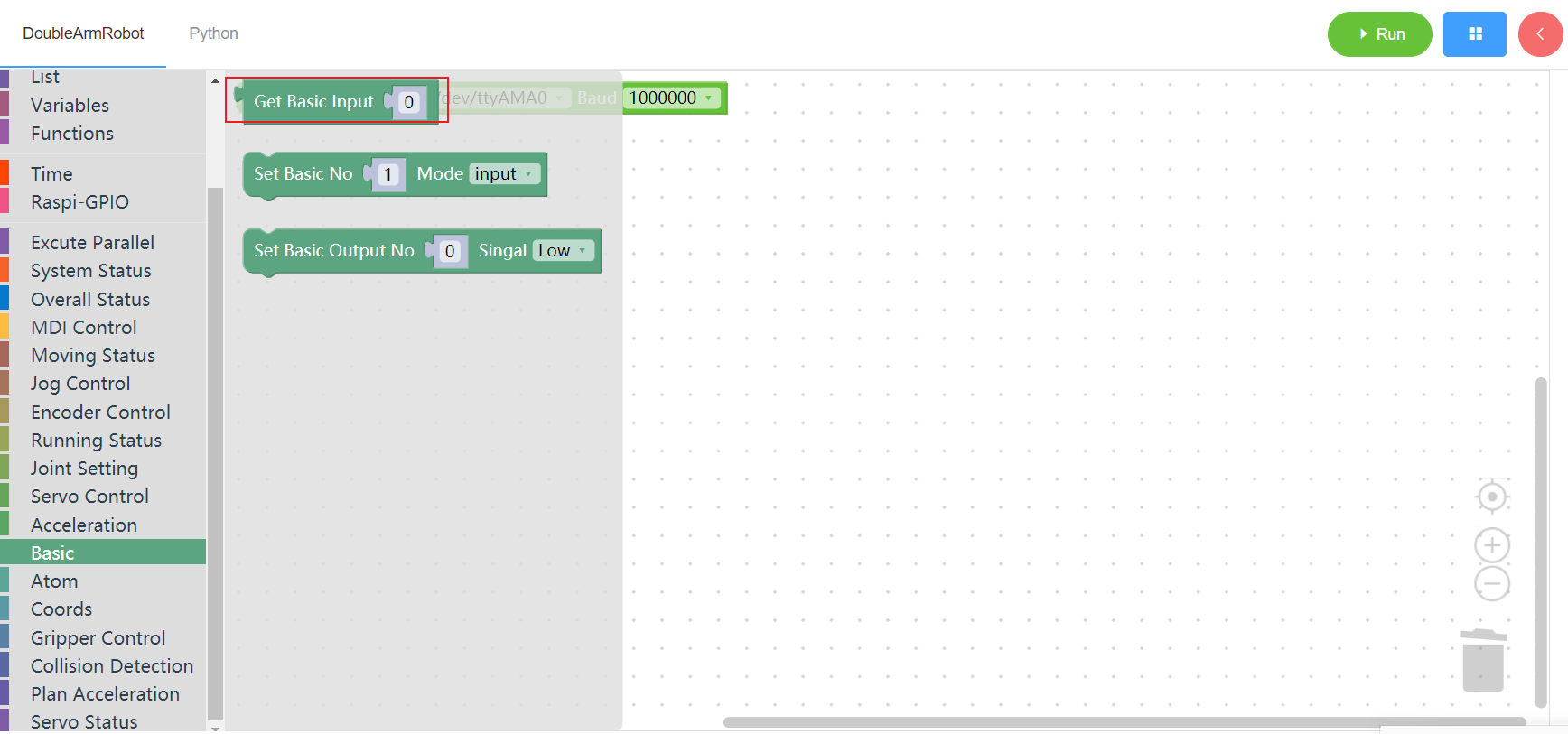
3.11.2 Set basic mode
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the base input/output mode
- Arguments:
PIN_NO:integer(1~5)PIN_MODE:input/output
- Return :none
2.Block display
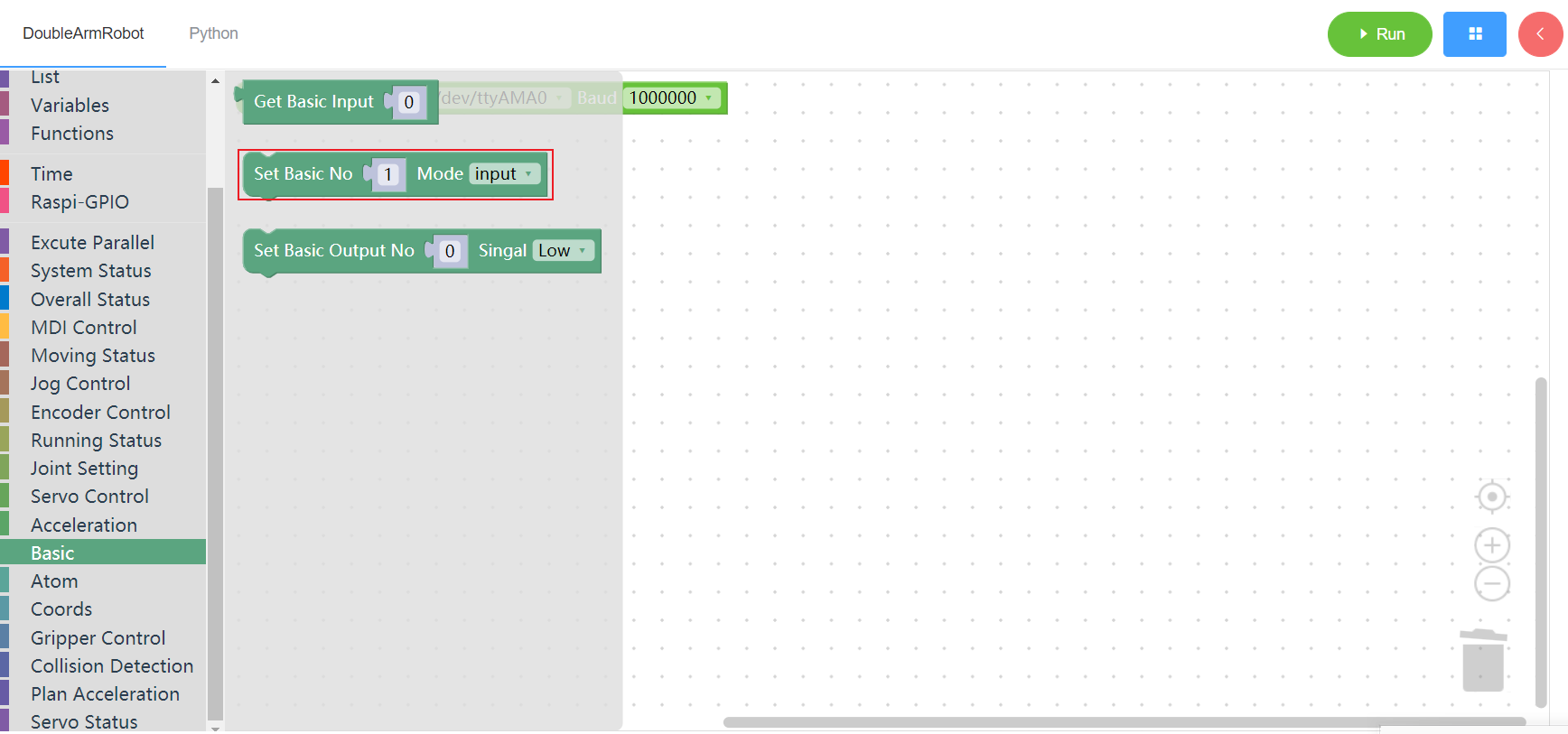
3.11.3 Set basic output
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set basic output
- Arguments:
PIN_NO:integer(0~20)PIN_SIGNAL:low/high
- Return :none
2.Block display

3.12 Atom
3.12.1 Get digital input
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get digital input
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armPIN_NO:integer(1~5)
- Return : singal value
2.Block display
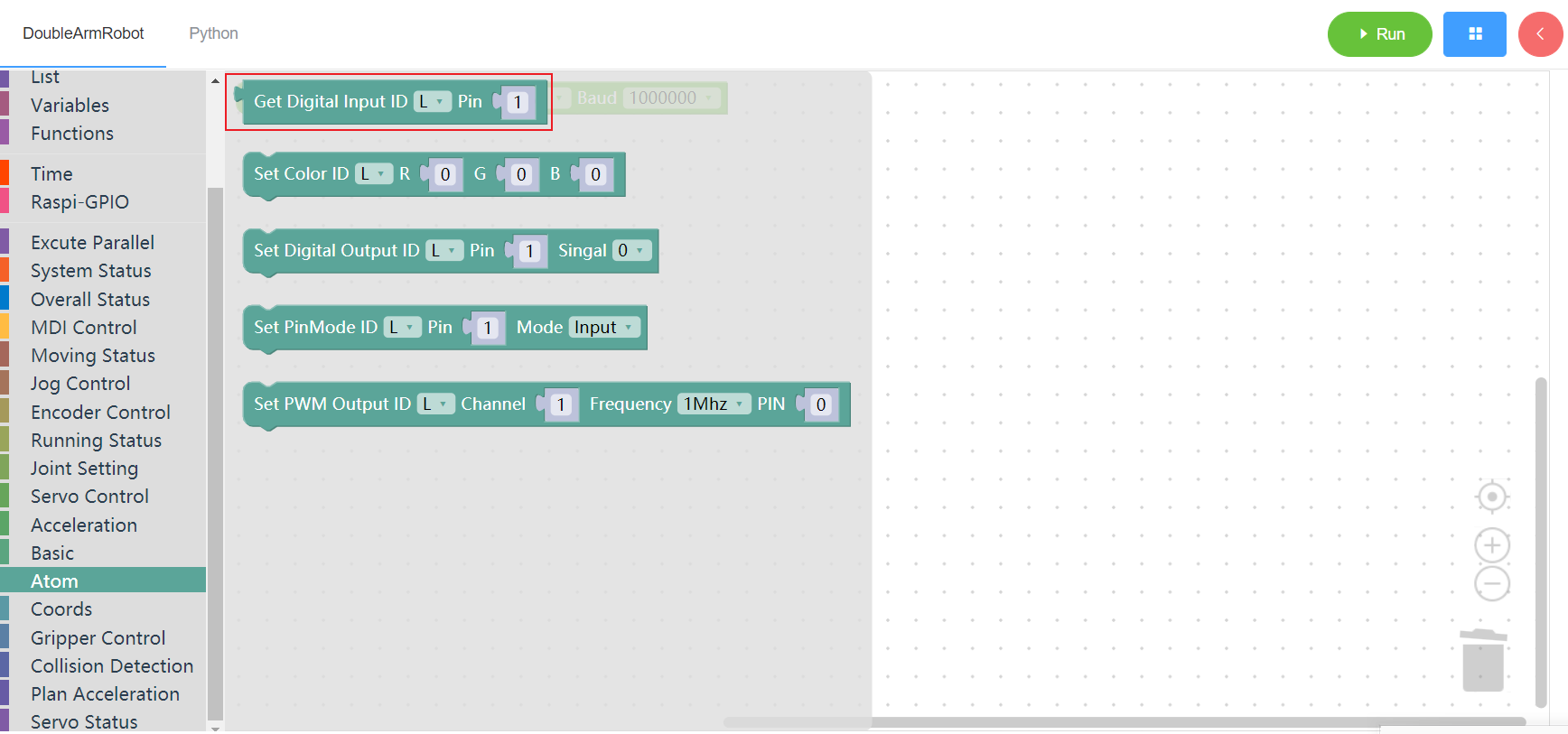
3.12.2 Set color
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the color of the arm at the top of the robot arm
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armRED:integer(0~255)GREEN: integer(0~255)BLUE: integer(0~255)
- Return :none
2.Block display
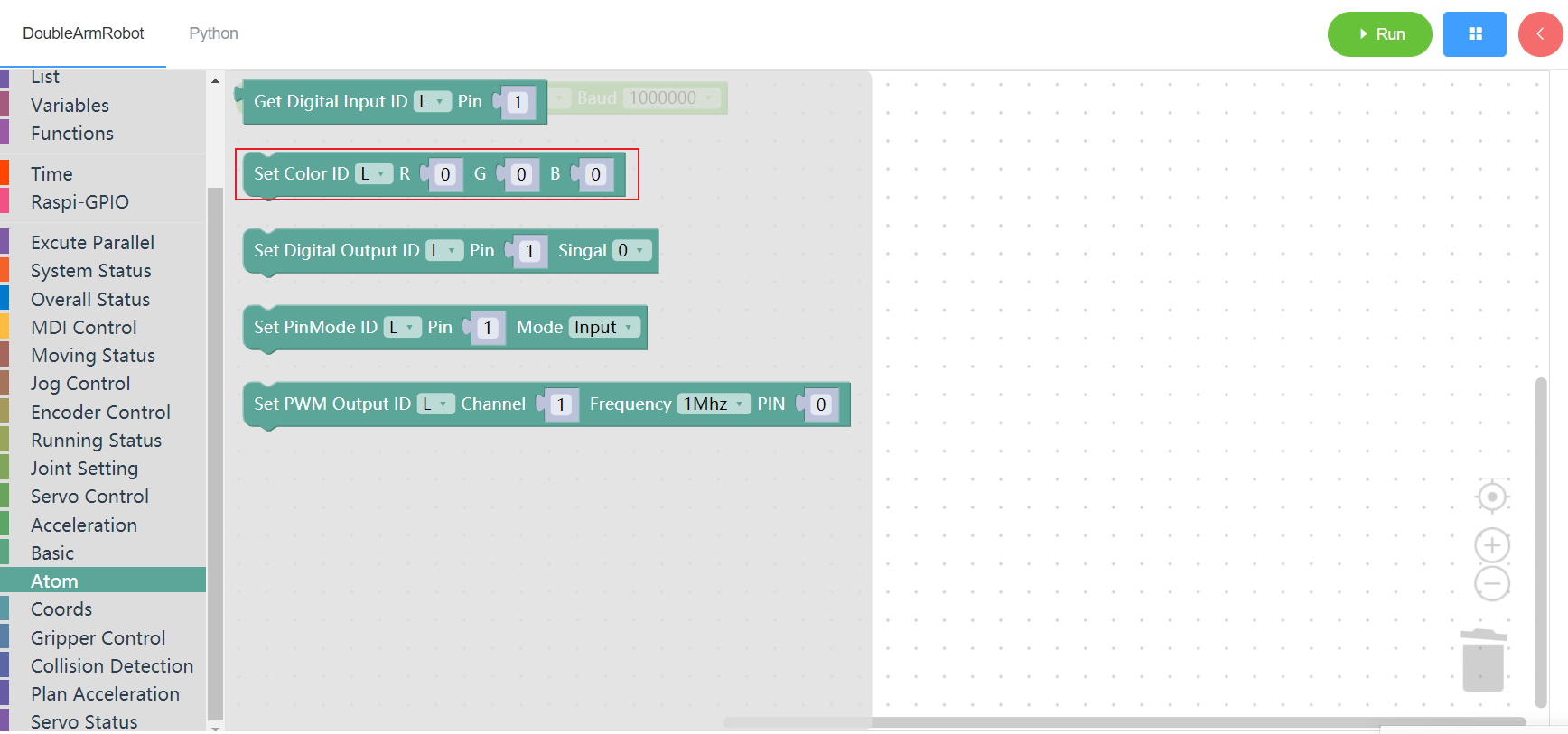
3.12.3 Set digital output
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set digital output
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armPIN_NO:integer(1~5)SIGNAL:0/1
- Return :none
2.Block display

3.12.4 Set PinMode
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Sets the state mode of the specified pin in the atom.
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armPIN_NO:integer(1~5)PIN_MODE:0 - input ,1-output
- Return :none
2.Block display
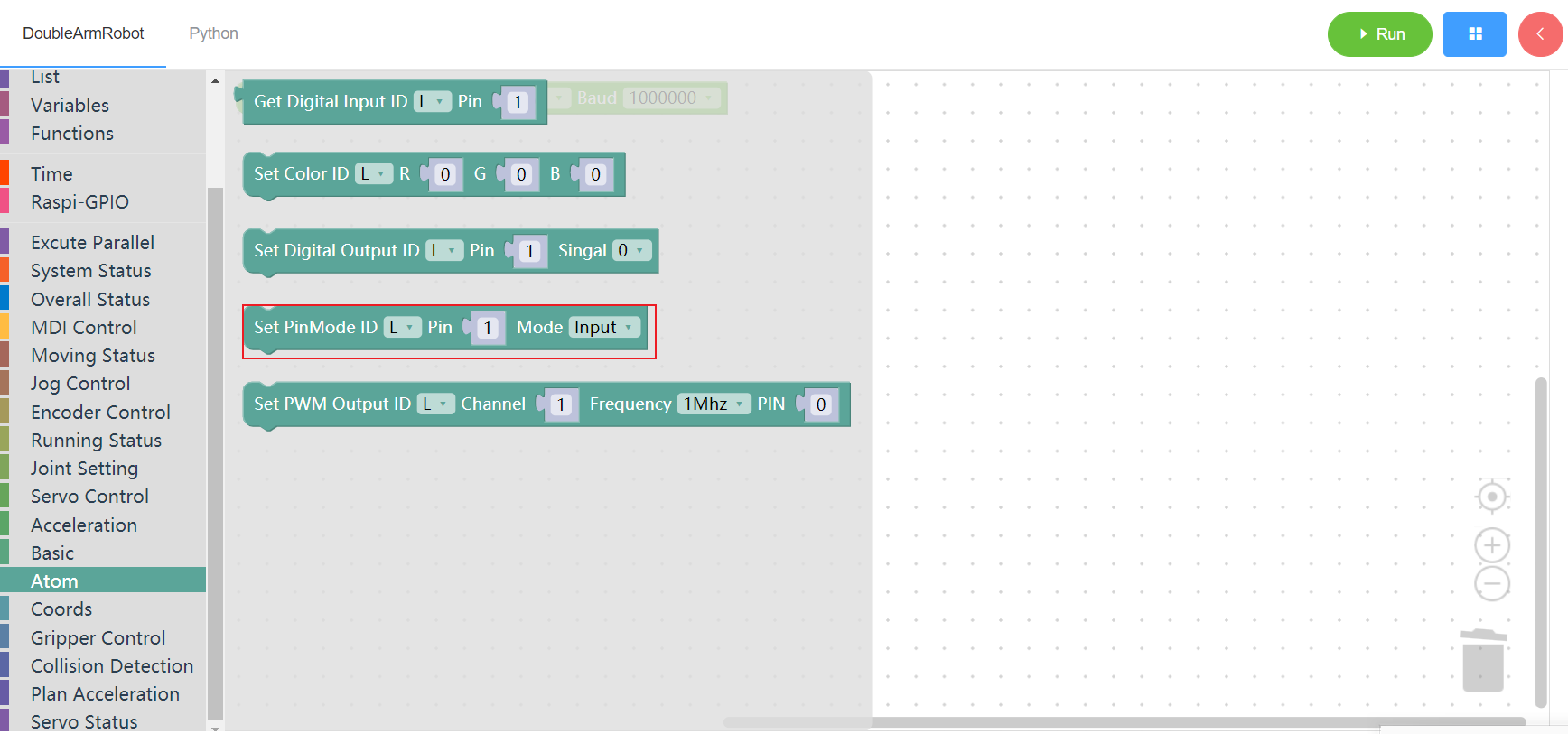
3.12.5 Set PWM output
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set PWM output
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armCHANNEL:integer(1~5)FREQUENCY:frequency 0 - 1Mhz ,1- 10MhzPIN_VAL:integer(0~100)
- Return :none
2.Block display

3.13 Coordinates
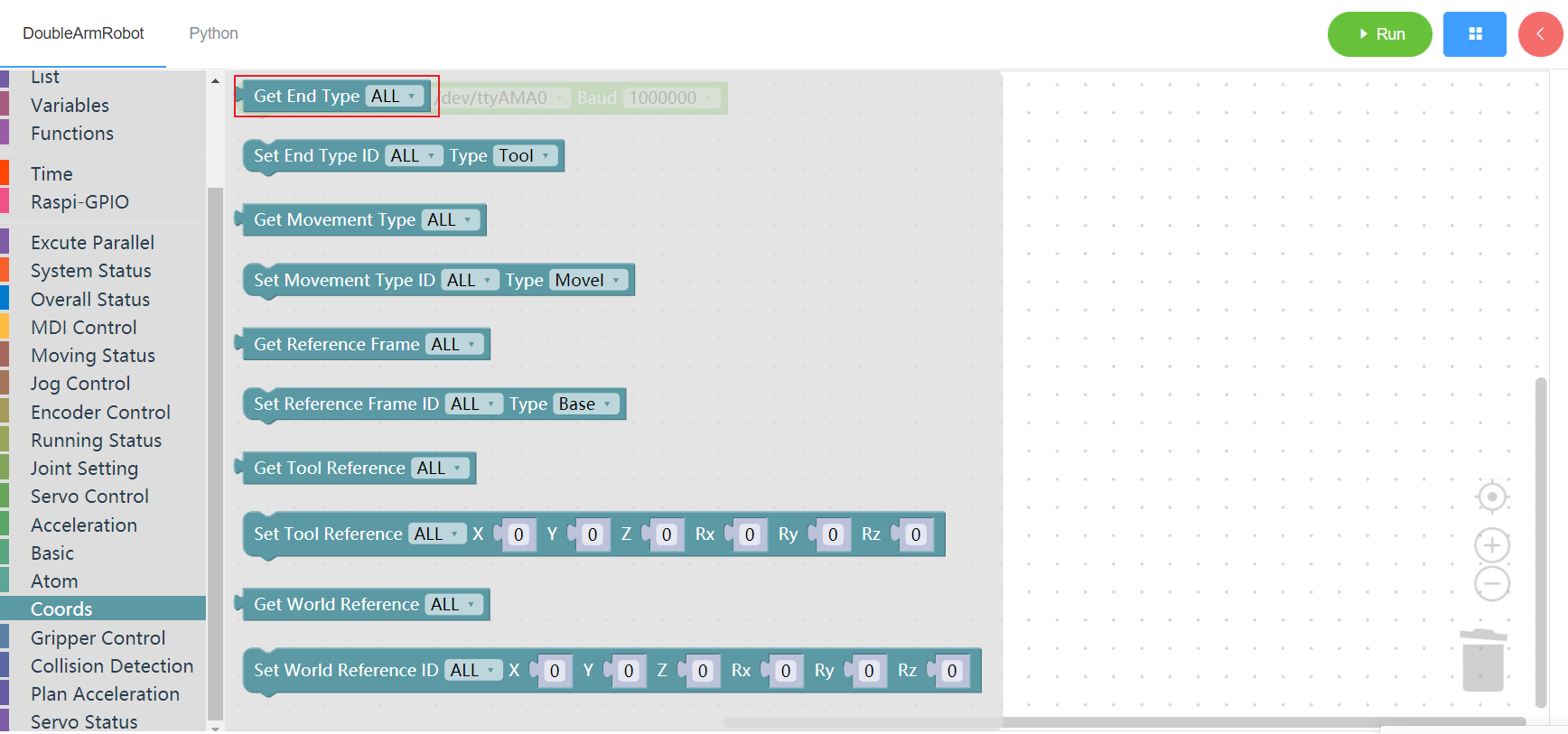
3.13.1 Get end coordinates system
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get end coordinates system
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm
- Return :
- 0 - flange,1 - tool
2.Block display
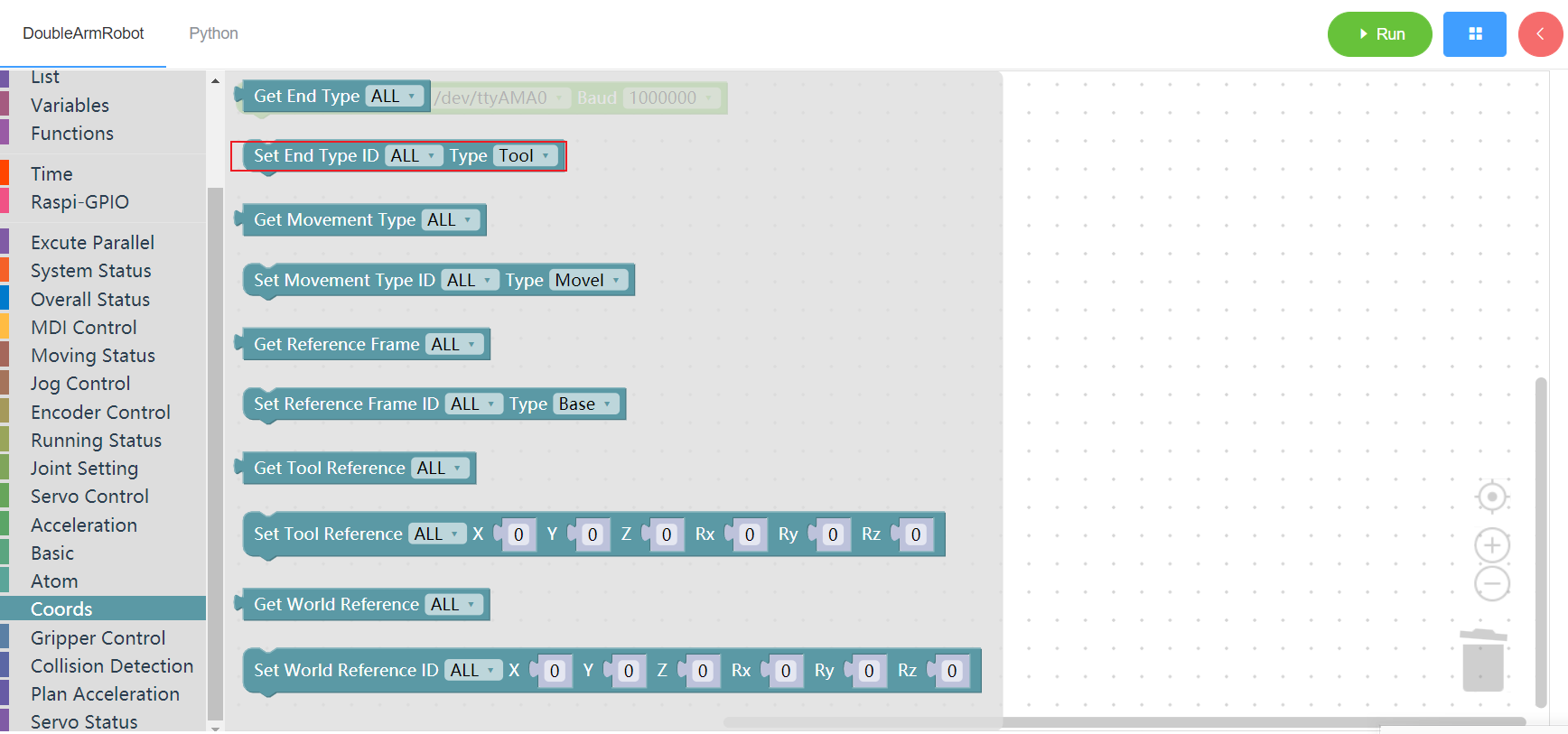
3.13.2 Set end coordinates system
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set end coordinates system
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right armEND:0 - flange ,1 - tool
- Return :none
2.Block display
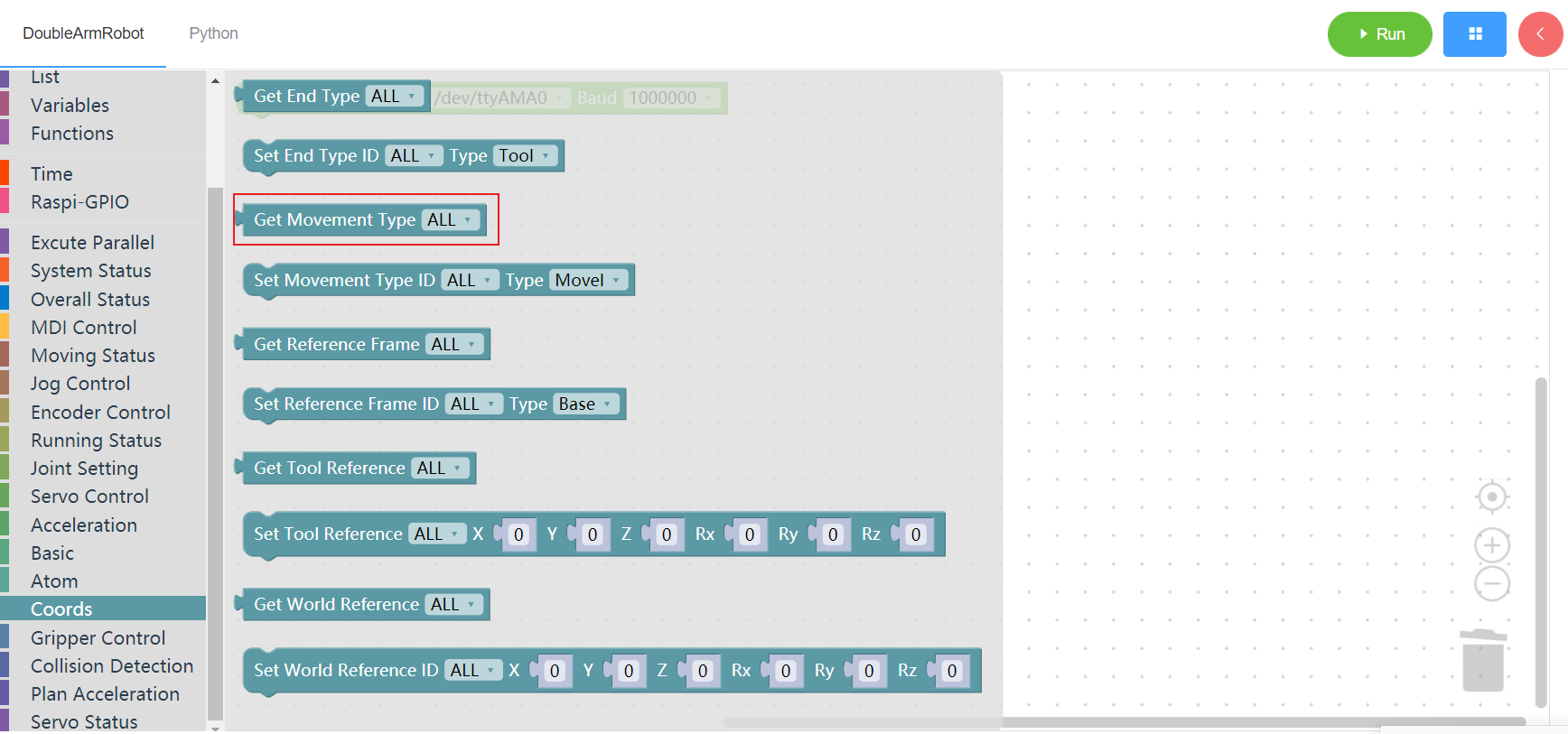
3.13.3 Get movement type
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get movement type
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm
- Return :
- 1 - movel , 0 - moveJ
2.Block display
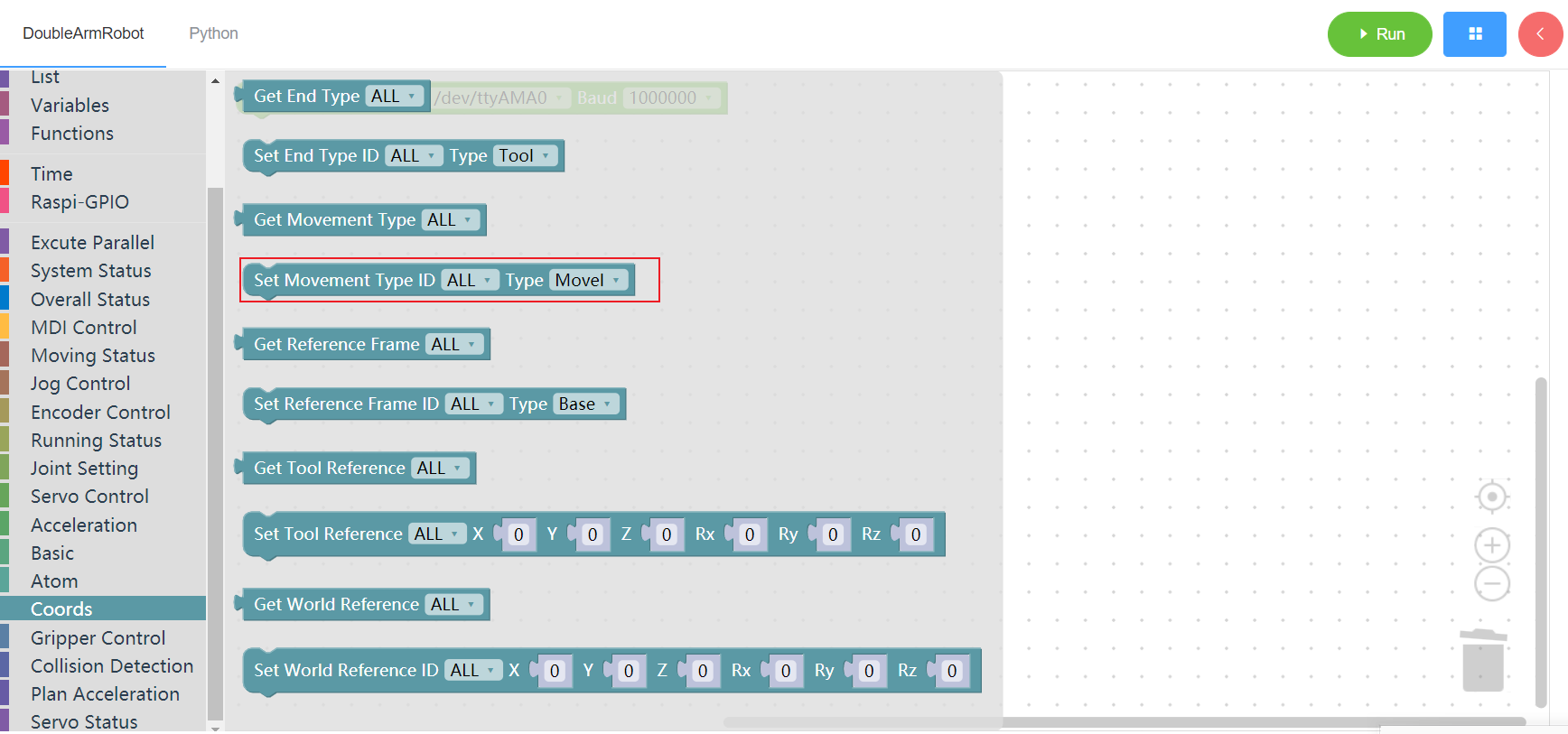
3.13.4 Set movement type
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set movement type
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right armTYPE:1 - movel , 0 - moveJ
- Return :none
2.Block display
3.13.5 Get basic coordinates system
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get basic coordinates system
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm
- Return :
- 0 - base , 1 - tool
2.Block display

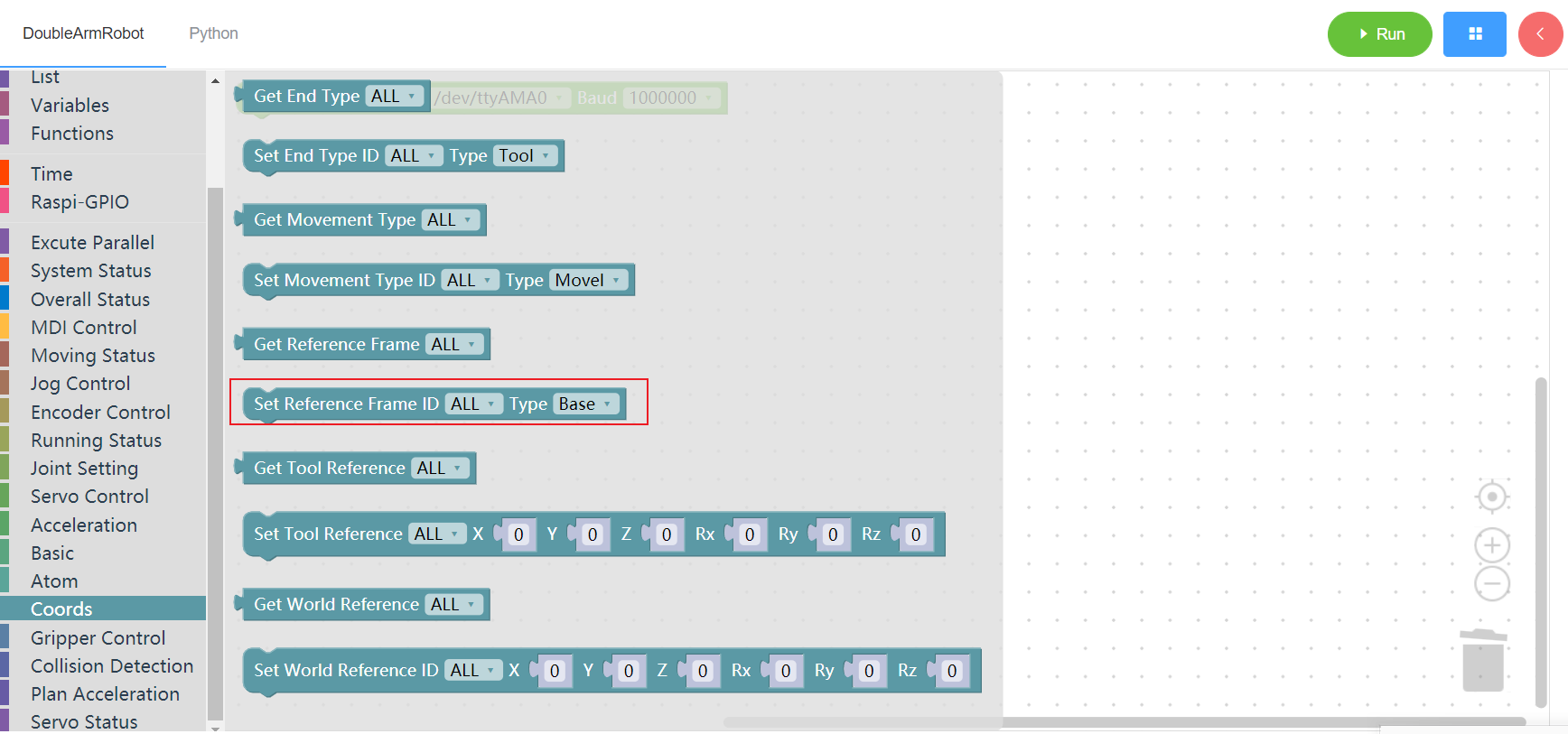
3.13.6 Set basic coordinates system
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set basic coordinates system
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right armTYPE:0 - base , 1 - tool
- Return :none
2.Block display
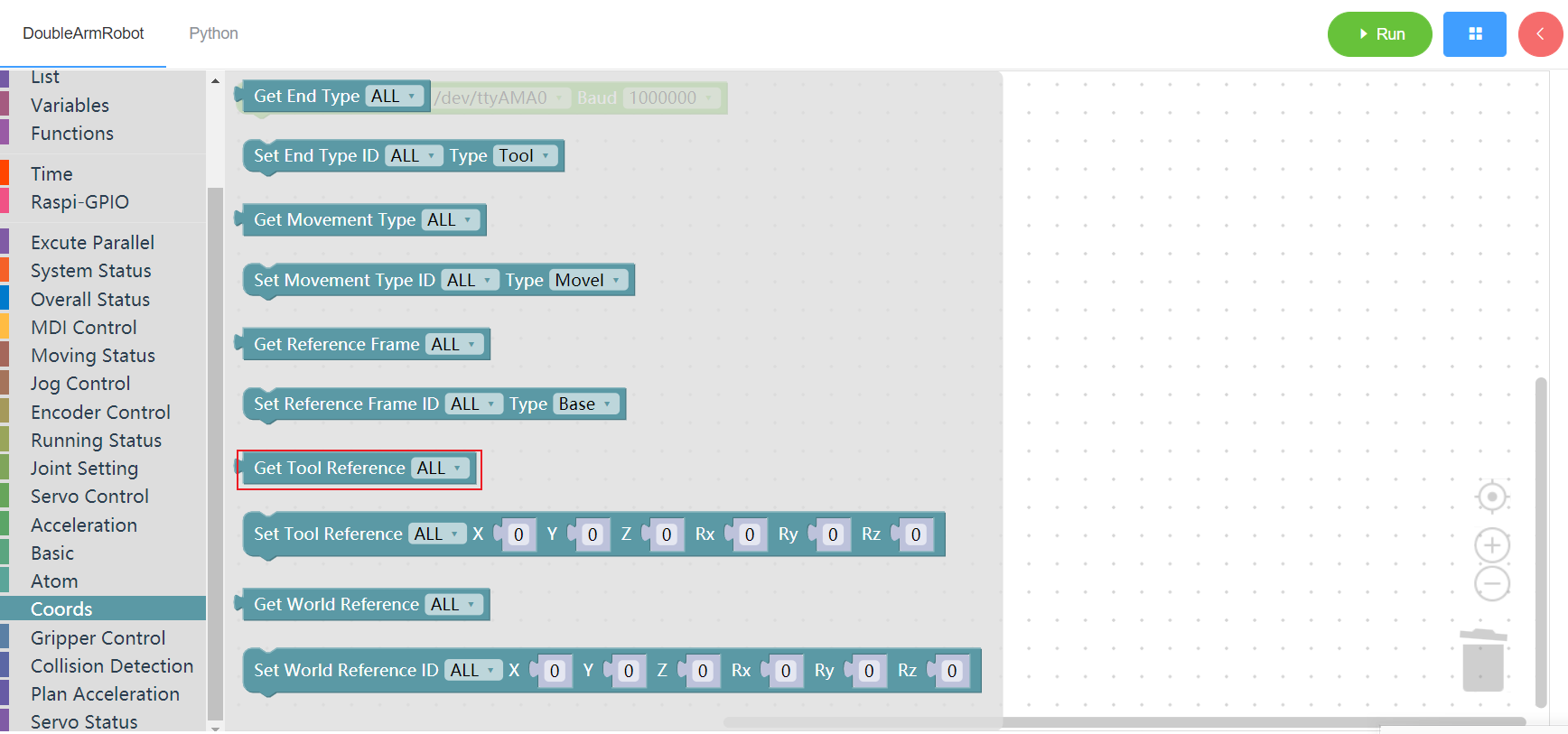
3.13.7 Get tool coordinates system
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get tool coordinates system
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm
- Return :
- unknown
2.Block display
3.13.8 Set tool coordinates system
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set tool coordinates system
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right armCOORDS:coordinates list(lenth 6)
- Return :none
2.Block display
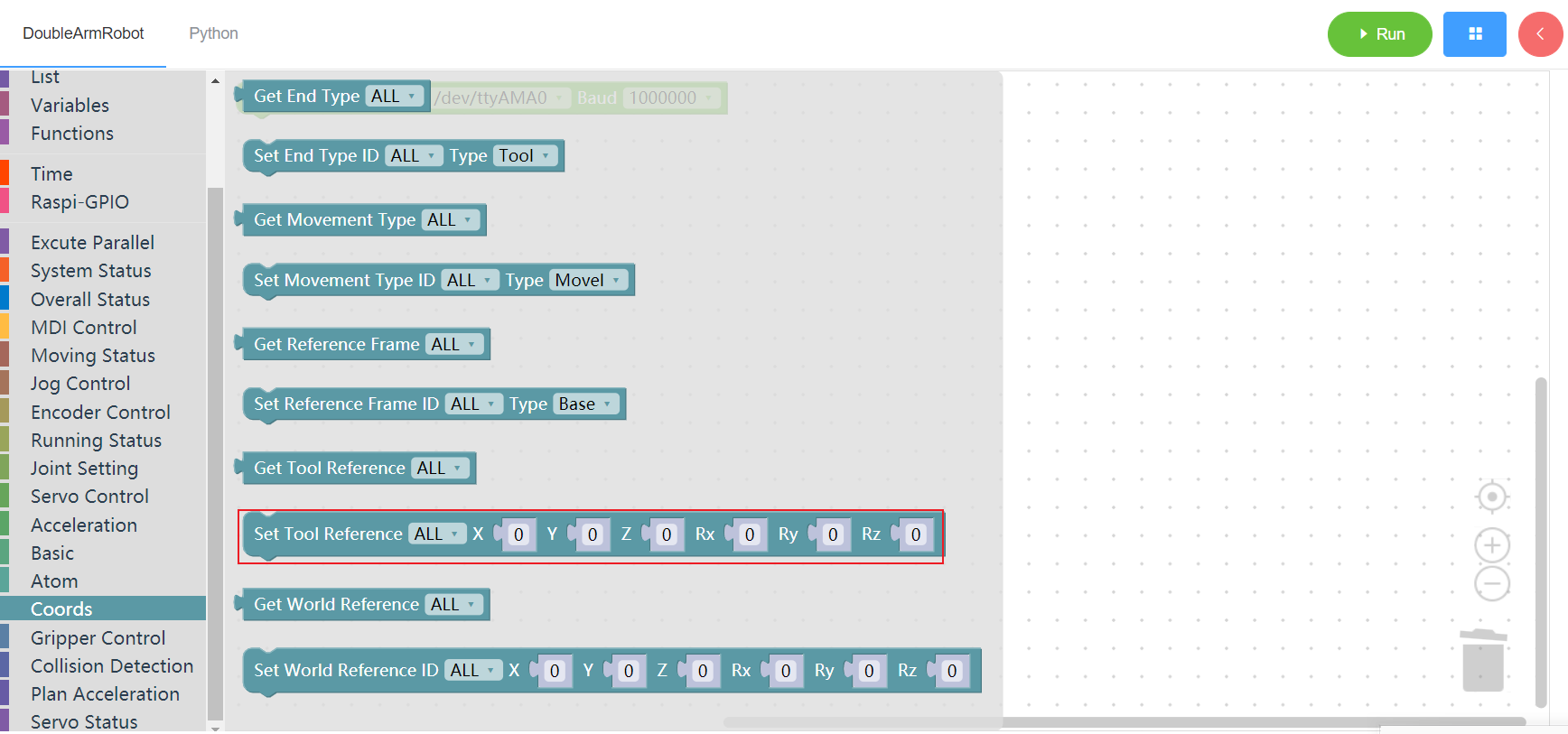
3.13.9 Get world coordinates system
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get world coordinates system
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm
- Return :
- unknown
2.Block display
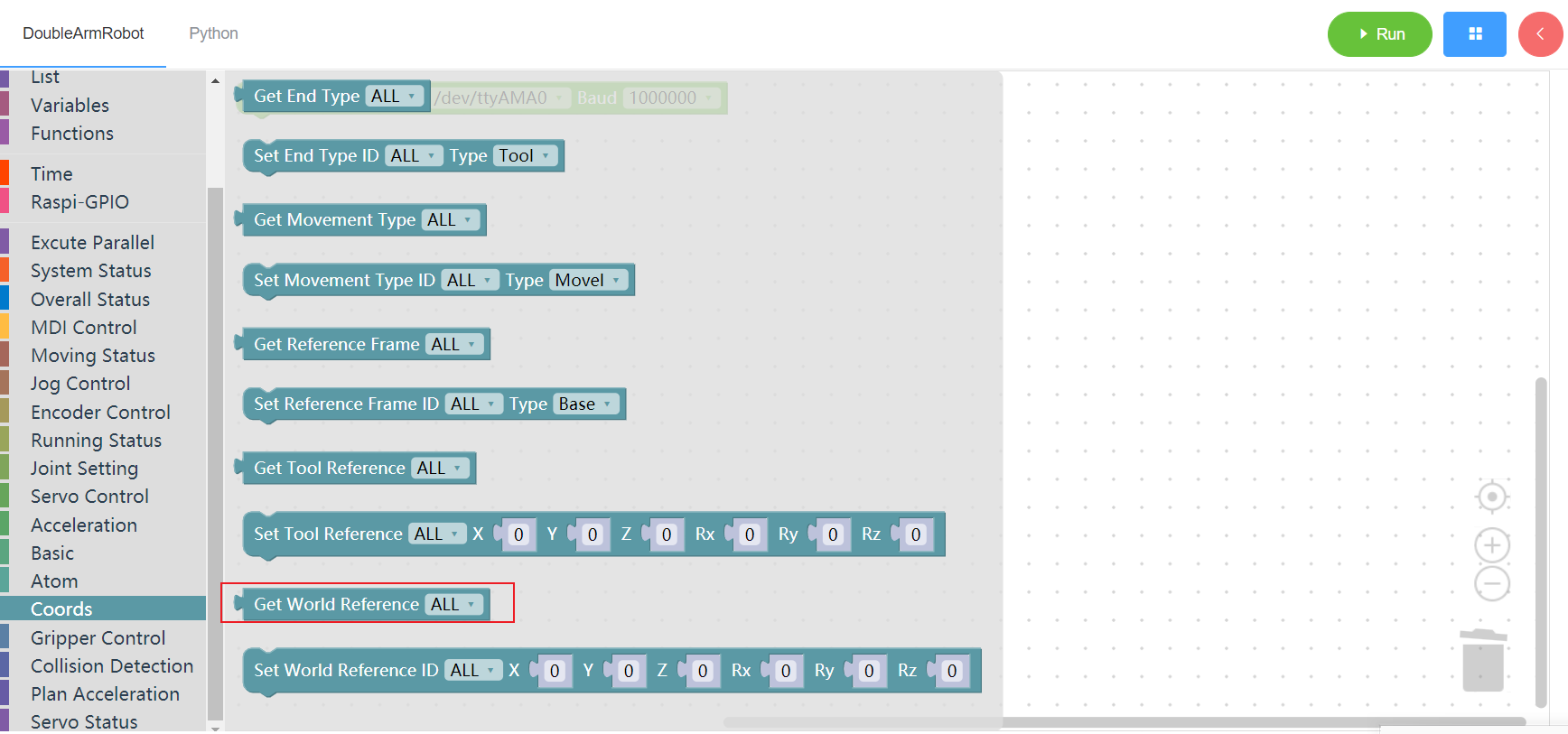
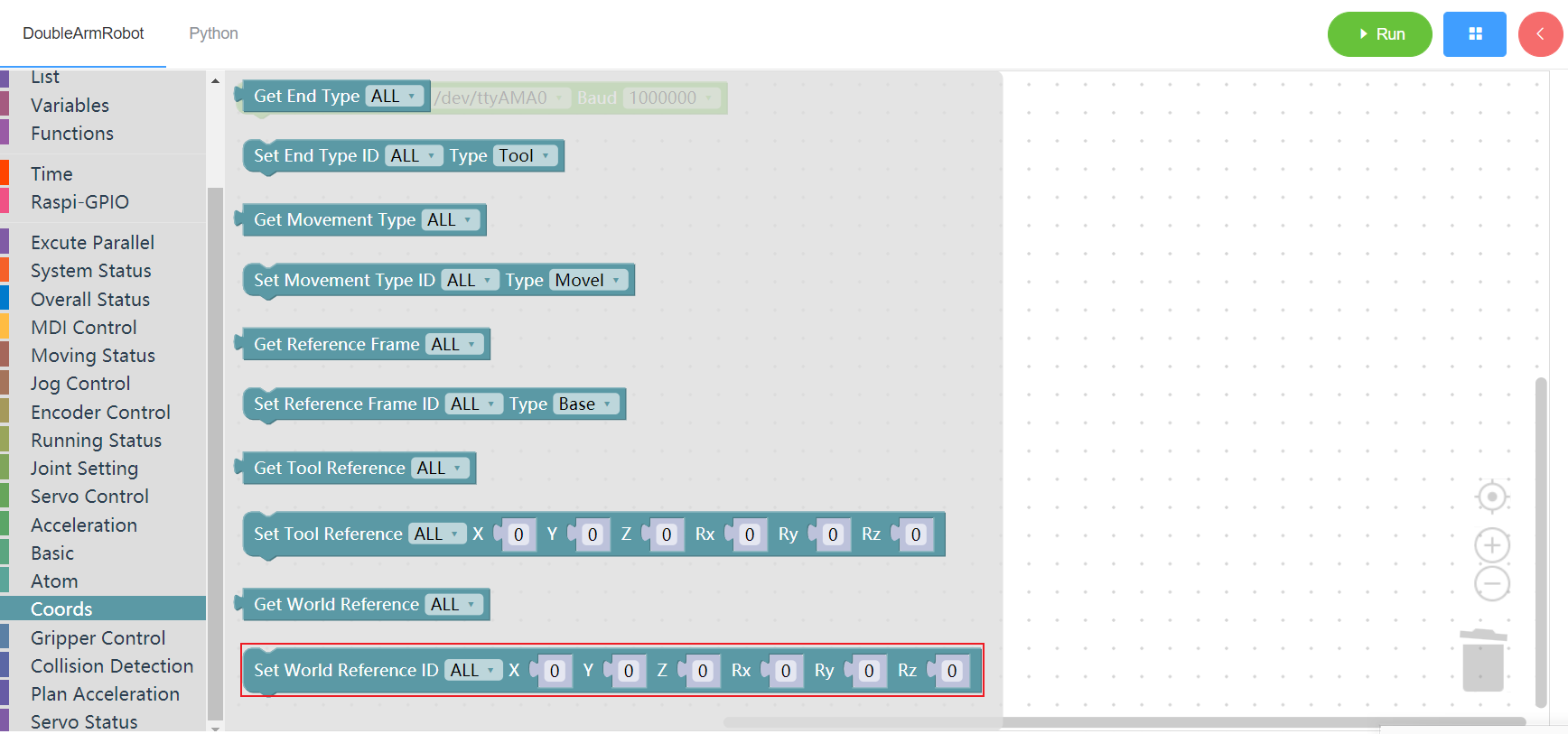
3.13.10 Set world coordinates system
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set world coordinates system
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right armCOORDS:coordinates list(length 6)
- Return :none
2.Block display
3.14 Gripper
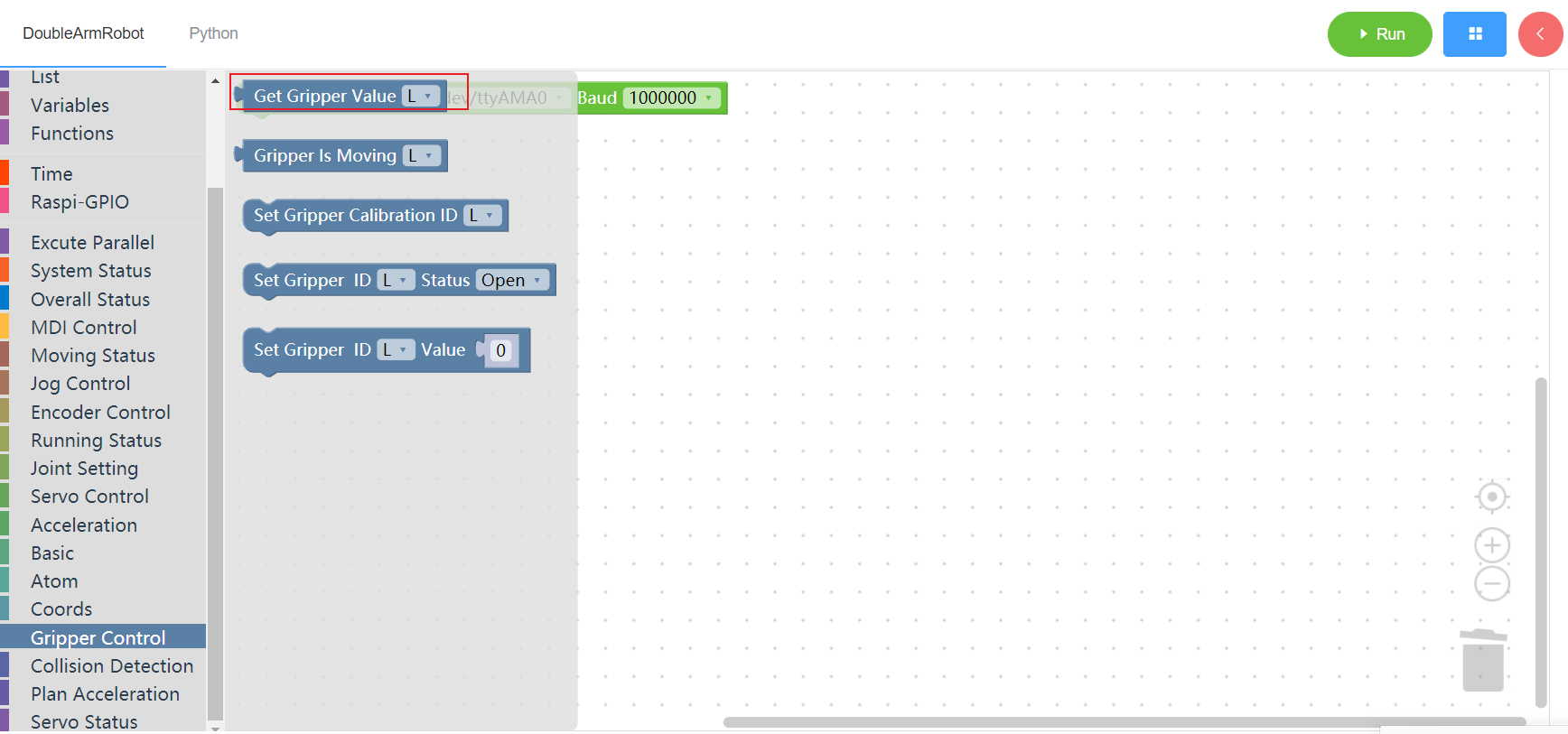
3.14.1 Get gripper angle
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get gripper value
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right arm
- Return :
GRIPPER_VALUE:gripper value
2.Block display
3.14.2 Check that the gripper is in motion
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Check whether the gripper of the mechanical arm is moving
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right arm
- Return :
VALUE:0 - did not move,1-moving , -1 error
2.Block display
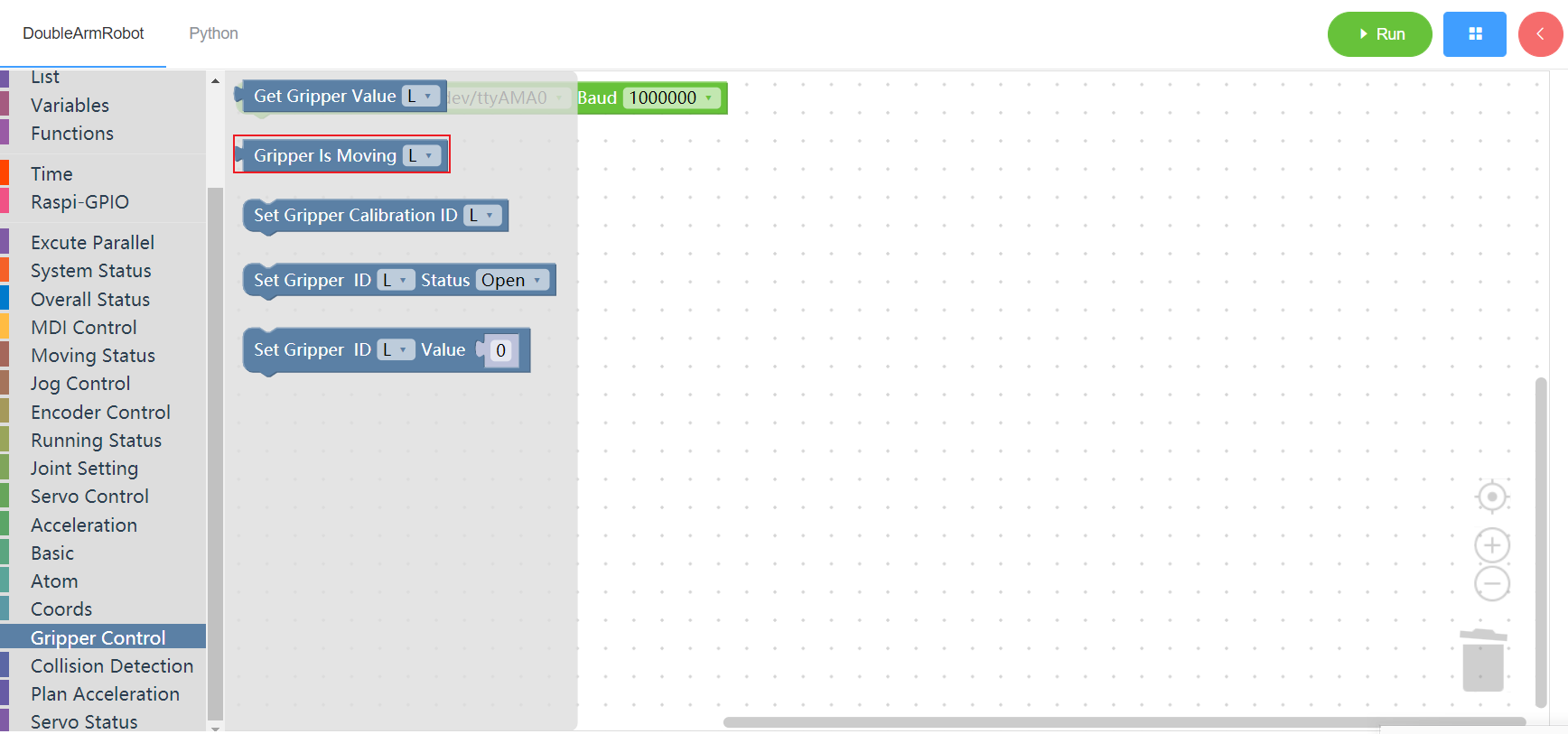
3.14.3 Set end claw zero
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the claw zero of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right arm
- Return :none
2.Block display

3.14.4 Set the terminal claw state
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the terminal claw state
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armSTATUS:0 - close 1 - open
- Return :none
2.Block display
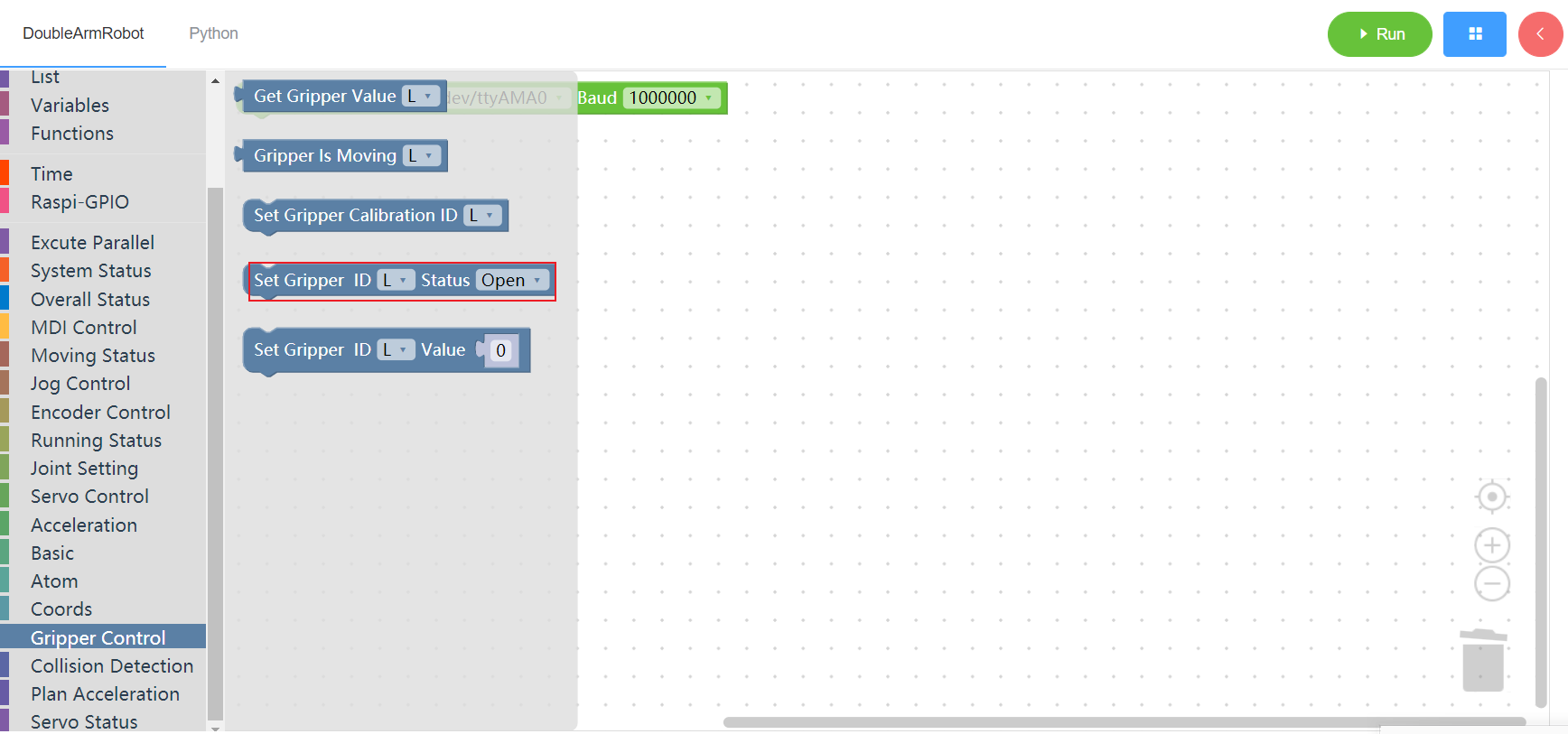
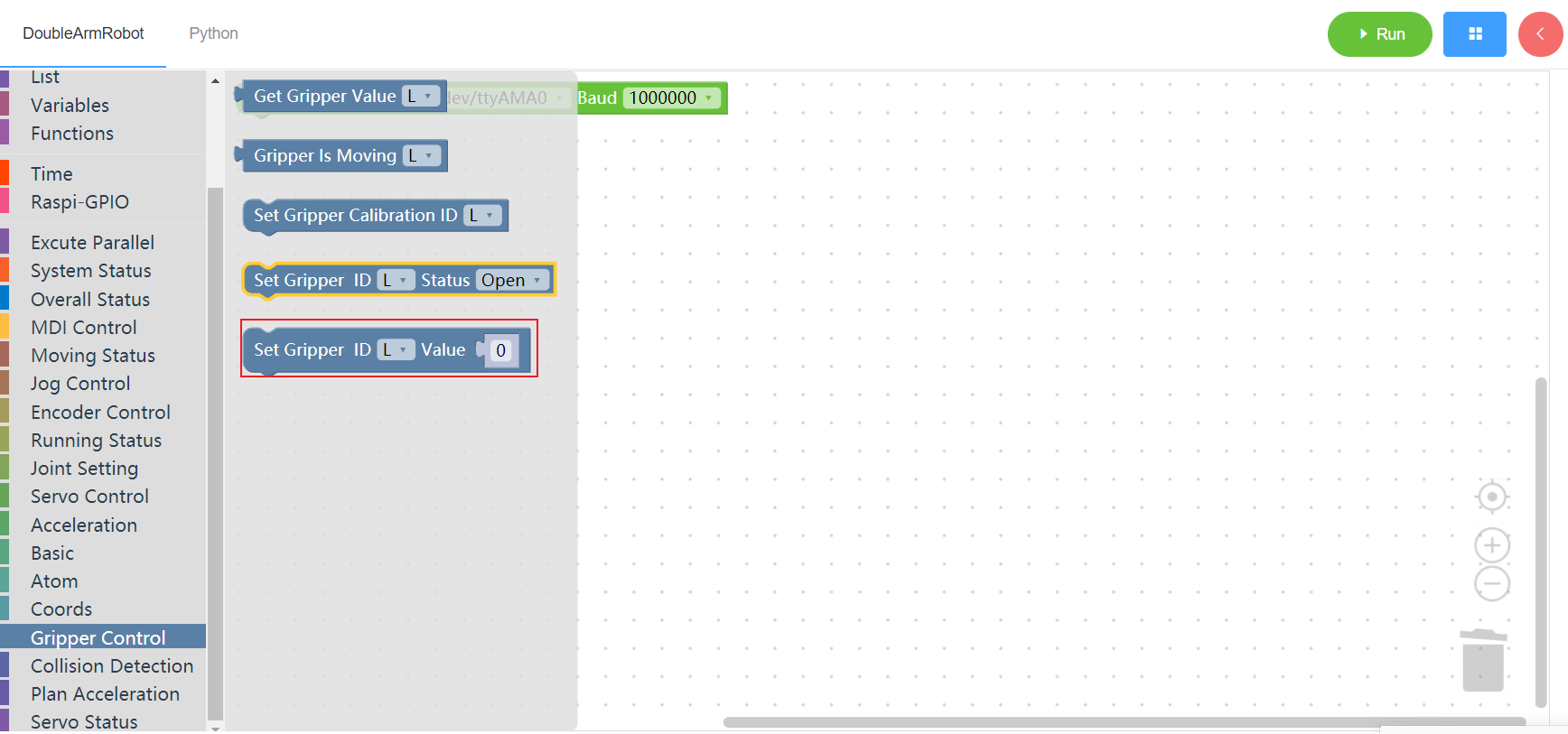
3.14.5 Set the claw range
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set the claw value of the manipulator
- Arguments:
ID(L/R):L for the left arm, R for the right armVALUE:integer(0~100)
- Return :none
2.Block display
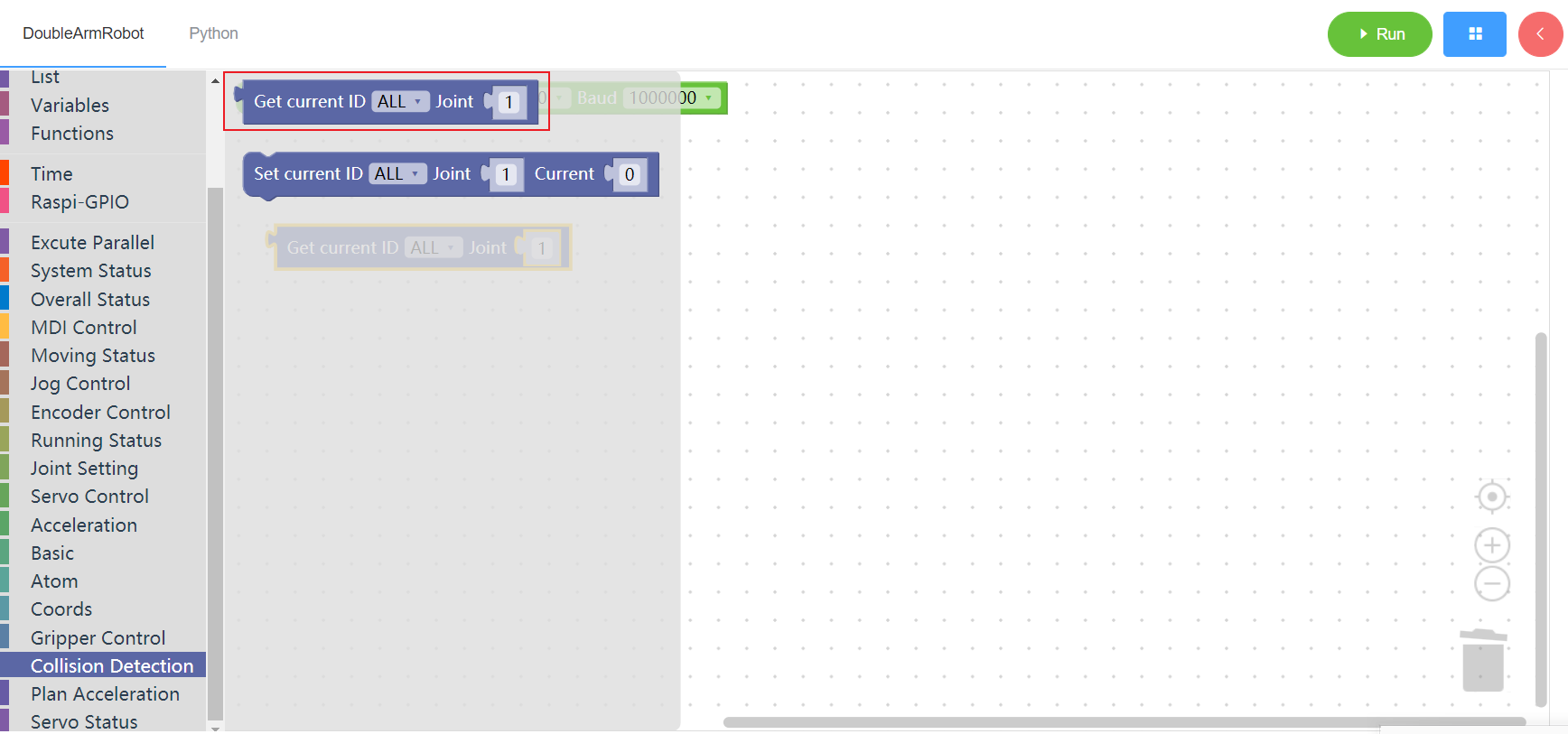
3.15 Collision detection
3.15.1 Get collision current
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get collision current
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right armJOINT_ID:joint id(1~6)
- Return :
CURRENT:current
2.Block display
3.15.2 Set joint collision
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set joint collision
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right armJOINT_ID:joint id(1~6)CURRENT:integer
- Return :none
2.Block display
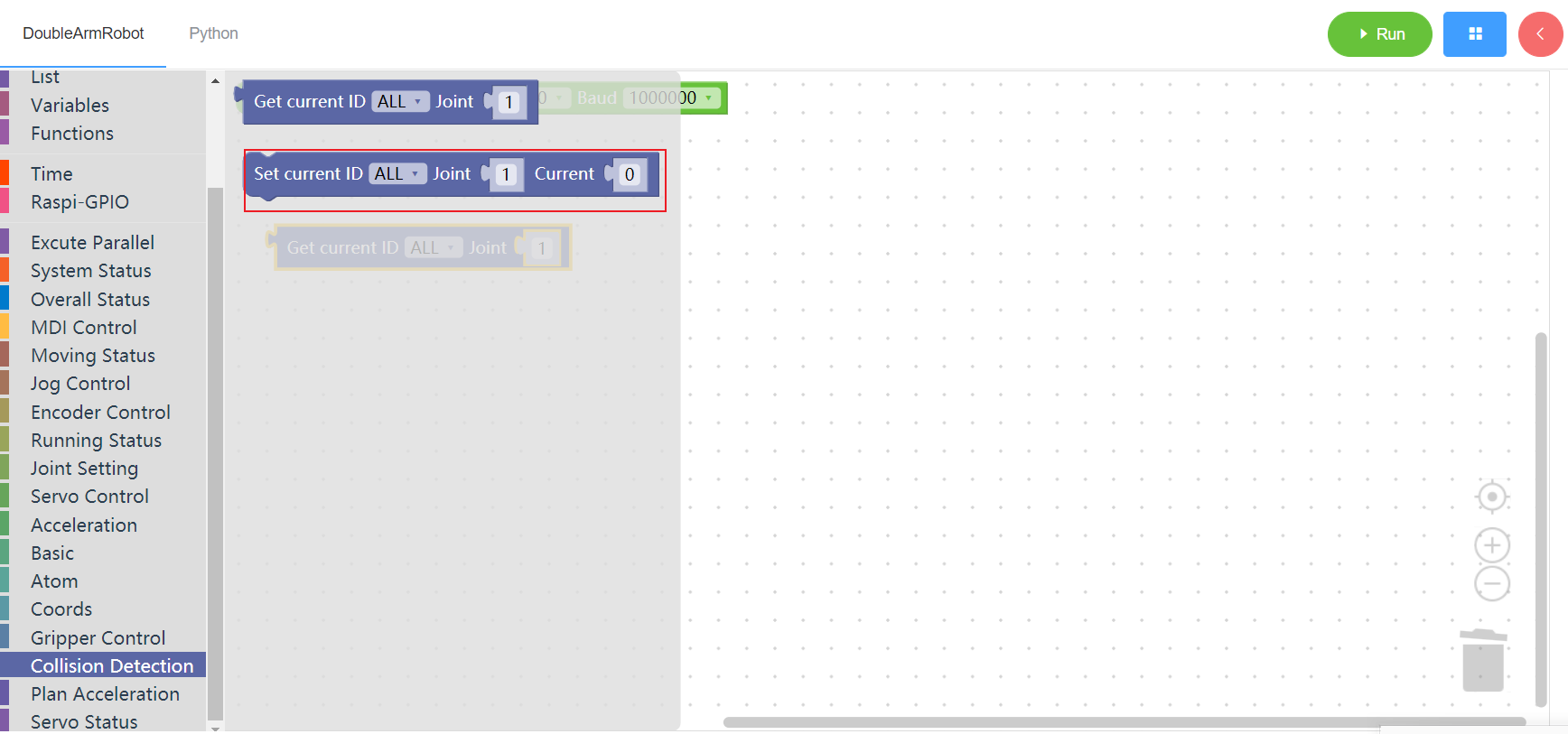
3.16 Plan speed
3.16.1 Get planned acceleration
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get planned acceleration
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :
PLAN_ACCELERATION:planned acceleration list
2.Block display
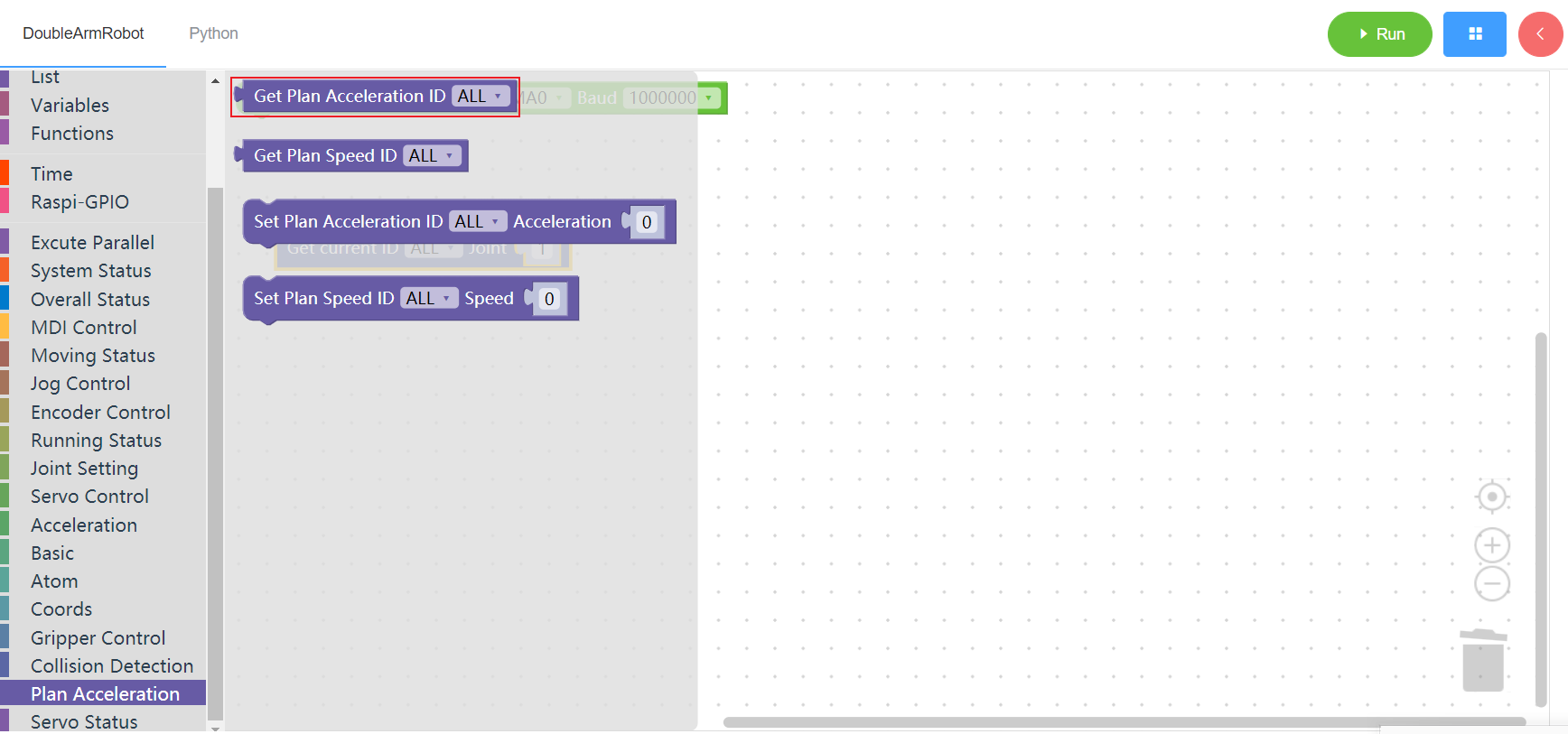
3.16.2 Get planned speed
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get planned speed
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :
PLAN_ACCELERATION:planned speed list
2.Block display
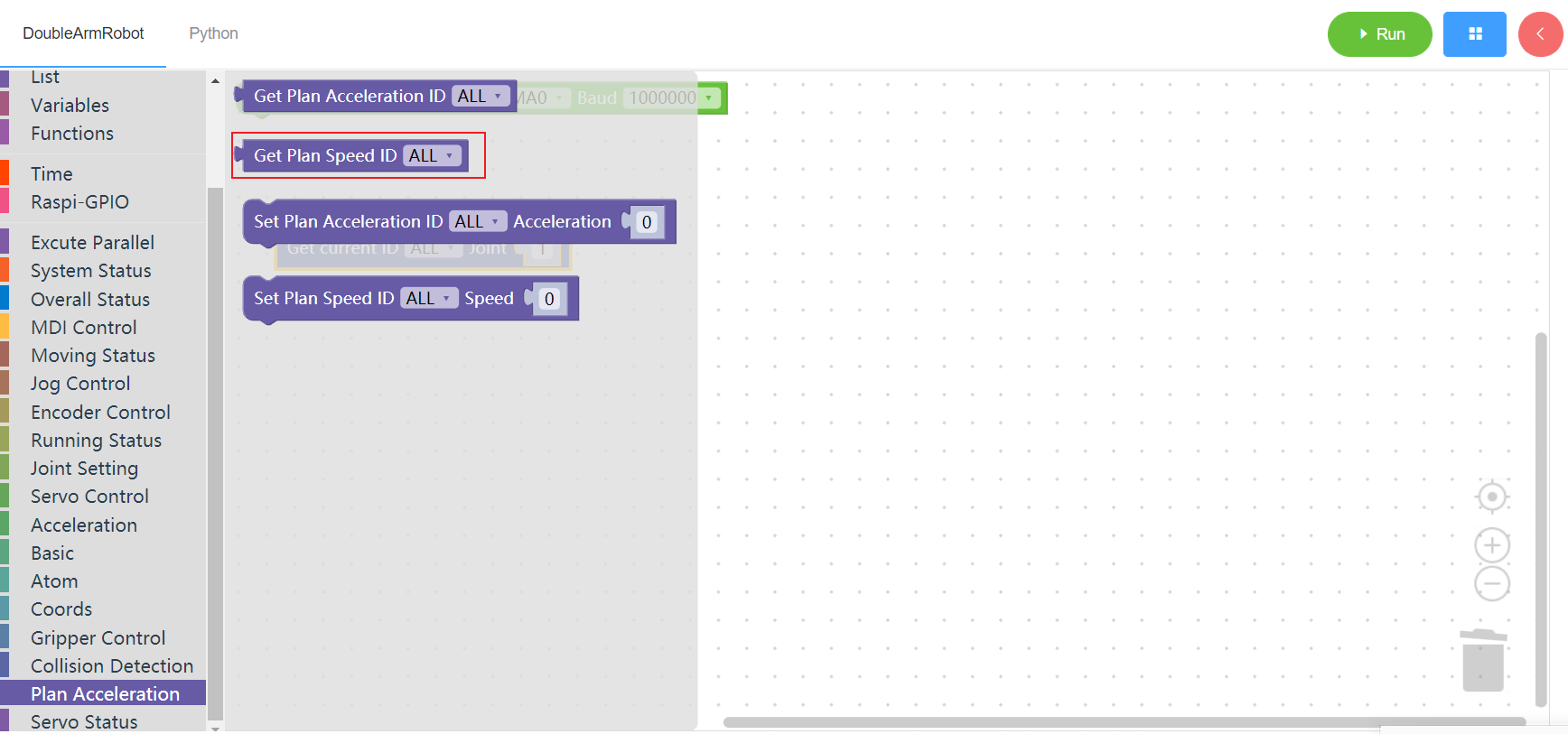
3.16.3 Set planned acceleration
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set planned acceleration
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistACCELERATION:acceleration(0~100)
- Return :none
2.Block display
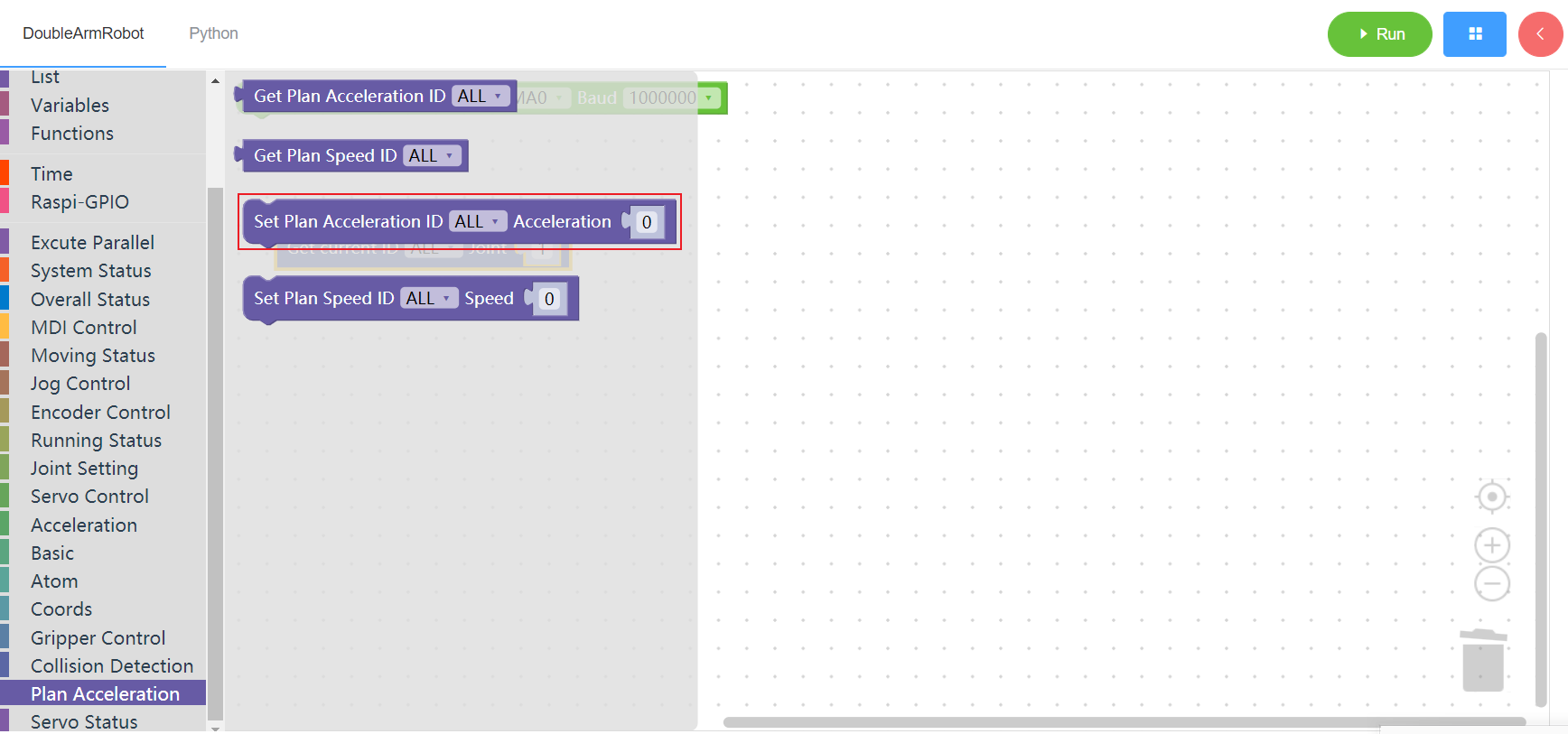
3.16.4 Set planned speed
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Set planned speed
- Arguments:
ID(ALL/L/R/W):ALL for all arms,L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waistSPEED:planned speed(0~100)
- Return :none
2.Block display
3.17 Servo status
3.17.1 Get joint current
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get joint current
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :
CURRENTS:joint currents
2.Block display
3.17.2 Get joint state
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get joint state
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :
LIST:List (voltage, sensor, temperature, current, Angle, overload, 0 indicates none error)
2.Block display

3.17.3 Acquisition of joint voltage
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Acquisition of joint voltage
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :
VOLTS:voltage(less than 24V)
2.Block display
3.17.4 Get joint temperature
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:Get joint temperature
- Arguments:
ID(L/R/W):L for the left arm, R for the right arm,W for waist
- Return :
TEMPERATURE:temperature
2.Block display
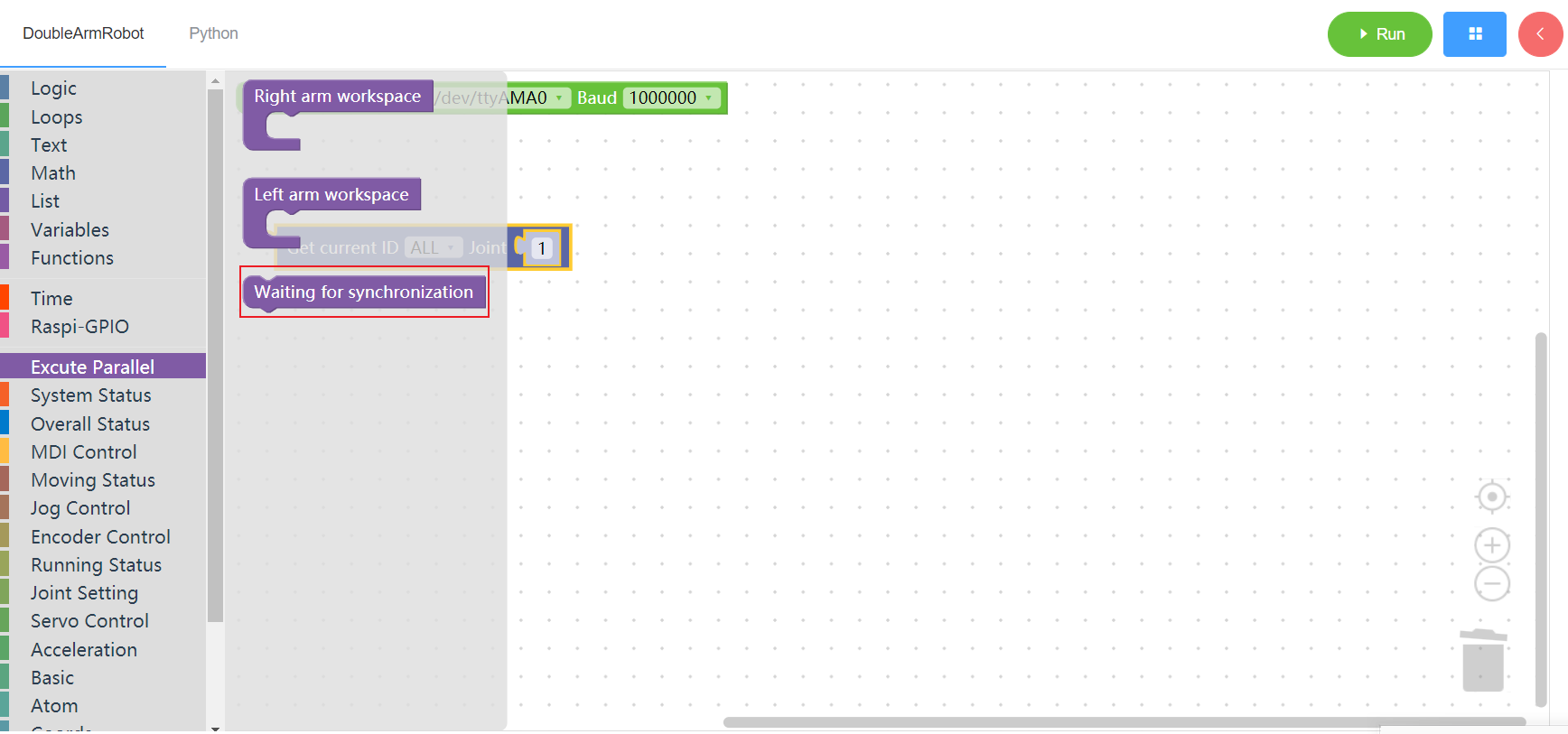
3.18 Execute in parallel
3.18.1 Right arm workspace
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:The mechanical arm is used synchronously. During the synchronous execution, the building blocks of the left and right arms need to be dragged to the working area to ensure the simultaneous movement of the two mechanical arms
- Arguments:none
- Return :none
2.Block display
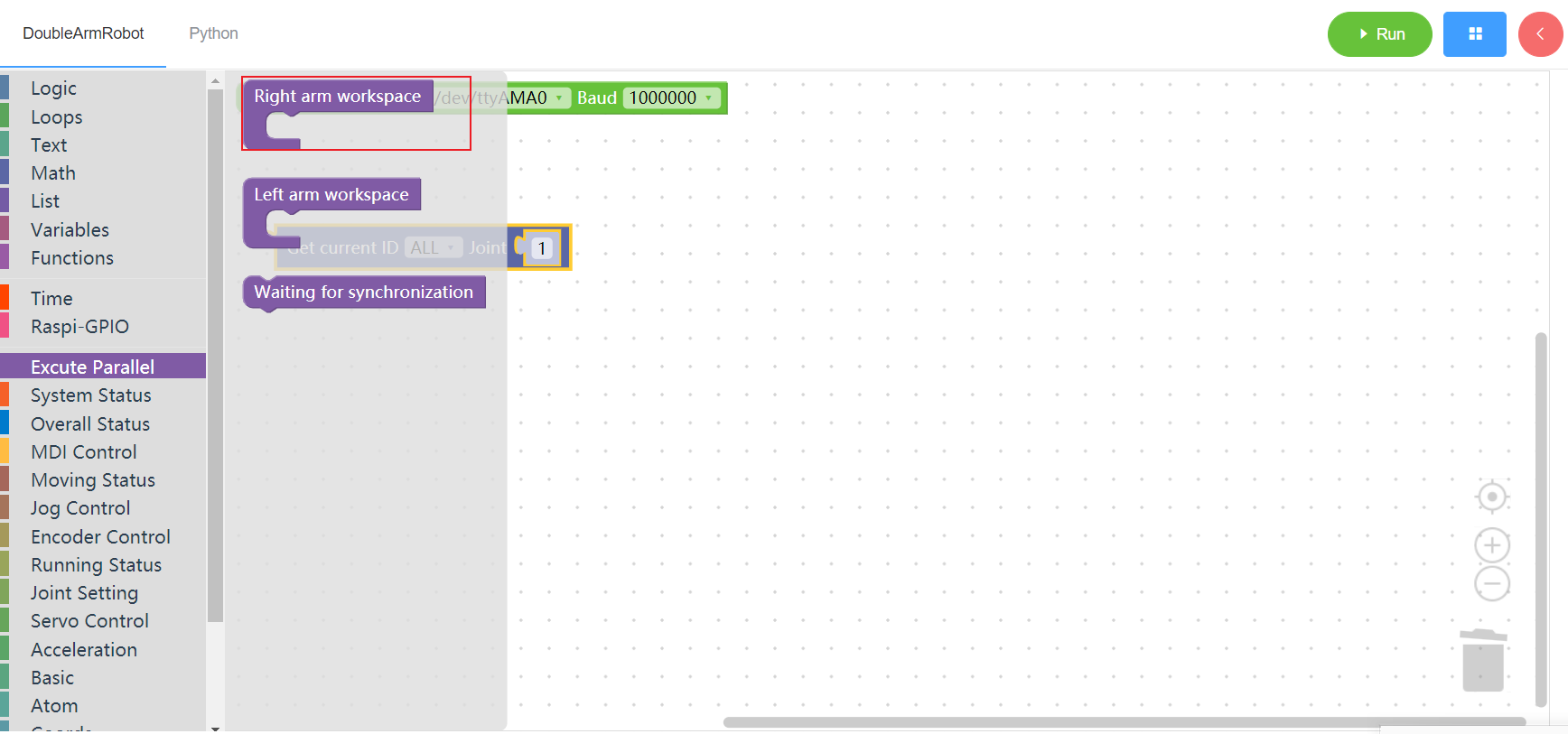
3.18.2 Left arm workspace
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:The mechanical arm is used synchronously. During the synchronous execution, the building blocks of the left and right arms need to be dragged to the working area to ensure the simultaneous movement of the two mechanical arms
- Arguments:none
- Return :none
2.Block display
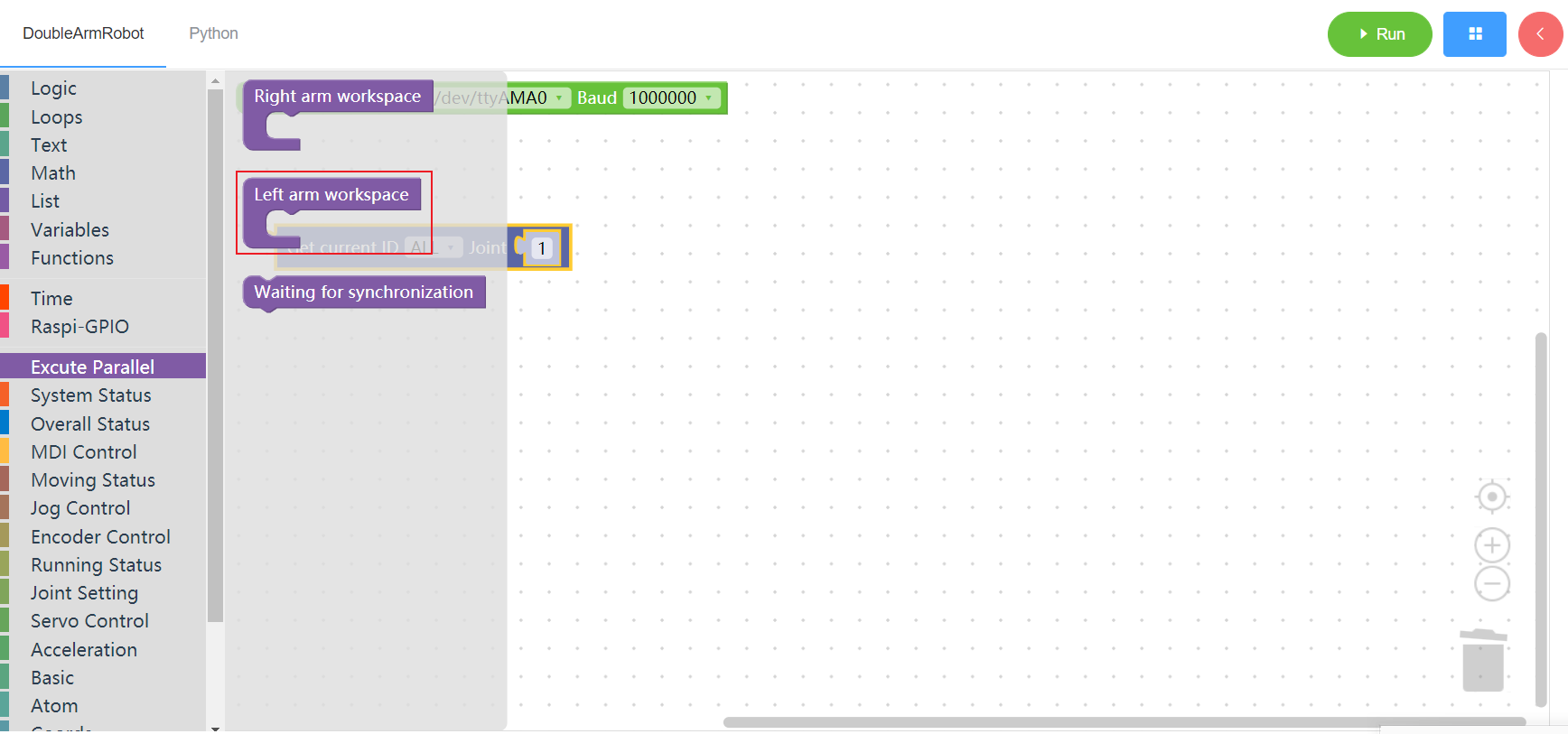
3.18.3 Sync dot
1. Runtime API Reference
- Function:It can only be used in the working area of left and right arms, and only takes effect when running both arms synchronously. Using the synchronization point, the mechanical arm can stop and wait for the completion of the execution of the other mechanical arm under specified conditions before performing subsequent operations
- Arguments:none
- Return :none
2.Block display