Identify color blocks
This case uses the eye_to_hand mode, uses the camera to locate the color through opencv, frames the color blocks that meet the conditions, and calculates the spatial coordinate position of the block relative to the mechanical arm through the relevant points. Set a set of related actions for the manipulator and place it in different barrels according to the different colors of the identified blocks. In the following chapters, the code implementation process of the whole case will be introduced in detail.
1 Update the mycobot_ai package
In order to ensure that users can use the latest official package in time (new users do not need to update), they can go to the /home/ubuntu/catkin_ws/src folder through the file manager and open the console terminal (shortcut Ctrl+Alt+T ) , enter the following command to update:
# Clone the code on github
mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src # Create a folder (if the folder already exists, you don't need to create it again)
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/elephantrobotics/mycobot_ros.git # Please check the attention section below before deciding whether to execute this command
cd ~/catkin_ws # Back to work area
catkin_make # Build the code in the workspace
source devel/setup.bash # add environment variable
Note: If the mycobot_ros folder already exists in the /home/ubuntu/catkin_ws/src (equivalent to ~/catkin_ws/src) directory, you need to delete the original mycobot_ros before executing the above command. Among them, ubuntu in the directory path is the user name of the virtual machine. If it is inconsistent, please modify it.
2 Camera adjustment
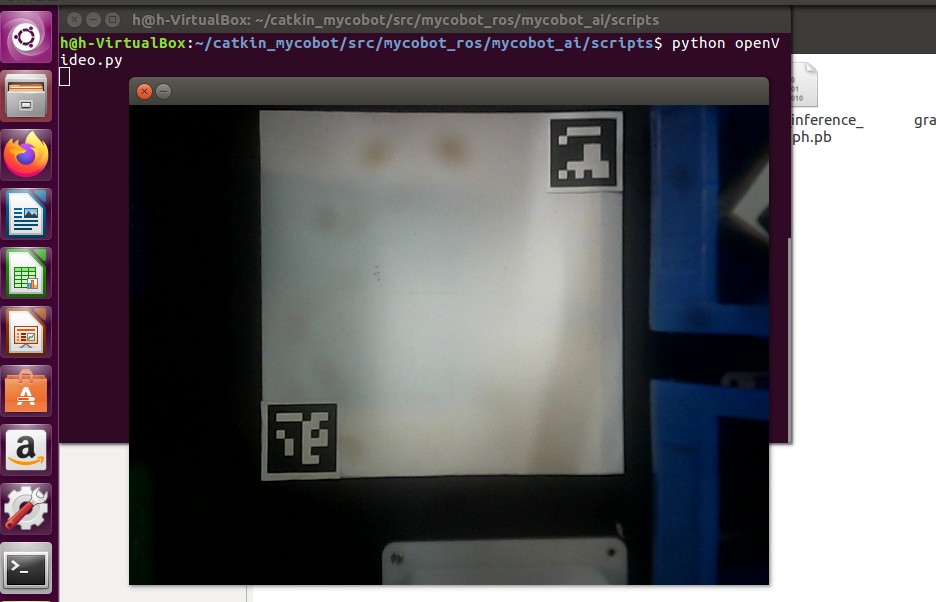
First, you need to use Python to run openvideo. Py under the mycobot_ai package. If the open camera is a computer camera, you need to modify cap_ Num, please refer to:matters needing attention Make sure that the camera completely covers the whole recognition area, and the recognition area is square in the video, as shown in the figure below. If the recognition area does not meet the requirements in the video, the position of the camera needs to be adjusted.
- Go to the target folder
cd ~/catkin_ws/src/mycobot_ros/mycobot_ai/ai_mycobot_280/
- Enter
python scripts/openVideo.pyto open the camera for adjustment.
3 Case reproduction
M5 version:
- Use the shortcut key combination Ctrl+Alt+T to open a terminal window, and enter the following command to start the master node
roscore
Type Ctrl+Shift+T in the command terminal to open another terminal window in the same directory and view the device name:
# View the name of the robotic arm device
ls /dev/ttyUSB* # old version myCobot280 M5
# If the terminal does not display the /dev/ttyUSB related name, you need to use the following command
ls /dev/ttyACM* # new version myCobot280 M5
- Grant permission to operate the robotic arm:
# The default device name is /dev/ttyUSB0. If the device name is not the default value, it needs to be modified.
sudo chmod 777 /dev/ttyUSB0 # old version myCobot280 M5
sudo chmod 777 /dev/ttyACM0 # new version myCobot280 M5
- Enter the following command to start the launch file.
# When the device name is not the default value, you need to modify the port value
roslaunch ai_mycobot_280 vision_m5.launch port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 baud:=115200 # old version myCobot280 M5
roslaunch ai_mycobot_280 vision_wio.launch port:=/dev/ttyACM0 baud:=115200 # old version myCobot280 M5
- Use the Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut to open another terminal window and enter the directory corresponding to the robotic arm:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src/mycobot_ros/mycobot_ai/ai_mycobot_280/
Enter python scripts/combine_detect_obj_color.py to open the color recognition program, and you can realize color recognition and capture.
Raspberry Pi version:
- Use the shortcut key combination Ctrl+Alt+T to open a terminal window, and enter the following command to start the master node
roscore
Type Ctrl+Shift+T in the command terminal to open another terminal window in the same directory and view the device name:
# View the name of the robotic arm device
ls /dev/ttyAMA*
- Grant permission to operate the robotic arm:
# The default device name is /dev/ttyAMA0. If the device name is not the default value, it needs to be modified.
sudo chmod 777 /dev/ttyAMA0
- Enter the following command to start the launch file.
# When the device name is not the default value, you need to modify the port value
roslaunch ai_mycobot_280 vision_pi.launch port:=/dev/ttyAMA0 baud:=1000000
- Use the Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut to open another terminal window and enter the directory corresponding to the robotic arm:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src/mycobot_ros/mycobot_ai/ai_mycobot_280/
Enter python scripts/combine_detect_obj_color.py to open the color recognition program, and you can realize color recognition and capture.
Matters needing attention
When the camera does not automatically frame the recognition area correctly, you need to close the program, adjust the position of the camera, and move the camera to the left and right.
If the command terminal does not appear ok and the color cannot be recognized, you need to move the camera slightly backward or forward, and the program can run normally when the command terminal appears ok.
OpenCV image recognition will be affected by the environment, and the recognition effect will be greatly reduced if it is in a darker environment.
4 Code explanation
This case is based on opencv and ROS communication control manipulator. First, calibrate the camera to ensure the accuracy of the camera. By identifying two aruco codes in the capture range, the recognition range is intelligently located, and the corresponding relationship between the center point of the actual recognition range and the video pixel is determined.
Use the color recognition function provided by opencv to identify the object block and determine the pixel position of the object block in the video, and calculate the coordinates of the object block relative to the center of the actual recognition range according to the pixel point of the object block in the video and the video pixel point of the center of the actual recognition range, Then, the relative coordinates of the object block relative to the manipulator can be calculated according to the relative coordinates between the center of the actual identification range and the manipulator. Finally, a series of actions are designed to grab the object block and place it in the corresponding bucket.
Don't worry about whether you still don't understand after reading. Next, we will explain the whole implementation process step by step.
4.1 Identify aruco modules
Use the aruco recognition function of opencv to identify the aruco of the picture, and conduct some brief information filtering to obtain the pixel position information of two aruco.
def get_calculate_params(self,img):
# Convert picture to gray picture
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Check whether there is aruco in the picture
corners, ids, rejectImaPoint = cv2.aruco.detectMarkers(
gray, self.aruco_dict, parameters=self.aruco_params
)
"""
It is required that there are two arucos in the picture in the same order.
There are two arucos in corners, and each aruco contains its four corner pixel bits.
The center position of aruco is determined according to the four corners of aruco.
"""
if len(corners) > 0:
if ids is not None:
if len(corners) <= 1 or ids[0]==1:
return None
x1=x2=y1=y2 = 0
point_11,point_21,point_31,point_41 = corners[0][0]
x1, y1 = int((point_11[0] + point_21[0] + point_31[0] + point_41[0]) / 4.0), int((point_11[1] + point_21[1] + point_31[1] + point_41[1]) / 4.0)
point_1,point_2,point_3,point_4 = corners[1][0]
x2, y2 = int((point_1[0] + point_2[0] + point_3[0] + point_4[0]) / 4.0), int((point_1[1] + point_2[1] + point_3[1] + point_4[1]) / 4.0)
return x1,x2,y1,y2
return None
4.2 Clip video module
According to the pixel points of two aruco, determine the pixel range of the recognition range in the video, and then cut it.
"""
Expand the video pixel by 1.5x, that is, enlarge the video size by 1.5x.
If two aruco values have been calculated, video clipping is performed.
"""
def transform_frame(self, frame):
# Enlarge the picture 1.5x
fx = 1.5
fy = 1.5
frame = cv2.resize(frame, (0, 0), fx=fx, fy=fy, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
if self.x1 != self.x2:
# The clipping scale here is adjusted according to the actual situation
frame = frame[int(self.y2*0.4):int(self.y1*1.15), int(self.x1*0.7):int(self.x2*1.15)]
return frame
4.3 Color recognition module
Chroma conversion is performed on the received picture, the picture is converted into gray picture, and the color recognition range is set according to HSV initialized by the user-defined class.
Corrode and expand the converted gray image to deepen the color contrast of the image. Identify and locate the color of the object block through filtering and checking the contour. Finally, through some necessary data filtering, color blocks are framed in the picture.
def color_detect(self, img): x = y = 0 for mycolor, item in self.HSV.items(): redLower = np.array(item[0]) redUpper = np.array(item[1]) # Convert picture to gray picture hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV) # Set color recognition range mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, item[0], item[1]) # The purpose of etching the picture is to remove the edge roughness erosion = cv2.erode(mask, np.ones((1, 1), np.uint8), iterations=2) # Expand the picture to deepen the color depth in the picture dilation =cv2.dilate(erosion, np.ones((1, 1), np.uint8), iterations=2) # Add pixels to the picture target = cv2.bitwise_and(img, img, mask=dilation) # Turn the filtered image into a binary image and put it in binary ret, binary = cv2.threshold(dilation, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # Obtain the image contour coordinates, where contour is the coordinate value. Here, only the contour is detected contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours( dilation, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) if len(contours) > 0: # Deal with the misidentification boxes = [ box for box in [cv2.boundingRect(c) for c in contours] if min(img.shape[0], img.shape[1]) / 10 < min(box[2], box[3]) < min(img.shape[0], img.shape[1]) / 1 ] if boxes: for box in boxes: x, y, w, h = box # Find the largest object that meets the requirements c = max(contours, key=cv2.contourArea) # Obtain the lower left and upper right points of the positioning object x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c) # Frame the block in the picture cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (153, 153, 0), 2) # Calculate Block Center x, y = (x*2+w)/2, (y*2+h)/2 # Judge what color the object is if mycolor == "yellow": self.color = 1 elif mycolor == "red": self.color = 0 # Judge whether the identification is normal if abs(x) + abs(y) > 0: return x, y else: return None
4.4 Grab the implementation module
A series of points are designed for the movement of the manipulator, such as the initialization point of the manipulator, the point to be grasped, the point above the blue bucket, the point above the green bucket, etc. In order to simulate the movement of the object block in rviz, a series of points are set for the movement of the object block. Since the model coordinates in rviz are in m and the manipulator coordinates are in mm, it is necessary to divide the data by 1000.
class Object_detect(Movement):
def __init__(self, camera_x = 160, camera_y = -5):
# inherit the parent class
super(Object_detect, self).__init__()
# get path of file
dir_path = os.path.dirname(__file__)
self.mc = None
# moving angle
self.move_angles = [
[-7.11, -6.94, -55.01, -24.16, 0, -15], # init the point
[18.8, -7.91, -54.49, -23.02, -0.79, -14.76], # point to grab
]
# move coords
self.move_coords = [
[120.8, -134.4, 258.0, -172.72, -5.31, -109.09], # above the red bucket
[219.8, -126.4, 249.7, -158.68, -7.93, -101.6], # green bucket
[124.7, 145.3, 250.4, -173.5, -2.23, -11.7], # blue bucket
[14.6, 175.9, 250.4, -177.42, -0.08, 25.93], # gray bucket
]
def move(self, x, y, color):
# send Angle to move mycobot
print (color)
self.mc.send_angles(self.move_angles[1], 25)
time.sleep(3)
# send coordinates to move mycobot
self.mc.send_coords([x, y, 190.6, 179.87, -3.78, -62.75], 25, 1) # usb :rx,ry,rz -173.3, -5.48, -57.9
time.sleep(3)
# self.mc.send_coords([x, y, 150, 179.87, -3.78, -62.75], 25, 0)
# time.sleep(3)
self.mc.send_coords([x, y, 96, 179.87, -3.78, -62.75], 25, 0)
time.sleep(3)
# open pump
if "dev" in self.robot_m5 or "dev" in self.robot_wio:
self.pump_on()
elif "dev" in self.robot_raspi or "dev" in self.robot_jes:
self.gpio_status(True)
time.sleep(1.5)
tmp = []
while True:
if not tmp:
tmp = self.mc.get_angles()
else:
break
time.sleep(0.5)
# print(tmp)
self.mc.send_angles([tmp[0], -0.71, -54.49, -23.02, -0.79, tmp[5]],25) # [18.8, -7.91, -54.49, -23.02, -0.79, -14.76]
time.sleep(4)
self.pub_marker(
self.move_coords[2][0]/1000.0, self.move_coords[2][1]/1000.0, self.move_coords[2][2]/1000.0)
self.mc.send_coords(self.move_coords[color], 25, 1)
self.pub_marker(self.move_coords[color][0]/1000.0, self.move_coords[color]
[1]/1000.0, self.move_coords[color][2]/1000.0)
time.sleep(3)
# close pump
if "dev" in self.robot_m5 or "dev" in self.robot_wio:
self.pump_off()
elif "dev" in self.robot_raspi or "dev" in self.robot_jes:
self.gpio_status(False)
time.sleep(4)
if color == 1:
self.pub_marker(
self.move_coords[color][0]/1000.0+0.04, self.move_coords[color][1]/1000.0-0.02)
elif color == 0:
self.pub_marker(
self.move_coords[color][0]/1000.0+0.03, self.move_coords[color][1]/1000.0)
# self.pub_angles(self.move_angles[0], 20)
self.mc.send_angles(self.move_angles[0], 25)
time.sleep(3)
4.5 Pick point calibration
When the suction pump is inaccurate in grasping the wooden block, it can be calibrated by modifying the code coordinates. The code modification position is as follows (both the coordinates of position 1 and position 2 can be modified, and one of the two can be selected):
~/catkin_ws/src/mycobot_ros/mycobot_ai/ai_mycobot_280/scripts/combine_detect_obj_color.py
class Object_detect(Movement):
# Position 1: Adjust the suction position of the suction pump, increase y, move to the left; decrease y, move to the right; increase x, move forward; decrease x, move backward
def __init__(self, camera_x = 160, camera_y = -5):
# inherit the parent class
super(Object_detect, self).__init__()
# get path of file
dir_path = os.path.dirname(__file__)
self.mc = None
# move angle
self.move_angles = [
[-7.11, -6.94, -55.01, -24.16, 0, -15], # init the point
[18.8, -7.91, -54.49, -23.02, -0.79, -14.76], # point to grab
]
# move coords
self.move_coords = [
[120.8, -134.4, 258.0, -172.72, -5.31, -109.09], # above the red bucket
[219.8, -126.4, 249.7, -158.68, -7.93, -101.6], # green
[124.7, 145.3, 250.4, -173.5, -2.23, -11.7], # blue
[14.6, 175.9, 250.4, -177.42, -0.08, 25.93], # gray
]
# which robot: USB* is m5; ACM* is wio; AMA* is raspi
self.robot_m5 = os.popen("ls /dev/ttyUSB*").readline()[:-1]
self.robot_wio = os.popen("ls /dev/ttyACM*").readline()[:-1]
self.robot_raspi = os.popen("ls /dev/ttyAMA*").readline()[:-1]
self.robot_jes = os.popen("ls /dev/ttyTHS1").readline()[:-1]
# decide whether grab cube
def decide_move(self, x, y, color):
print(x, y, self.cache_x, self.cache_y)
# detect the cube status move or run
if (abs(x - self.cache_x) + abs(y - self.cache_y)) / 2 > 5: # mm
self.cache_x, self.cache_y = x, y
return
else:
self.cache_x = self.cache_y = 0
# Position 2: Adjust the suction position of the suction pump, increase y, move to the left; decrease y, move to the right; increase x, move forward; decrease x, move backward
self.move(x, y, color)
4.6 Location calculation
By measuring the pixel positions of two aruco in the capture area, the pixel distance M1 between two aruco can be calculated, and the actual distance M2 between two aruco can be measured, so that we can obtain the ratio of pixels to actual distance ratio = m2 / M1.
We can calculate the pixel difference between the color object block and the center of the capture area from the picture, so we can calculate the relative coordinates (x1, Y1) of the actual distance of the object block from the center of the capture area.
- Add the relative coordinates(x1, Y1) from the center of the gripping area to the manipulator (X2, Y2) to obtain the relative coordinates (X3, Y3) of the object block to the manipulator. The specific code implementation can view the program source code.
If you want to have a thorough understanding of the implementation of the whole program, you can directly view the program source code, which provides a detailed annotation reference.